Polynomials - Wilson`s School
advertisement

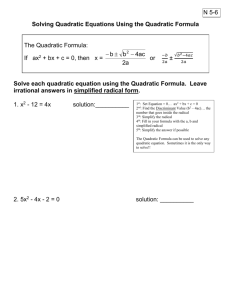
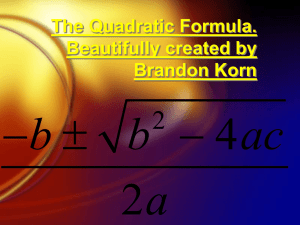
Wilson’s School Core 1 Revision Sheet 2 of 5 Polynomials Stuff to memorise: b b 2 4ac 2a 2 2 The discriminant of ax bx c is b 4ac The solution of ax 2 bx c 0 is x b 2 4ac 0 b 2 4ac 0 b 2 4ac 0 If The equation ax 2 bx c 0 has 2 distinct real roots 1 (repeated) real root no real roots I can: Add, subtract and multiply polynomials Complete the square for a quadratic expression Use the discriminant to determine the number of real roots of a quadratic equation Solve quadratic equations by factorising, completing the square and using the quadratic formulae Solve linear and quadratic inequalities Solve simultaneous equations where one equation is linear and the other quadratic Recognise and solve ‘hidden’ quadratic equations Tick! Test yourself: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Solve 6 x 2 x 15 , giving each answer as an exact fraction Hence write down the solution set of the inequality 6 x 2 x 15 Find integers p and q such that x 2 8 x 11 ( x p) 2 q Hence solve x 2 8 x 11 0 giving your answers in surd form 4 16 2 c) And solve 2 11 0 (hint: let x in part b) x a x 2 Solve the inequality ( x 7) 4 Solve x 4 5 x 2 6 0 using the substitution a x 2 Find the constants a , b and c such that 3x 2 5 x 1 a( x b) 2 c . Hence find the coordinates of the vertex. Find the range of values of k for which the equation x 2 3kx k 0 has any real roots. Solve the inequality x x 3 0 3x y 7 Solve the simultaneous equations 2 x 2 xy 5 y 11 a) b) a) b) a) Factorise 9 3x 2 x 2 b) Sketch the graph y 9 3x 2 x 2 showing intercepts Given that ( x 2 ax 2)( x b) x 3 7 x 2 14 x c , find the possible values of a, b and c. Expand and simplify the expression (3x 4)( x 1)( 2 x 3) Solutions 1 a) 3/2 or -5/3 b) x 3 / 2 or x 5 / 3 2 a) p=4, q=-5 b) 4 5 3 4 c) 4 5 9 x 5 6 5 a=3, b=-5/6, c=-13/12 5 13 vertex= , 6 12 4 9 7 -1<x<0 and x>1 8 25 8 (3,2) , 7 7 9 a) (3-2x)(x+3) b) 10 a=4, b=3, c=-6 or a=3, b=4 c=-8 11 6 x 3 5 x 2 13x 12 6 2 k 0 and k 2(4 5 ) 11 d) -5