Incidence and Hospital Mortality of Acute Kidney Injury in the
advertisement

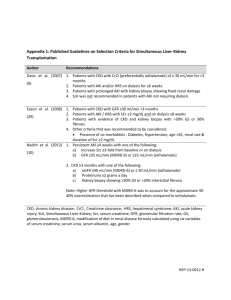
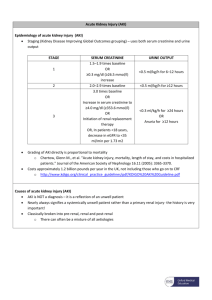
Incidence and Hospital Mortality of Acute Kidney Injury in the Surgical Intensive Care Units in Taiwan: report from NSARF 臺灣外科加護病房急性腎傷害之發生率及住院死亡率:NSARF 報告 Chieh-Li Wang1, Vin-Cent Wu1 , Tao-Min Huang2, Yu-Feng Lin1, Wen-Yi Li2, Ming-Shiou Wu1, Yung-Ming Chen1, Pi-Ru Tsai 3, Wen-Je Ko3, Kwan-Dun Wu1, and the NSARF Study Group 王介立 1、吳允升 1、黃道民 2、林裕峰 1、李玟儀 2、吳明修 1、陳永銘 1、蔡壁如 3、柯文哲 3、吳寬 墩 1、NSARF 研究群 1 Department of Internal Medicine and 3Surgery, National Taiwan University Hospital, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan 2 Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital Yun-Lin Branch OBJECTIVE: The incidence and outcome of acute kidney injury defined by he acute kidney injury network (AKIN) criteria in the surgical intensive care units has never been reported i. PATIENTS and METHODS: In the National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH) from Jan 2002 to Dec 2007, all patients admitted to the surgical intensive care units (SICU) with length of stay over 2 days were selected for analysis. Records of serum creatinine, measured by the Jaffe kinetic method, were retrospectively retrieved from the computer database. Acute kidney injury was defined by the AKIN criteria based on the creatinine rise during the first 2 days of stay in SICU. Records of renal replacement therapy (RRT) in the first 2 days were extracted from the NTUH-SICU-ARF (NSARF) Study database. Mortality data were extracted from the Department of Health. RESULTS: Of the 12,106 admissions (male, 60.8%, 60.0±16.7 years) were included for analysis, 4,252 admissions were excluded because of no repeated creatinine measurement during the first two days. The hospital mortality rate was 8.8%. Of the remaining 7854 admissions, the incidence of stage 1, 2, and 3 AKI were 15.9%, 1.6%, and 1.6% individually. The Incidence of RRT for AKI and ESRD accounted for 5.1% and 3.3%. The hospital mortality rates for stage 1, 2, and 3 AKI were 13.8%, 23.6%, and 27.0% (p < 0.0001). For patients receiving RRT for AKI and ESRD, hospital mortality rates were 35% and 14.5%. Comparing with the patients with stable creatinine in the first 2 days, those with a rise of creatinine more than 0.3 mg/dL but less than 150% (defined by the AKIN criteria but not by the RIFLE criteria) in the first 2 days had a relative risk of hospital death of 1.88 (1.63~2.17 of 95% CI). CONCLUSIONS: Changes of serum creatinine, even a minor rise, in the first 2 days in the SICU have significant impact on hospital mortality. Despite the fact that most of the patients with severe AKI received RRT, mortality remained high among this patient group. Key words: acute kidney injury (AKI), creatinine, intensive care unit (ICU), 關鍵字: 急性腎傷害、肌酣酸、加護病房