Practice Test Ch. 1
advertisement

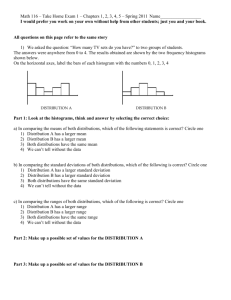
Chapters 1-5 Practice Test Name______________________________ Part I: Multiple Choice (Questions 1-10) - Circle the answer of your choice. 1. Mr. Garcia’s strings class had a standard deviation of 2.4 on a performance exam, while Mr. Hart’s percussion class had a standard deviation of 1.2 on the their performance exam using the same criteria. What can be said about these two classes? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Mr. Hart's class did less well on the test than Mr. Garcia’s class. Mr. Garcia’s class performed twice as well on the test as Mr. Hart's class. Mr. Garcia’s class performed 1.2 points better on the test as Mr. Hart's class. Mr. Garcia’s class is more homogeneous than Mr. Hart's class. Mr. Hart's class is more homogeneous than Mr. Garcia’s class. E; 2. The following is the DataDesk statistical summary of the gold medal performance in the men's long jump (measured in inches) for the modern Olympic series starting in 1900. Approximately what percent of the data lie between 298 and 350.5? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 25% 33% 50% 68% 75% E; 3. Weights of seals are given in the following histogram. For this data, which values are appropriate estimates of the data’s mean and standard deviation? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 100, 50 100, 100 200, 50 200, 100 300, 50 D; 4. A data set with seven data points has a mean of 5. One of the seven values in the data set is 8. What numerical contribution did the data point 8 make to the variance? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 1.25 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.25 B; 8 5 9 ; 2 9 1.5 7 1 5. In a frequency distribution of 3000 scores, the mean is 78 and the median as 95. One would expect this distribution to be: (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) skewed to the right skewed to the left symmetrical and mound-shaped symmetrical and uniform bimodal B; 6. A study was conducted on the weights of three different species of fish found in a lake in Finland. These three fish (bream, perch and roach) are commercial fish. Their weights are displayed in the boxplots below. Which of the following statements comparing these boxplots is NOT correct? (A) The median weights of the three species differ. (B) The spread of roach is less than the spread of the other two species. (C) The distributions of weights are approximately symmetric for all three species. (D) There are no outliers in weight for the three species. (E) The variability in the weights for the three species exceeds the variation in the three species’ means. C 7. Which of the following are true statements? I. The variance is the square root of the standard deviation. II. The standard deviation is zero only when all values are the same. III. The standard deviation is strongly affected by outliers. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) I and II I and III II and III I, II, and III None of the above gives the complete set of true responses. C; I is false, the standard deviation is the square root of the variance. II and III are both true. 8. The stemplot displays the 1988 per capita income (in hundreds of dollars) of the 50 states. Which of the following best describes the data? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Skewed distribution, mean greater than median Skewed distribution, median greater than mean Symmetric distribution, mean greater than median Symmetric distribution, median greater than mean Symmetric distribution with outliers on high end A; 9. A study was conducted to determine the effectiveness of varying amounts of vitamin C in reducing the number of common colds. A survey of 450 people provided the following information in the table. What conclusion can be made? No colds At least one cold None 57 (.204) 223 (.796) Daily amount of Vitamin C taken 500 mg 26 (.236) 84 (.764) 1000 mg 17 (.283) 43 (.717) (A) The data proves that vitamin C reduces the number of common colds. (B) The data proves that vitamin C has no effect on the number of common colds. (C) There appears to be a strong association between consumption of vitamin C and the occurrence of common colds. (D) There appears to be little association between consumption of vitamin C and the occurrence of common colds. (E) Since common colds are caused by viruses, there is no reason to conclude that vitamin C could have any effect. D; the conditional distribution for the incidence of colds for each given daily amount is shown above. The percentages are somewhat similar. 10. In the accompanying display, which has the larger mean and which has the larger standard deviation? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) D; Larger mean, A; larger standard deviation, A Larger mean, A; larger standard deviation, B Larger mean, B; larger standard deviation, A Larger mean, B; larger standard deviation, B Larger mean, B; same standard deviation Part II: Free Response (Questions 11-13) – Show your work and explain your results clearly. 11. Is it easier for the best National Basketball Association (NBA) players to get a rebound or an assist? The data was taken during the 1994-1995 season. The top 20 rebounding leaders averaged the following numbers of rebounds per game: 16.8 (Rodman), 12.6, 11.4, 11.1, 11.0, 10.9, 10.9, 10.9, 10.8, 10.8, 10.6, 10.6, 10.6, 10.4, 10.3, 9.9, 9.7, 9.7, 9.6, and 9.4 The top 20 assist leaders averaged the following number of assists per game: 12.3 (Stockton), 9.4, 9.3, 8.8, 8.7, 8.3, 8.2, 7.9, 7.7, 7.7, 7.6, 7.5, 7.3, 7.2, 7.1, 6.9, 6.4, 6.2, 6.1, and 5.7 (a) Compare these data using back-to-back stemplots. 16 | 8 16.8 Rebounding 97764 999886643 410 6 8 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Assist 7 1249 12356779 2378 34 3 (b) Compare the distributions. Shape-both are mound-shaped although rebounding appears to be skewed right. Center-Rebounding has a higher center (mean = 10.9, median = 10.7) than assists (mean = 7.815, median = 7.65); the cluster for rebounding is above the cluster for assists. Spread-the standard deviations are similar (1.568 for rebounding and 1.472 for assists). The IQR is greater for assists (1.5) than rebounding (.85) indicating a larger spread for the middle 50% of the scores for assists. Unusual Features-both have outliers. The outlier for assists is 12.3 and the outliers for rebounding are 12.6 and 16.8. 12. The histogram displays the number of children in a set of Brookwood High School families. 16 14 Frequency 12 10 8 6 4 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Children (a) How many families are represented in this study? n = 40 (b) What is the shape of the distribution? skewed right (c) Determine the mean and standard deviation and the median and IQR. mean = 3.15, standard deviation = 2.214 median = 2, IQR = 2 (d) Determine whether the distribution contains outliers. Show your work and include the fences in your calculations. 1.5 2 3.5 Q1 3.5 2 3 1 Q3 3.5 4 3 7 Since 8, 9, and 10 are greater than 7, they are outliers. (e) Comment on the most appropriate measures to report the center and spread of the distribution. Due to the skewness, the median and the IQR are the most appropriate measures of center and spread. 13. Hallux abducto valgus (call it HAV) is a deformation of the big toe that is not common in youth and often requires surgery. Doctors used X-rays to measure the angle (in degrees) of deformity in 40 consecutive patients under the age of 21 who came to a medical center for surgery to correct HAV. The angle is a measure of the seriousness of the deformity. Here are the data. 28 13 21 26 32 20 22 28 25 21 20 31 34 17 18 38 38 16 26 32 26 21 16 21 25 23 30 50 30 14 20 59 26 32 50 18 28 25 25 30 Make a graphical representation of the data and give a numerical description of this distribution. Write a brief discussion of the shape, center, and spread and anything unusual about the display of the data of the angle of deformity among young patients needing surgery for this condition. Stem-and-Leaf Display: Angle (degrees) Stem-and-leaf of Angle (degrees) Leaf Unit = 1.0 7 (20) 13 3 3 1 2 3 4 5 N = 40 3466788 00011112355556666888 0001222488 009 Stem-and-Leaf Display: Angle (degrees) Stem-and-leaf of Angle (degrees) Leaf Unit = 1.0 2 7 16 (11) 13 5 3 3 3 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 34 66788 000111123 55556666888 00012224 88 00 9 N = 40 Boxplot of Angle (degrees) 10 20 30 40 Angle (degrees) 50 60 Dotplot of Angle (degrees) 14 21 28 35 42 Angle (degrees) 49 56 Histogram of Angle (degrees) 10 Frequency 8 6 4 2 0 20 30 40 Angle (degrees) 50 60 Shape – cluster is symmetric, unimodal, skewed right Center – median = 25.5 Spread – IQR = 10 Unusual Features – 3 outliers In general, the angle of deformity is between 13 and 38 with 50% of patients having deformity angles from 20.5 to 30.5 .