Ch7 Notes
advertisement

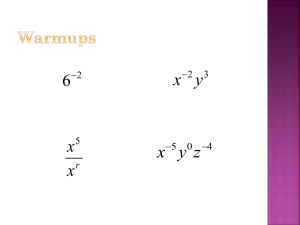
Algebra 2 Notes 7-1 Name________________________ Date____________Period______ 7-1: Roots and Radical Expressions Def: The nth root of an equation: For any real numbers a and b , and any positive integer n , if a n b then a is the nth root of b . Type of Number Number of Real nth Roots When n Is Even Number Of Real nth Roots When n is Odd Positive 0 Negative Radical Expressions Vocab index na radicand The principal root is the positive root of a number that has a positive and negative root. Property: nth root of a n , a 0 For any negative real number a , n a n a when n is even. Ex: Simplify each radical expression 4x 6 3 a 3b 6 4x 2 y 4 3 27c 6 4 4 x 4y 8 x 8 y 12 HW: ______________________________________________ Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) page 1 of 8 Algebra 2 Notes 7-2 Name________________________ Date____________Period______ 7-2: Multiplying and Dividing Radical Expressions Multiplying Radical Expressions If n a and n b are real numbers, then n a n b n ab . Ex: Multiply and simplify answer if necessary. 3 12 3 3 3 4 4 4 3x 40n 2 3 2n 3 9 3 4 Simplify 3 54x 2 y 3 3 5x 3 y 4 . Assume all variables are positive. 24x 2 Dividing Radical Expressions If n a and n Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) b are real numbers and b 0 , then n a na . n b b page 2 of 8 Ex: Divide. Assume all variables are positive. 3 32 3 4 3 162 x 5 3 3x 2 4 1024x 15 4 4x Rationalizing the denominator To be in simplest form, a radical expression should have all perfect roots taken out of the radicand, and it should not have a radical in the denominator. Ex: Rationalize the denominator of each expression. Assume all variables are positive. 2 3 7 5 x3 5xy 3 2 3x 2x 3 3 10xy 3 HW: _________________________________________________ Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) page 3 of 8 4 6x Algebra 2 Notes 7-3 Name________________________ Date____________Period______ 7-3: Binomial Radical Expressions Like Radicals are radicals that have the same index and the same radicand. If radical terms are “like”, we can add or subtract them. Ex: Add or subtract if possible. It may be necessary to simplify the radicals first to see if you have like terms.: 5 75 2 12 2 3 3 27 53 x 33 x 50 4 32 3 12 5 3 7 12 3 75 Multiplying and Dividing Binomial Radical Expressions Ex: 3 2 5 2 4 5 7 6 8 2 Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) 2 2 5 6 2 5 5 6 5 6 page 4 of 8 Rationalizing Binomial Denominators Multiply by a fraction of conjugate of denominator . Simplify. conjugate of denominator 3 5 5 7 1 5 4 3 HW: _________________________________________________________ Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) page 5 of 8 Algebra 2 Notes 7-4 Name________________________ Date____________Period______ 7-4: Rational Exponents Another way to write a radical expression is with a rational (fraction) exponent. See the examples below: 1 25 5 2 1 3 27 27 3 4 16 16 4 1 Try these. Simplify each expression: 1 1 125 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 3 100 3 52 52 1 22 82 22 22 What to do when the numerator of a rational exponent is other than 1: If the n th root of a is a real number and m is an integer, then 1 an na and a m n n am n a m . If m is a negative, a 0 . Ex: Convert from radical to rational exponent form, or vice versa. 3 x5 Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) y 2.5 z3 b 5 2 page 6 of 8 Ex: Simplify: 32 3 5 6 15 25 5 81 2 32 5 8x 4 3.5 1 3 3 2 16 y 8 7 43 1 x x 8 x 6 HW: _________________________________________________________ Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) page 7 of 8 3 4 Algebra 2 Notes 7-5 Name________________________ Date____________Period______ 7-5: Solving Radical Equations Isolate the radical expression/rational exponent on one side of the equation. Raise both sides of the equation to the same power. (If trying to undo a square root, square both sides. If trying to undo a cube root, cube both sides. If solving for an x raised to the 2 3 power, raise both sides to the 3 , etc.) 2 Check for extraneous roots! Plug your answer(s) back into the original equation to make sure they work! Ex: Solve 2 3x 2 6 5x 1 6 0 2 3 2 x 2 3 50 2x 1 0.5 3x 4 3 x 3 2 54 0.25 0 3x 2 2 x 7 0 HW: ______________________________________________________________ Brashear Alg 2 Ch 7 notes (3/23/09) page 8 of 8