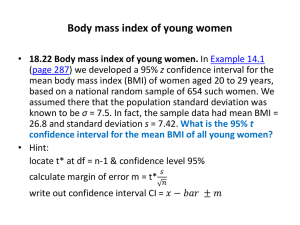
The standard error of the mean is $25
advertisement

Desperate Times. Desperate People? Desperate Answers! Sometimes I feel like I’m taking a multiple-choice test. And you think it’s hard to find an answer to my questions! Anyway, I offer the following for your practice—better try for the best not the correct answer. 1. The standard error of the mean is $25. Interpret the $25. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. I. J. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. R. S. T. U. V. X. Y. 25 dollars is the average of all sample distances from the mean measured in standard errors. The X s have a standard error of being $25 from the mean. There is a $25 range from the mean of which your sample mean should fall between. The difference about the mean out of the sample taken from the population. Out of the sample from the population, the margin of error is $25 from the mean. It is 25 above or below the mean. The standard deviation is $25. Observations will fall between (-25> X <25). 1 standard error above or below the mean of the population. The answer is within $25. The average distance of all values from the average mean of all sets in the population is $25. The mean of the population, which the sample represents, could be different than the sample by $25. The outcome will most likely be $25 or less away from the mean. For an increase in 1 deviation there is an error of $25. The average distance from the mean in either direction is $25. The $25 is the average distance3 from the mean. $25 is the average number of amount. $25 is the amount above or below the mean. 25 is 1.5 away from the mean. The $25 is 25 units away from the mean in either direction—It is how many units that are between X on an average. The average distance from the mean is $25. This means that the standard errors of $25, is above and below the mean and can go three standard deviation to complete an approximate 100%. The average distance of all X s is $25 from the population mean. 25 standard deviation from the mean. $25 below the mean. It is 25 from the mean. Out of all possible the sample mean $25 is the average of all possible deviations from all possible sample means. 2. The sample mean, $25, has a z-value of 0.8. Interpret the 0.8. A. The 0.8 is the average distance interval from the mean. B. The value is 0.8 standard errors from the mean. C. The outcome is 0.8 standard deviations above the mean. D. 0.8 is the distance from the mean. E. 0.8 is how many standard deviations from mean. F. Average distance from the mean measured in standard deviation is 0.8. G. The z value is 0.8 units right of the mean. H. The average distance of a value is 0.8 values away from the mean, 25, measured in standard deviations. I. The average value is 0.8 standard deviations from $25. J. It is the amount of the standard errors above the mean. K. L. M. N. O. P. Q. R. S. T. U. V. W. X. 0.8 standard deviations from the mean. X0 is 0.8 standard deviations from the mean. The Z is 0.8 standard deviations from the mean, 25. Each standard deviation is 0.8 above or below the mean, and from each other. $25 is 0.8 standard deviation above the mean. The Z value is 0.8 is 0.8 units above the sample mean. The average amount is 0.8 standard deviations from the sample size $25. The sample is 0.8 standard errors away from the mean. The z value is 0.8 above the mean. The z-value represents a number is the sample that is 0.8 standard error above the mean. Z value is 0.8 standard deviations from the mean of $25. the values is within 0.8 + or – from the mean. 0.8 is the average distance from X $25. The sample mean being $25 with a z value of 0.8 means the 0.8 is how many standard deviations it is away from $25. 3. Sample size increases but nothing else that affects width of confidence interval changes. Will the confidence interval expand, contract, or stay the same? Explain. A. Stay the same. Although you have more samples the size of the graph is the same just more numbers. B. Contract. As sample size increases the confidence interval will contract, due to the increase observations into the interval. Also the mean number will change due to the added numbers. C. Contract. When the sample size increases, the shape of the distribution gets to a more normal shape and closer to the mean, so as sample size increases, a confidence interval would get smaller. D. Contract. If the sample increases, then you have more information. So it makes it a better estimate. E. Contract, because you are more confident that the mean is within that interval. because you have more observations. F. Contract. The confidence interval will contract because with more information you get a more of a correct answer. G. Stay the same. CI is a percentage it will not change only if the CI is changed itself will the percentage change. H. Expand. If you have an increased sample size, you have a sample that is more likely to represent the population. I. Contract. because the more samples you are given, the more precise the outcome will fall in the given interval. J. Contract. As the sample size increases the standard error decreases. K. Contract. With more information, you can give a more precise answer. L. Expand. Because the more values you have, the more accurate your data and it will help increase the chance of getting the actual mean for the population. M. Contract. The larger sample will make it more representative of the population. N. Expand. The sample will start to look like the population. O. Expand. The sample size increases and in order to find the same percentage the CI must expand. P. Expand. the larger the number of observations, the larger the interval will be. Q. Contract. Because as the sample size increases, there is less room for outliers to have an affect on the confident interval. R. Contract. get smaller to give a more precise answer, closer to the mean. S. Expand. Because with more samples you get closer to the actual population result. More samples will allow you to be more confident than if you had lesser samples. T. Expand. You have more numbers to chose from. U. Contract. The reason for this is because as the # of observations increases towards the population the more confident will that interval be. Sample size is most normal when it is closest to the population. V. Expand. The more samples there are the wider the graph will get. Thus the confidence interval will increase to include the mean. W. Expand. With a larger sample you would be more confident that your sample would be in that interval.