Completed EBP Form for Case Study #2
advertisement
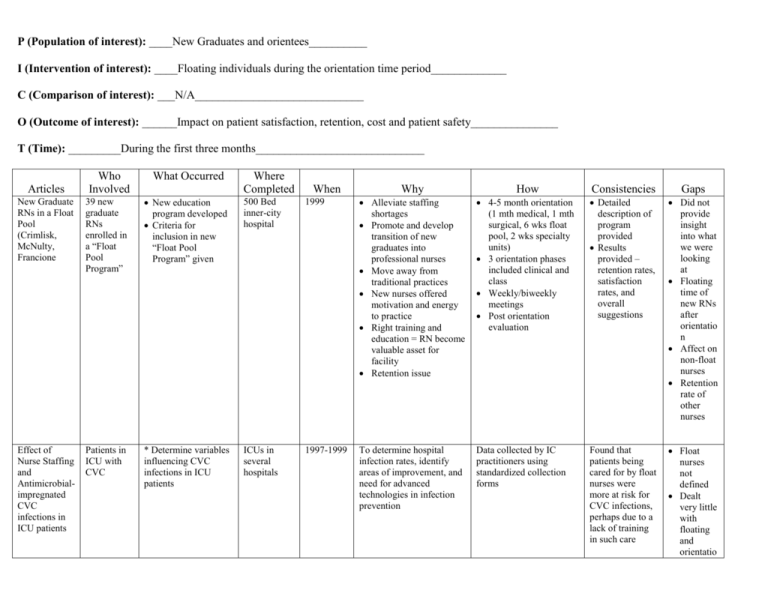
P (Population of interest): ____New Graduates and orientees__________ I (Intervention of interest): ____Floating individuals during the orientation time period_____________ C (Comparison of interest): ___N/A_____________________________ O (Outcome of interest): ______Impact on patient satisfaction, retention, cost and patient safety_______________ T (Time): _________During the first three months_____________________________ Articles Who Involved New Graduate RNs in a Float Pool (Crimlisk, McNulty, Francione 39 new graduate RNs enrolled in a “Float Pool Program” Effect of Nurse Staffing and Antimicrobialimpregnated CVC infections in ICU patients Patients in ICU with CVC What Occurred Where Completed Why How Consistencies Gaps New education program developed Criteria for inclusion in new “Float Pool Program” given 500 Bed inner-city hospital 1999 When Alleviate staffing shortages Promote and develop transition of new graduates into professional nurses Move away from traditional practices New nurses offered motivation and energy to practice Right training and education = RN become valuable asset for facility Retention issue 4-5 month orientation (1 mth medical, 1 mth surgical, 6 wks float pool, 2 wks specialty units) 3 orientation phases included clinical and class Weekly/biweekly meetings Post orientation evaluation Detailed description of program provided Results provided – retention rates, satisfaction rates, and overall suggestions Did not provide insight into what we were looking at Floating time of new RNs after orientatio n Affect on non-float nurses Retention rate of other nurses * Determine variables influencing CVC infections in ICU patients ICUs in several hospitals 1997-1999 To determine hospital infection rates, identify areas of improvement, and need for advanced technologies in infection prevention Data collected by IC practitioners using standardized collection forms Found that patients being cared for by float nurses were more at risk for CVC infections, perhaps due to a lack of training in such care Float nurses not defined Dealt very little with floating and orientatio n issues The Wild Blue Yonder Any staff nurses floating to unfamiliarly units The authors and her clinical supervisors Insufficient staffing causing nurse to float to unfamiliar area and told to act as nurse’s aides Author floated to ICU without orientation, instructed to work as NA, Legal still a RN, Acute care facility Assumption is a hospital setting with an ICU Working extra shift as float after completing routine shift PerAugust 2000; Short Staffing Intended to express author’s belief about floating nurses to units without providing adequate orientation results in problems with patient safety As result of nursing shortage and current float policy Author’s own experiences and conversations. Nursing shortage resulting in use of floating as solution to short staffing Writing documents consistency of feelings voices. Lack of policy/proce dure governing floating resulting in unsatisfactor y work environment for nurses and unsafe conditions for patients Strictly personal and opinionated Floating: Managing a Recruitment and Retention Issue Any staff nurse floating West Virginia University Hospital used staff and float pool RNs Insufficient staffing causing nurses to float either to unfamiliar areas resulting in increased rates of RN/LVN turnover at facility Float using unassigned RN and floor RNs on a rotating basis Acute care facility West Virginia University Hospital Floating at beginning of shift as solution to short staffing 8/2000 Short staffing due to high rate of RN/LVN nursing turnover d/t low retention, low patient satisfaction, low RN stress satisfaction Nursing shortage resulting in use of floating as solution to short staffing Success from nurses Lack of policy/proce dure governing floating resulting in unsatisfactor y work environment for nurses and unsafe conditions for patients Said Another Way: Our Obligation to Float N/A N/A N/A N/A To defend floating as a short term fix to the nursing shortage and promote patient safety As result of nursing shortage and high rate of turnover due to dissatisfaction with floating policy Improved by increasing 10% pay to float nurses by 10% per hour, used a resource person for the floated nurse, used a float log, written responsibilities from the floor that expected from the floor for the nurse to do; feedback to managers Review of professional literature, electronic resources, nursing textbooks, statements Discussed out obligation to float as an ethical and Doesn’t suggest how we are to pay for the from AACN, Joint Commission, Sigma, legal cases, and personal experiences patient safety issue; used credible sources to justify statements; opposition to floating was addressed with suggestions for improvement; offer proper orientation as staffing allows extra orientation Summary of findings: Definition of “float” needs to be clarified Legality of working as an “aide” when licensed as an RN Validated prior understanding and perceptions about floating Structured policies and procedures related to findings need to be in place and initiated during orientation Only two of the articles reviewed were true research projects, the rest of the articles were information Validated the increased comfort level – stated with idea they will be floated Application of findings to evidence-based practice that validates/changes policies and procedures: Need to evaluate the efficacy of float nurses in regards to infections and morbidity/mortality rates Clean up orientation process prior to floating – ensure knowledge based Patient safety and nurse comfort levels must be paramount Validated policy as written – full outline of orientation to be given at orientation, discuss policy and procedure for floating at orientation, 3 to 4 months prior to floating Orientees – regardless of experience upon hire are novices for a while due to change of setting Stress comes up when individual knows they are the next to float During orientation, all nurses will be told that they will eventually be required to float Suggestions for next steps o Tool related to assessment of readiness to float o Float policy needs to be revised o Identification of resource float person on each unit – potential research project Reference List Alonso-Eshanove, J., Edwards, J.R., Richards, M.J., Brennan, P., Venesia, R.A., Keen, J., Ashline, V., Kirkland, K., Chou, E., Hupert, M., Veeder, A.V., Speas, J., Kaye, J., Sharma, K., Martin, A., Moroz, D., & Gaynes, R.P. (2003, December). Effect of nurse staffing and antimicrobial-impregnated central venous catheters on the risk for bloodstream infections in intensive care units. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, 2412), 916-925. Crimlist, J.T., McNulty, J.J., & Francione, D.A. (2002, April). New graduate RNs in a float pool: An inter-city hospital experience. JONA, 32(4), 211-217. Kane-Urrabazo, C., (2206, April/June). Said another way: Our obligation to float. Nursing Forum, 41(2), 95-101. Kany, K., (2000, August). The wild blue yonder. American Journal of Nursing, 100(8), 79. Kirchhoff, K.T. & Dalh, N., (2006, January). American association of criticalcare nurses’ national survey of facilities and units providing critical care. American Journal of Critical Care, 15(1), 13-27. Robert, D. (2004, June). Editorial: Competence increases comfort for float nurses. Medsurg Nursing, 13(3), 142. Rudy, S. & Sions, J., (2003, April). Floating: Managing a recruitment and retention issue. JONA, 33(4), 196-198.








