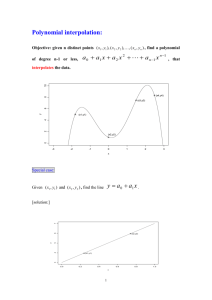
5-4A Factor and Solve Polynomial Equations
advertisement
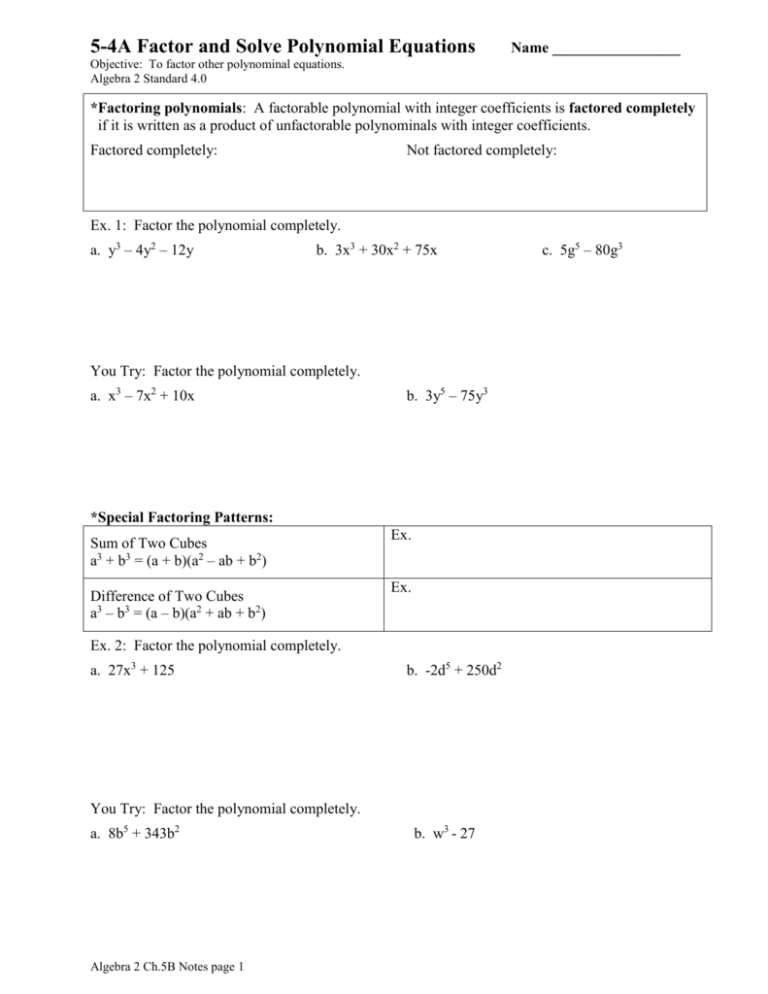
5-4A Factor and Solve Polynomial Equations Name _________________ Objective: To factor other polynominal equations. Algebra 2 Standard 4.0 *Factoring polynomials: A factorable polynomial with integer coefficients is factored completely if it is written as a product of unfactorable polynominals with integer coefficients. Factored completely: Not factored completely: Ex. 1: Factor the polynomial completely. a. y3 – 4y2 – 12y b. 3x3 + 30x2 + 75x You Try: Factor the polynomial completely. a. x3 – 7x2 + 10x b. 3y5 – 75y3 *Special Factoring Patterns: Sum of Two Cubes a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 – ab + b2) Difference of Two Cubes a3 – b3 = (a – b)(a2 + ab + b2) Ex. Ex. Ex. 2: Factor the polynomial completely. a. 27x3 + 125 b. -2d5 + 250d2 You Try: Factor the polynomial completely. a. 8b5 + 343b2 Algebra 2 Ch.5B Notes page 1 b. w3 - 27 c. 5g5 – 80g3 *Factoring by Grouping: For some polynomials, you can factor by grouping pairs of terms that have a common monomial factor. The pattern is shown below: ra rb sa sb r a b s a b a b r s Ex. 3: Factor the polynomial completely. 27r3 + 45r2 – 3r – 5 You Try: Factor the polynomial completely. x3 + 7x2 – 9x – 63 *Quadratic Form: An expression in the form au2 + bu + c, where u is any expression in x, is said to be in Quadratic Form. Ex. 4: Factor the polynomial completely. a. 10x4 – 10 b. 3m12 + 54m7 + 51m2 You Try: Factor the polynomial completely. a. 16g4 – 625 Algebra 2 Ch.5B Notes page 2 b. 4h6 – 20h4 + 24h2 5-4B Factor and Solve Polynomial Equations Objective: To factor other polynominal equations. Algebra 2 Standard 4.0 Name _________________ Algebra 2 Notes *Solving polynomial equations: To solve polynomial equations by factoring, factor the polynomial and use the zero product property. Ex.1: What are the real number solutions of each equation? a) 4x5 – 40x3 + 36x = 0 b) 2x5 = 12x3 – 16x ? c) -27x3 + 15x2 = -6x4 ? You Try: What are the real number solutions of each equation? a) 2x5 + 24x = 14x3 b) 6x3 + x2 = 2x c) 17x3 + 6x2 = 3x4 Algebra 2 Ch.5B Notes page 3 5-5 Dividing Polynomials Name__________________ Objective: To divide polynomials using long division and synthetic division. Algebra 2 Standard 3.0 *When you divide a polynomial f(x) by a divisor d(x), you get a quotient polynomial q(x) and a remainder polynomial r(x). f x r x q x d x d x *Polynomial Long Division: When dividing polynomials, set it up just as you would with numbers 1 2 means 2 1 . * How to set up polynomial division: 1) Write the dividend and divisor in descending powers of the variable. 2) Insert placeholders with zero coefficients for missing powers of the variable. Ex. 1: Divide f(x) = x3 + 3x2 – 7 by x2 – x – 2 (Notice f(x) is missing x-term, use 0x) Ex. 2: Divide f(x) = 3x3 + 17x2 + 21x – 11 by x + 3 Algebra 2 Ch.5B Notes page 4 You Try: Divide using long division. a. (2x4 + x3 + x – 1) ÷ (x2 + 2x – 1) b. (x3 – x2 + 4x – 10) ÷ (x + 2) *Synthetic Division can be used to divide any polynomial by a divisor in the form x – k. Ex. 3: Divide f(x) = 2x3 + 9x2 + 14x + 5 by (x – 3) You Try: Use Synthetic Division to divide. a. x3 4 x 2 x 1 x 3 Algebra 2 Ch.5B Notes page 5 b. 4x 3 x 2 3x 7 x 1