All Example work
advertisement
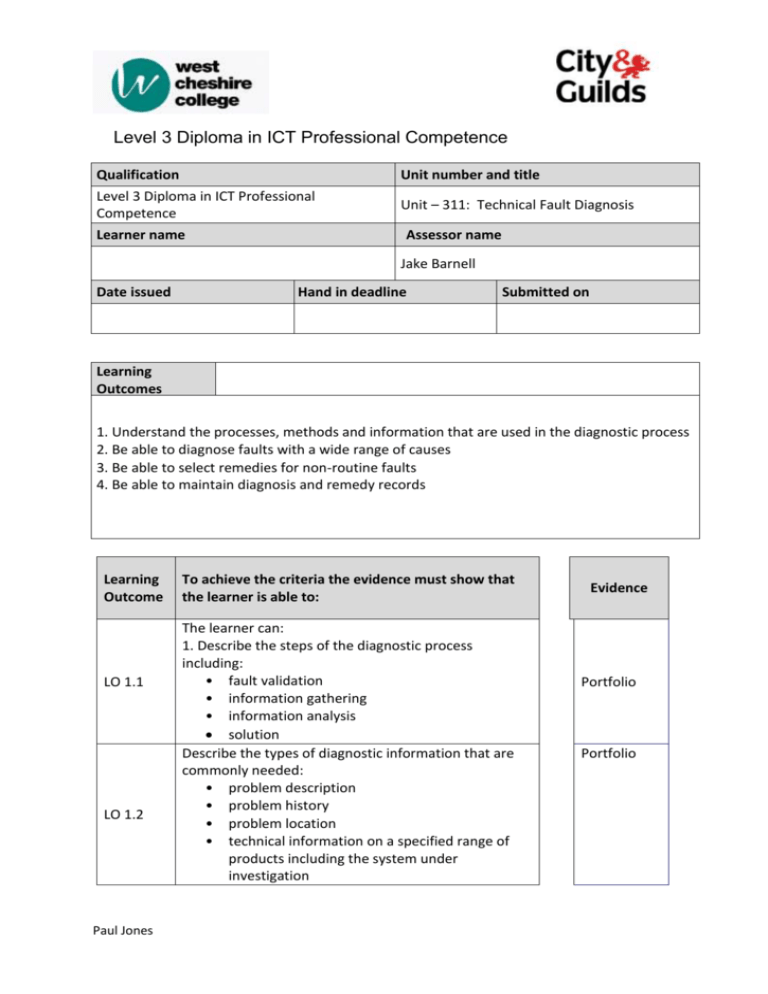
Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Qualification Unit number and title Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Unit – 311: Technical Fault Diagnosis Learner name Assessor name Jake Barnell Date issued Hand in deadline Submitted on Learning Outcomes 1. Understand the processes, methods and information that are used in the diagnostic process 2. Be able to diagnose faults with a wide range of causes 3. Be able to select remedies for non-routine faults 4. Be able to maintain diagnosis and remedy records Learning Outcome LO 1.1 LO 1.2 Paul Jones To achieve the criteria the evidence must show that the learner is able to: The learner can: 1. Describe the steps of the diagnostic process including: • fault validation • information gathering • information analysis solution Describe the types of diagnostic information that are commonly needed: • problem description • problem history • problem location • technical information on a specified range of products including the system under investigation Evidence Portfolio Portfolio Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Portfolio LO 1.3 Explain the following diagnostic methods and give examples of their appropriate use: • substitution • replication • performance and functional testing • environment change Explain how the following considerations can affect fault diagnosis. • minimisation of service disruption during diagnostics • individual responsibility and authority • escalation procedure • service level agreements Portfolio LO 1.5 Interpret detailed technical information on a range of products Portfolio The learner can: Select and correctly use appropriate diagnostic tools to carry out non-routine diagnosis Portfolio LO 2.1 LO 2.2 Select and use given sources of diagnostic and other technical information LO 2.3 Identify and interpret relevant information to support the diagnosis LO 1.4 Portfolio Portfolio Portfolio LO 2.4 Analyse information to diagnose faults with a wide range of causes, using at least three of the following approaches: • trend analysis • what-if scenarios • gap analysis • identification of cause and effect • flow charts Portfolio LO 2.5 Paul Jones Describe possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence LO 3.1 Select a suitable remedy to rectify identified faults taking into account the following: • business or service impact • resource and skill availability • ease of implementation • cost effectiveness • performance • compatibility • time • permanence LO 3.2 Identify possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults Portfolio Portfolio LO 4.1 Accurately document the diagnosis activities undertaken including: • fault description • supporting information • diagnostic tools etc used • cause of fault • remedy selected Portfolio Learner declaration I certify that the work submitted for this assignment is my own. I have clearly referenced any sources used in the work. I understand that false declaration is a form of malpractice. Learner signature: Paul Jones Date: Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assignment brief Assignment title Technical Fault Diagnosis Portfolio Purpose of this assignment This unit is about the ability to apply processes and techniques designed to diagnose the causes of faults within a technical context. In most situations this will be followed by the identification of an appropriate remedy for the identified fault (see Technical Fault Remedy Selection AOC). Faults in the context of IT and telecoms, normally relate to the failure of a system or equipment to act according to normal operating specifications. Faults can be manifested as complete or intermittent failures to operate; erratic or irregular operation; or operation below specified capacity. Scenario You are the newest member of the Network Helpdesk team at WCC. Your manager wants to put you through your paces and has set you several tasks, the results of which he will use to gauge your readiness for the post and identify any areas that require training. The work you produce and practical tasks you undertake will also provide you with invaluable resources and experience for your use and development throughout your IT career. Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Task 1 Produce a training manual explaining and demonstrating the importance of: the steps of the diagnostic process including: o fault validation o information gathering o information analysis o solution identification the types of diagnostic information that are commonly needed: o problem description o problem history o problem location o technical information on a specified range of products including the system under investigation Explain the following diagnostic methods and give examples of their appropriate use: o substitution o replication o performance and functional testing o environment change Explain how the following considerations can affect fault diagnosis. o minimisation of service disruption during diagnostics o individual responsibility and authority o escalation procedure o service level agreements The manual should be created in Word, contain appropriate screenshots or images as examples and laid out in such a way as to be appropriate for a technical document. This task covers LO1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4 Due: 14th November Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Task 2 You have been asked to carry out basic repairs on a computer system but before you begin you must be able to: Interpret detailed technical information on a range of products Once you have done this you must show that you are able to: Select and correctly use appropriate diagnostic tools to carry out non-routine diagnosis Select and use given sources of diagnostic and other technical information Identify and interpret relevant information to support the diagnosis Analyse information to diagnose faults with a wide range of causes, using at least three of the following approaches: o trend analysis o what-if scenarios o gap analysis o identification of cause and effect o flow charts Document your repair ensuring that you: Accurately document the diagnosis activities undertaken including: o fault description o supporting information o diagnostic tools etc used o cause of fault o remedy selected This task covers LO1.5, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 4.1 Evidence will be gathered by witness statement and video for the practical aspects and as fault repair logs with regard to the written aspects Due 5th December Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Task 3 Once the repair is complete you must then produce a report: Describing possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults And then in your report: Select a suitable remedy to rectify identified faults taking into account the following: o business or service impact o resource and skill availability o ease of implementation o cost effectiveness o performance o compatibility o time o permanence Identify possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults This tasks covers LO 2.5, LO 3.1, LO 3.2 Due 30th January Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Evidence checklist Describe the steps of the diagnostic process including: fault validation information gathering information analysis solution identification Describe the types of diagnostic information that are commonly needed: • problem description • problem history • problem location • technical information on a specified range of products including the system under investigation Explain the following diagnostic methods and give examples of their appropriate use: • substitution • replication • performance and functional testing • environment change Explain how the following considerations can affect fault diagnosis. • minimisation of service disruption during diagnostics • individual responsibility and authority • escalation procedure • service level agreements Interpret detailed technical information on a range of products Select and correctly use appropriate diagnostic tools to carry out non-routine diagnosis Select and use given sources of diagnostic and other technical information Identify and interpret relevant information to support the diagnosis Analyse information to diagnose faults with a wide range of causes, using at least three of the following approaches: Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence • • • • • trend analysis what-if scenarios gap analysis identification of cause and effect flow charts Describe possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults Select a suitable remedy to rectify identified faults taking into account the following: • business or service impact • resource and skill availability • ease of implementation • cost effectiveness • performance • compatibility • time • permanence Identify possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults Accurately document the diagnosis activities undertaken including: • fault description • supporting information • diagnostic tools etc used • cause of fault • remedy selected Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assessor's comments Qualification Unit number and title Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Unit – 311: Technical Fault Diagnosis Assessor name Learner name Jake Barnell Criteria To achieve the criteria the evidence must show that the learner is reference able to: Describe the steps of the diagnostic process including: • fault validation • information gathering LO 1.1 • information analysis • solution identification LO 1.2 LO 1.3 LO 1.4 LO 1.5 LO 2.1 LO 2.2 LO 2.3 Paul Jones Describe the types of diagnostic information that are commonly needed: • problem description • problem history • problem location • technical information on a specified range of products including the system under investigation Explain the following diagnostic methods and give examples of their appropriate use: • substitution • replication • performance and functional testing • environment change Explain how the following considerations can affect fault diagnosis. • minimisation of service disruption during diagnostics • individual responsibility and authority • escalation procedure • service level agreements Interpret detailed technical information on a range of products Select and correctly use appropriate diagnostic tools to carry out nonroutine diagnosis Select and use given sources of diagnostic and other technical information Identify and interpret relevant information to support the diagnosis Achieved? Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence LO 2.4 Analyse information to diagnose faults with a wide range of causes, using at least three of the following approaches: • trend analysis • what-if scenarios • gap analysis • identification of cause and effect • flow charts LO 2.5 Describe possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults LO 3.1 Select a suitable remedy to rectify identified faults taking into account the following: • business or service impact • resource and skill availability • ease of implementation • cost effectiveness • performance • compatibility • time • permanence LO 3.2 Identify possible ways to prevent reoccurrence of diagnosed faults LO 4.1 Accurately document the diagnosis activities undertaken including: • fault description • supporting information • diagnostic tools etc used • cause of fault • remedy selected Learner feedback Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assessor feedback Assessor signature Date Learner signature Date Unit 311 Terms of Reference This report investigates errors or faults to do with a PC and will help describe the faults that the PC has and give information on what to do to fix it Introduction The purpose of this report is to make a PC manual to help find faults and errors with the PC itself such as the inside of the PC. PC Manual 1. Steps of diagnostic process 1.1 Fault Validation When finding the error of a PC make sure to check the PC such as inside the case so that you are able check the fault and find out itself where it is coming from and you are able to validate the problem or fault occurs. 1.1 Information Gathered Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence When gathering information you would need to identify what the problem itself is such as if you hear a noise you must need to ask help to be able to know what the problem is and where is it coming from. When checking for the problem you might get an error message that can be displayed on the monitor and if there is an error and if it doesn’t give what the main error is then there is a problem. What you do from here is check the inside of the case of the computer and locate your problem by smelling for any burns or looking things such as a faulty cable. Form here ask for help so you are able to have information given to you by a teacher or from searching the internet to see what people say or suggest to do. 1.2 Information Analysis When you have received all information that you have gathered you know need to analysis all the information so you can analysis the problem and then you decide what the problem is that you are encountering. An example will be of you are trying to boot up a pc to get it to work but you can’t. From this problem you have received all the information gathered about it and what could possibly be wrong. From here it could be that you have a faulty cable or port in the computer when you put the power lead into the computer. 1.3 System analysis/ Identification When all the information has been gathered you need to come up with a solution on how you are going to deal with the problem that the PC has so it is important that you do some identification to make sure that you have the right solution so that you are able to handle it with no problems for when you come to fix it. 2 Types of diagnostic information 2.1 Problem history When dealing with a problem with the PC itself you need to a problem history for the whole PC so you are checking for problems that you might have before by checking over the problem history so that you are able to have an idea on what problem it could be that you have had with the PC before. 2.2 Problem description When you are dealing with the PC you need to go over the description of what the problem is itself by going over what is the issue is that has happened and it needs to addressed with a solution on how you are going to fix it before you try and solve the problem of what has happened to the PC. 2.3 Problem Location Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence When dealing with the problem you need to know where to locate the problem by finding where it is coming from so that you know which area inside the PC it is so you can locate it without any problems because if you’re not able to find it then there can be an issue. 2.4 Technical information on a range of components When you have find the location on the problem what you would need to do from here is to gather technical information on all the components within the PC so you can identify what is working or what might not be working by looking and going over every components within the area you are looking at. 3. Diagnostic methods 3.1 Substitution When you attempt to fix the PC with a solution what you would need is a substitution PC where you can test parts of the PC form all the components so that you are able to find out which parts don’t work so you don’t damage your main computer from the parts that do not work. 3.2 Replication When you are trying to fix your PC you should always try and replicate the problem itself by trying to recreate the problem so that you are able to understand of what the problem is with the PC so you can understand of what the problem can be so that you are able to deal with that problem. 3.3 Environment change A method that you could try if there is a problem with the PC is an environment change so if you have moved you PC to another room it can be affected by the temperature of the room so if it’s more warm or cold then it can have an effect on the PC. This can also happen with the humid of the room that you are or with another room where you might have you PC in. 3.4 Performance & functional testing A method that you could use when checking for problems should be by doing a performance and functional test which can also be known as stress testing by pushing your PC to its limits to see if there are any problems when you are performing this because it is able to help you find the problems that the PC has found. Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence 4. Considerations that affect fault diagnosis 4.1 Minimising service disruption Trying to solve a problem as quick and easy as it can be with the lowest amount of time possible to help decrease downtime then you need to get a company to help you by sending them the PC to repair at a certain time that you want it back so that the PC is fixed the best way that it can be. 4.2 Individual responsibilities and authority When dealing with a PC you need to making sure that you have the responsibilities to deal with the problem that is wrong with the PC because you need to make sure that what you are doing you have the authority to do because you could be doing to the PC itself that you don’t have the authority to do so you would need someone else to do it who has those responsibilities and authority to do that type of job. 4.3 Escalation procedure When trying to fix a PC you need to make sure that you try and escalate the problem by doing an escalation procedure where you have to get people from a company who are more qualified to be able to deal with the task at hand so that they are less able to damage or make the problem worse than it already is. 4.4 Service level agreements When you are getting another person or company to deal you need service level agreements where you are given a level of service that you agree to for the other person or company to be able to do things to your PC that you have agreed to. Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assignment brief – QCF BTEC Assignment front sheet Qualification Unit number and title Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Unit 4520-377 Website software Learner name Assessor name Dave Fitzgibbon Date issued Hand in deadline Submitted on Assignment Research, Document, Design and Create title In this assessment you will have opportunities to provide evidence against the following criteria. Indicate the page numbers where the evidence can be found. Criteria reference To achieve the criteria the evidence must show that the learner is able to: LO1 1. Be able to create structures and styles and use them to produce websites LO2 LO3 2. Be able to select and use website software tools and features to develop multiple page websites with multimedia and interactive features 3. Be able to publish and test multiple page websites with multimedia and interactive features Task no. Evidence 1&2 3 4 Learner declaration I certify that the work submitted for this assignment is my own. I have clearly referenced Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence any sources used in the work. I understand that false declaration is a form of malpractice. Learner signature: Paul Jones Date: Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assignment brief Qualification BTEC Extended Diploma in ICT Unit number and title Unit 28 Website Production Assessor name Dave Fitzgibbon Date issued Hand in deadline Assignment title Research, Document, Design and Create Purpose of this assignment Scenario Uncle Sam is responsible for the Sammie’s world famous Circus. The organisation recognises that the future of marketing is on the web. They currently employ a large number of acts that they would like marketing further in order to increase the number of tickets sold for each show by listing information on their acts. They would also like to show customers their up and coming dates and locations as listed below. They also require a gallery page to showcase their acts along with customer testimonials. They currently use a red, white and blue colour scheme on all promotional material. Acts A variety of acrobatics, gymnastics, including tumbling and trampoline, trapeze. contortion, stilts and juggling. Dates/Locations Williamson Wednesday 10th Aug 2015 Thursday 11th Aug 2015 Friday 12th Aug 2015 Saturday 13th Aug 2015 Sunday 14th Aug 2015 Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Redwood Tuesday 16th Aug 2015 Wednesday 17th Aug 2015 Thursday 18th Aug 2015 Friday 19th Aug 2015 Saturday 20th Aug 2015 Sunday 21st Aug 2015 Task 1 – Create Structures and Styles 1. In order to determine what is required for your client requirements you are to complete a client requirements specification. 2. In order to plan what website content and layout will be needed for each page and for the site you are to create 3 digital storyboards to illustrate your design to your client. Each storyboard must be different from one another to allow the client to see a range of possible solutions to the brief. Your client will then select a design for you to continue with. 3. Once your client has selected an appropriate design you are to make a template page ready to populate with the required content. Your webpages must be created using HTML 5 and an external CSS style sheet. You must ensure that your site is accessible, consistent and easy to navigate. Deadline 6/11/14 by 5pm This provides evidence for Part LO1 Task 2 – Constraints in Website Design 1. Provide guidance on laws, guidelines and constraints that affect the content and use of website. These are to include the following Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Copyright Act Computer Misuse Act Data Protection Act WCAG 2.0 W3C Validators Browser Compatibility You are to give an overview of each including what they are, how they affect web designers and the consequences of ignoring them. 2. Explain what access issues may need to be taken into account 3. Explain when and why to use different file types for saving content 4. Store and retrieve files effectively, in line with local guidelines and conventions where available DEADLINE 19/12/14 This provides evidence for Part LO1 Task 3 - Website Design Write a statement outlining the Client’s requirements and the purpose of the website. Particular attention should be paid to defining the requirements and purpose of the site clearly and realistically, as this is essential to gain D3 in the next task. Carry out the planning work for a multi-page, two-way interactive website. The plan should take the form of 3 different annotated digitally produced drawings which accurately portray your intended design. Your client will then choose which design they would like you to produce. Build a multi-page website with two-way interactivity, to meet the client and user needs. Prime evidence for this is the website itself in electronic form uploaded to the college server. Your website must consist of a minimum of 4 pages, include a chat-room function, meet your client requirements and use only copyright free images. This provides evidence for [P4 P5] Task 4 - Review and Adapt You are to carry out a self-review of your site detailing a minimum of 3 positives and 3 Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence negatives of your design. In addition to this, in order for you to gain constructive criticism, you are to ask 3 of your peers to review your website. Each of your peers is to give you a minimum of 3 positives and 3 negatives of your design. You are to make note of their views alongside your self-review. Based upon your peers’ feedback you are to improve your website in line with their views, you are to make a minimum of 4 changes. You are to provide screenshots of your original and updated site Within your self-review you are to create a series of annotated screen grabs to demonstrate that you have created a website which meets the defined requirements and purpose. You MUST link back to your client requirements. Further to this you are to outline the tools and techniques you used to plan and build the website. Ensure you cover the entire design and production process from conception to uploading the site to the server. You are to provide screenshots to aid in your explanations. This provides evidence for [P4 P5] Evidence checklist Web Architecture and Components Web 2.0 Risks and Prevention Methods Web Accessibility User & Server Side factors Client requirements and Storyboards TCP/IP Self and Peer review Website uploaded to server Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Screen shots of original and updated site. Tool and Techniques Analysis of website meeting client requirements Sources of information Web Architecture: http://prezi.com/osfgnbytvdzr/outline-the-web-architecture-and-components-whichenable-int/ Web 2.0: Web 2.0: Concepts and Applications By Gary Shelly, Mark Frydenberg Web Accessibility: http://www.w3.org/Talks/WAI-Intro/slide3-0.html Risks: http://www.w3.org/Security/ TCI/IP: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc958821.aspx http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2011/11/tcp-ip-fundamentals/ User and Server Side Factors: http://webperformanceandserverfactors.blogspot.co.uk/ Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assessor's comments Qualification BTEC Extended Diploma in ICT Unit number and title Unit 28 Website Production Assessor name Learner name Dave Fitzgibbon Criteria To achieve the criteria the evidence must show that the referenc learner is able to: e P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 M1 M2 M3 D1 D2 D3 Learner feedback Assessor feedback Paul Jones Achieved ? Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence Assessor signature Date Learner signature Date Unit 377 web development Constraints in Website design Contents Copyright Act: ....................................................................................................................................... 24 Computer misuse act: ........................................................................................................................... 25 Data protection act: .............................................................................................................................. 26 WCAG 2.0: ......................................................................................................................................... 26 W3C Validators: ................................................................................................................................ 26 Browser compatibility: ...................................................................................................................... 27 Copyright Act: Can’t use anyone else’s content without their permission because it goes against the copyright act. If you want to be able to use someone content that they have made then you need to be given the rights such as paying to use that person’s content for a certain amount of time. This is known as royalty which is a usage-based payment where you are paying someone to use their content for a certain price if the person allows it. If you are caught using any content that is not created by you it is known as copyright and you can face up to 20 years in prison for using content that is not made or owned by you. Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence You can also receive a fine of up £5 million for copyright because you are using content illegally that you are not meant to do so. You can also be given restrictions on what type of things you can do if you were to use anyone’s content such as an image if you paid to use it the owner can give you certain restrictions on what you can use it for but if you don’t follow these restrictions you can be fined. Intellectual property is where a company or someone owns the right to a certain thing such as a song or a word that if used by anyone else they get money of it. For example is two bug companies such as Apple or Samsung where making a new phone with certain features such as apps one of them such as apple can have the rights to make the word “apps” their own so no one else can use that word for anything on phones etc. Computer misuse act: This act helps to stop people for misusing computers to do things with them that can affect others such as hacking others, spying on people, making websites to target hatred or violence on someone and also slander. Hacking: This is where people are able to hack into another person’s computer system or network where they can have access to all of the things that people own on that computer system and use the things that are on there to make money or even attack the things that are stored such as using Viruses that they can put on your computer or network that will always allow then to have control. Spying: This is where people are able to use computers to spy on others by using spying software etc. to be able to spy on you when you are using your computer or not or even on a website that you have made so they can monitor what goes on when you use a computer or when someone access your website they will be able to retrieve information etc. that these people have because they are spying on them. Hate/Violence: This is where people using computers to make websites or use websites such as Facebook so they can use to cause hate and violence to others for no reason (this is also known as cyber bullying) so they can make a website and put images and hateful words against others that will affect these people. These days if you are ever caught doing this you can put into prison for 3 years because it is not right to be able to do this for no reason. Slander: This where people use the internet to make a crime or a statement to someone that will damage that persons reputation all because of people just wanting to make people feel bad or just want them to suffer by using slander Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence against them with computers. Doing this can also get you 3 years in jail for it because you are hurting someone. Data protection act: This act helps to stop people from being able to steal data from other because the data protection act is about keeping all data and information in a stored place so that data is protected at all times. When you are using a computer you need to make sure that all data is protected by keeping it stored in a safe place so that if others try to gain access to your data they wont be able to have access to your data because it is in a stored place that only you can access. With the data protection it can also been used to keep information safe when you opt-in information to others by giving others the option to receive the information that you are giving them. Opt out with the act gives you the option to be able to avoid receiving any information given to you that you do not want to see or receive at all. WCAG 2.0: WCAG 2.0 (web content accessibility guidelines 2.0) helps with web content by making it more accessible for people who have disabilities. WCAG 2.0 contains these four important steps perceivable, operable, understandable and robust. Perceivable is all about making sure that you provide text alternatives for all non-text content. To be able to provide captions and any other alternatives that can be used for multimedia. Being able to create content so that it can presented in many different ways. They need to also make sure that there content can be easy to see and hear content. Operable is about being able to make all functions on your content available from a keyboard, to be able to give a user enough time to be able to read and also use your content, not to use any content that could cause seizures and also to make the website to help users navigate and also find content easy and simple. Understandable is where you need to make your content more readable and understandable for people, make sure that content appear and also with the content to operate in predictable ways, and also being able to make content which can help user to avoid and correct mistakes. Robust is where when you make content you need to maximize the compatibility with all of the current user tools and with future user tools. W3C Validators: The W3C validator is a validator by the World Wide Web, which allows Internet users to be able to check html, or xhtml documents that have been well made to the current standards. It is mainly a mark-up validity Of web documents which all include HTML, XHTML, SMIL, MATHML etc. The W3C Paul Jones Level 3 Diploma in ICT Professional Competence validator is also a service where you can donate to which helps the validators to build better tools for people to make better website. Browser compatibility: This includes all web browsers such as Firefox, chrome, opera, safari and the worst of them all is Internet explorer, which is the most out, dated browser to date. It is important for websites creators and current websites to be able to have there website compatible with all other browsers because some browsers such as Internet explorer wont display the website the same as it would on other browsers. Each web browser is able to access the Internet and to be able to access nearly any website that is on the Internet. The most popular browsers that people and web designers use is Firefox and Google chrome because these web browsers and always up to date unlike others such as Internet explorer where it is not up to date all the time because they need to keep coming out with more versions of it. When web designers come to make a website they need to take into consideration that if you ignore some things with other web browsers when designing a website then their website would be missing some features that only certain browsers use so the finished website that they have created would look great on one browser but not the other just because on some small little things that they missed. When coming to make a website you need to take into consideration the different types of web files and image files because with the different types of web files such as html, php and asp they only display on a certain type of browsers that will support that type of file so you will need to make sure that when using web files that you use one that will be compatible with all web browsers. Web designers will also need to take into consideration with image files as well because each image file such as jpeg or gif allow you to do things different with each other such as jpeg allows you to save image files where gif allows you to save animated images and with jpeg you can use them on many web browsers but with gif you are only able to use it on certain browsers that allow gif images so when you make a website you need to make sure that the type of files which you use can be displayed on all sites and the way you want them to be so they work on any web browser. Paul Jones





