Fourth Grade Math Learning Targets
advertisement

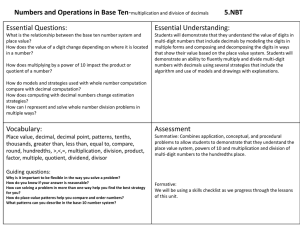
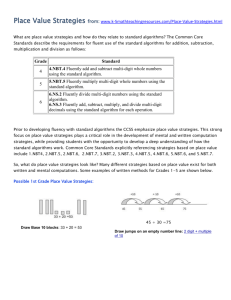
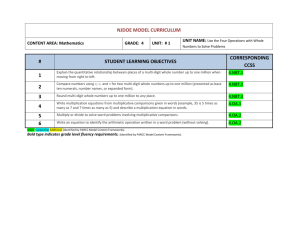
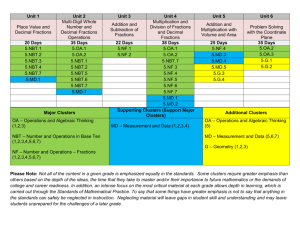
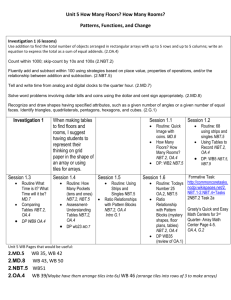
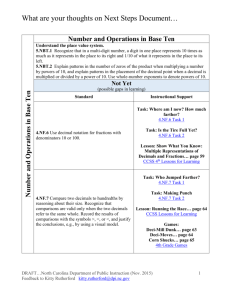
Roselawn Elementary School 4th Grade Math Units and Learning Targets Unit 1 Naming and Constructing Geometric Figures (25 days) Essential Question: Why geometry? Can we discover why and how geometry is used in our lives and where can it be found in our world? Learning Targets 1. The students will fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. (4.NBT.4) 2. The students will identify, draw, and describe points, intersecting and parallel line segments and lines, rays, and right angles. (4.G.1) 3. The students will describe and classify plane figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines, including polygons and circles using appropriate geometric terms including congruent. (4.G.2) 4. The students will measure angles using a protractor. (4.MD.6) 5. The students will compute the measurement of angles using addition and recognize lines of symmetry and justify their placement. (4.MD.6, 4.MD.7, 4.G.3) Unit 2 Using Numbers and Organizing Data (20 days) Essential Question: How are numbers used in real life situations through given data, displays, and base-ten place value system? Learning Targets 1. The students will read and write whole numbers up to 1,000,000,000 (by 10s, 100s, 1000s, 10,000s, etc.); identify places in such numbers and the values of the digits in those places (ie: a digit in the ones place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. (4.NBT.1, 4.NBT.2) 2. The students will use numerical expressions to give equivalent names for whole numbers (ie including words, base-ten numerals and expanded form). (4.NBT.2) 3. The students will make reasonable estimates for whole-number addition and subtraction problems in both story problems and standard algorithms. (4.OA.3, 4.NBT.3) 4. The students will use place value to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. (4.NBT.3) 5. The students will use a tally chart and create a bar graphs and line plots to display data including whole and fractional measurement. (4.MD.4) 6. The students will find the maximum, minimum, range, median, and mode of a data set. (4.OA.3) Unit 3 Exploring Multiplication and Division in Various Ways (20 days) Essential Question: What strategies can be used to find the value of an unknown variable in a number sentence and guide exploration of the relationships between multiplication and division? Learning Targets 1. The students will calculate multiples and factors and know multiplication and division facts. (4.OA, 4.NBT.5) 2. The students will relate multiplication to real world situations when applying the area and perimeter formulas. (4.MD.3) 3. The students will compute multi-digit multiplication problems using an algorithm. (4.NBT.5) 4. The students will solve number stories using all operations. (4.OA.2, 4.OA.3) 5. The students will generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. (4.OA.5) 6. The students will compare two multi-digit numbers using place value and >, <, and = symbols to keep track of the comparisons. (4.NBT.2) 7. The students will find whole number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors using a variety of strategies. (4.NBT.6) Unit 4 Decimals and Their Uses (20 days) Essential Question: What is the relationship between fractions, decimals, and percentages and how do they apply/are used in our daily life? Learning Targets 1. The students will read, write and compare decimals through hundredths using a visual model to justify the comparison. (4.NF.7) 2. The students will convert easy fractions to decimals. (4.NF.6) 3. The students will add and subtract decimals to hundredths. (4.MD.2) Unit 5 Big Numbers, Estimation, and Computation (20 days) Essential Question: What different algorithms can we use to solve multiplication problems? Learning Targets 1. The students will solve extended multiplication facts. (4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.5, 4.OA.2) 2. The students will multiply multi-digit whole numbers including story problems. (4.NBT.2, 4.NBT.5, 4.OA.2) 3. The students will make estimates for all four operations. (4.OA.3, 4.NBT.5) 4. The students will interpret a multiplication equation using the distributive property of multiplication. (4.OA.1, 4.OA.3, 4.NBT.5) Unit 6 Division and Interpreting Remainders (20 days) Essential Question: Are we able bridge our background knowledge of basic operations and computations to solving word stories and interpret what to do with the remainder in division problems? Learning Targets 1. The students will solve multiplication and division number stories and problems. (4.OA.2) 2. The students will interpret a remainder in the context of a division problem. (4.OA.3) 3. The students will make reasonable estimates for whole number multiplication and division problems and explain how estimates were obtained. (4.OA.3, 4.NBT.3, 4.NBT.6) Unit 7 Fractions and Their Uses (25 days) Essential Question: Why is it important for students to understand that fractions are parts of a whole, sets, and regions, equivalent fractions and decimals and handle objects and look at pictures in order to understand what fractions mean? Learning Targets 1. The students will apply and extend previous understanding of multiplication to multiply a fraction by a whole number understanding that each part refers to the whole. (4.NF.3a, 4. NF.4a,4b,4c, 4.MD.4) 2. The students will find equivalent fractions and explain why they are equivalent. (4.NF.1, 4.NF.3b, 4.NF.5 ) 3. The students will compare and order fractions with different numerators and different denominators and use mathematical language and logical reasoning to justify the solution. (4.NF.2) 4. The students will add and subtract mixed numbers and fractions with like denominators by replacing each mixed number with an equivalent fraction. (4.NF.3c, 4.MD.4) 5. The students will use decimal notation for fractions with denominators 10 or 100. (4.NF.6) 6. The students will compare two decimals to hundredths (using symbols <, >, =)by reasoning about their size and understand that comparisons of decimals is only valid when the two decimals refer to the same whole and justify their conclusions. (4.NF.7) Unit 8 Perimeter and Area (20 days) Essential Question: Are we able to activate our prior knowledge to develop formulas as mathematical models for finding the areas of rectangles, parallelograms and triangles? Learning Targets 1. The students will apply the four operations to solve story problems involving various types of measurement (distances, intervals of time, money, liquid volumes, masses of objects, etc.). (4.MD.2) 2. The students will recognize relative sizes of measurement units within a system of measurement including metric and express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit (ie: one foot is 12 times as long as one inch, etc.). (4.MD.1) 3. The students will describe and use strategies to measure an angle with reference to a circle and state that measurement using degrees (with a protractor). (4.MD.5a, 4.MD.5b, 4.MD.6) Unit 9 Reflection and Symmetry (5 days) Essential Question: Will the child incorporate/apply the concepts of property as it relates to lines and angles? Learning Targets 1. The students will draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, obtuse, acute) and perpendicular and parallel lines. (4.G.1) 2. The students will classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines. (4.G.2) 3. The students will create lines of symmetry and identify symmetric figures. (4.G.3)