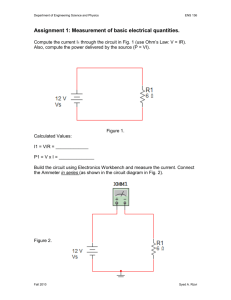
Assignment 1: Measurement of basic electrical quantities
advertisement

Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 Assignment 2: Analysis of series and parallel combinations of resistive circuits. Resistances in series: A set of resistors will be connected is series if the same current passes through all the resistors. The total resistance of the series combination of resistors is the sum of individual resistors. Compute the equivalent (total) resistance of the circuit shown in Fig. 1. Figure 1. Equivalent resistance RE = R1 + R2 = ______________ Current provided by the voltage source IS = VS/RE = ______________ V1 = I1 x R1 = _______________ V2 = I1 x R2 = _______________ V1 + V2 = ________________ Do you see any relationship between VS and V1 and V2? Please explain. Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 Compute power dissipated by R1 P1 = V1 x I1 = ________________ Power can also be computed as: P1 = I12 x R1 = ________________ and P1 = V12/R1 = _________________ Compute power dissipated by R2 P2 = V2 x I1 = ________________ also P2 = I12 x R2 = ________________ and P2 = V22/R2 = _________________ Compute power delivered by the voltage source: PS = VS x IS = __________________ Do you see any relationship between power delivered by the voltage source and the power dissipated by the resistors R1 and R2? Please explain. Now measure the equivalent resistance of the circuit in Fig. 1. Note that you’ll measure the equivalent resistance with respect to the source terminals. Disconnect the voltage source and connect the Ohmmeter at those terminals. Record your measurement below. RE = ____________ Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 Is the measure RE is the same as the computed RE? Now measure the current IS and voltage V1 and V2 (see the circuit diagram in Figure 2). Figure 2. IS = ___________ V1 = ______________ V2 = _______________ Are the measured values of the current IS and voltage V1 and V2 the same as their computed values? Now measure the power delivered by the source PS, power dissipated by the resistor R1 (P1) and the power dissipated by the resistor R2 (P2) (see the circuit diagram in Figure 3). PS = ___________ P1 = ______________ P2 = _______________ Are the measured values of PS, P1 and P2 the same as their computed values? Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 Figure 3. Resistances in parallel: A set of resistors are connected is parallel if the same voltage appears across all the resistors. The reciprocal of equivalent (total) resistance of the parallel combination of resistors is the sum of reciprocals of the individual resistors. Compute the equivalent (total) resistance of the circuit shown in Fig. 4. Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 Figure 4. Note that R2 and R3 are in parallel and the parallel combination of R2 and R3 is in series with R1. First find the equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of R2 and R3 1/RE23 = 1/R2 + 1/R3 RE23 = ______________ Equivalent resistance RE = R1 + RE23 = ______________ V1 = IS x R1 = _______________ V2 = IS x RE23 = _______________ V1 + V2 = ________________ = VS Current provided by the voltage source IS = VS/RE = ______________ Current through R2 = I2 = V2/R2 = ______________ Current through R3 = I3 = V2/R3 = ______________ What is the current through R1? I1 = _______________ Compute power dissipated by R1 P1 = V1 x I1 = ________________ Power can also be computed as: P1 = I12 x R1 = ________________ and P1 = V12/R1 = _________________ Compute power dissipated by R2 P2 = V2 x I2 = ________________ also P2 = I22 x R2 = ________________ Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 and P2 = V22/R2 = _________________ Compute power dissipated by R3 P3 = V2 x I3 = ________________ also P3 = I32 x R3 = ________________ and P3 = V22/R3 = _________________ Compute power delivered by the voltage source: PS = VS x IS = __________________ Do you see any relationship between power delivered by the voltage source and the power dissipated by the resistors R1, R2, and R3? Please explain. Now measure the equivalent resistance of the circuit in Fig. 4. Record your measurement below. RE = ____________ Is the measure RE is the same as the computed RE? Now measure the current IS , I2, I3, and voltage V1 and V2 (see the circuit diagram in Figure 5). Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi Department of Engineering Science and Physics ENS 136 Figure 5. IS = ___________, I2 = ______________, I3 = ______________ V1 = ______________ V2 = _______________ Are the measured values of the current IS,I2, I3, and voltages V1 and V2 the same as their computed values? Now measure the power delivered by the source PS, power dissipated by the resistor R1 (P1), the power dissipated by the resistor R2 (P2), and the power dissipated by the resistor R3 (P3). PS = ___________ P1 = ______________ P3 = _______________ P2 = _______________ Are the measured values of the PS, P1, P2 and P3 the same as their computed values? Fall 2010 Syed A. Rizvi