HORMONES
advertisement

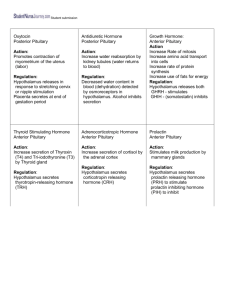
HORMONES HORMONE SOURCE OF HORMONE CRH (corticotropin RH) Hypothalamus ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) GHRH (growth hormone RH) and GHIH (growth hormone IH) Anterior pituitary (tropic hormone) Hypothalamus AKA somatostatin hGH (human growth hormone) Anterior pituitary gnRH (gonadatropin releasing hormone) LH(luteinizing hormone) AKA (lutotropin) Hypothalamus FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)AKA (follitropin) PIH (prolactin Inhibiting Hormone) dopamine PRL (Prolactin) AKA mammotropin Anterior pituitary (tropic hormone) PRH (Prolactin releasing hormone) TRH (thyrotropin releasing hormone) TSH(thyroid stimulating hormone) AKA(thyrotropin) MSH (melanocyte Stimulating Hormone) AKA (melanotropin) Anterior pituitary (tropic hormone) TARGET TISSUE OR ORGAN Anterior pituitary Adrenal cortex Anterior pituitary ALL cells; bone and skeletal muscles Anterior pituitary Ovaries (follicle cells) and testes (interstitial cells) Ovaries and testes REGULATORY HORMONE HORMONES EFFECT ON TARGET CRH stimulated by low levels of glucocorticoids and inhibited by high levels of glucocorticoids Stimulated by CRH Stimulates release of ACTH GHRH inhibited by high levels of somatomedins GHIH stimulated by high levels of somatomedins (compounds stimulating tissue growth; released by liver) GHRH and GHIH Triggers the release of glucocorticoids (cortisol) Stimulates release of hGH Inhibits release of hGH Stimulates growth, protein synthesis, lipid mobilization and catabolism gnRH stimulated by estrogen and inhibited by high levels of testosterone and progesterone Stimulated by GnRH Stimulates release of LH and FSH Stimulated by GnRH and inhibited by inhibin Stimulates gamete production; sperm and egg Stimulates maturation of the ovaries; stimulates the testes to produce testosterone to produce sperm; Sex hormone Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary PIH stimulated by high levels of prolactin Inhibits release of PRL(prolactin) Anterior pituitary Mammary glands Stimulates production of milk Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary Prolactin Releasing hormone (PRH) with high estrogen levels; and Prolactin inhibiting hormone (PIH) with low estrogen levels; accounts for swollen breast prior to menstruation PRH inhibited by high levels of Prolactin Hypothalamus Anterior pituitary Stimulates release of TSH and hGH Anterior pituitary (tropic hormone) Thyroid Stimulates to produce and secrete Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Stimulated by TRH Anterior Pituitary Melanocytes Inhibited by dopamine; MSHIH Increase the production of melanin in the epidermis; secreted during fetal dev., early childhood, pregnancy, and certain diseases Stimulates release of PRL Stimulates secretion of T3 and T4 OT (oxytocin) Neurohypophyseal hormones Positive Feedback ADH (Antidiuretic hormone) Neurohypophyseal hormone Produced by hypothalamus and secreted by Posterior pituitary Uterus, mammary glands Stimulated by nipple stimulation, drug pitocin, and start of labor Uterine contractions; release of milk (let down) from PRL; sometimes used to stop postpartum bleeding; cuddling hormone Produced by hypothalamus and secreted by Posterior pituitary Kidneys, sweat glands ADH production and release stimulated by low blood volume, low blood pressure, high osmotic pressure in the blood, turned off by alcohol and caffeine Increase water retention; inhibits urine formation; AKA vasopressin T4 (thyroxin) Thyroid gland Thyroid Hormone Secreted by follicle cells Main hormone of metabolism T3 (triiodothyronine) Calcitonin PTH (Parathyroid hormone) AKA parathormone Thyroid gland Most formed at target tissues by converting T4 to T3 Thyroid gland Produced by the parafollicular cclear cells Chief cells of Parathyroid gland Most body cells except adult brain, spleen, testes, uterus, and the thyroid gland itself Stimulated by TSH Increase energy utilization, body heat production oxygen consumption, growth, and development; stimulates enzymes concerned with glucose oxidation, increase BMR; Increase # of adrenergic receptors in BV Most body cells Stimulated by TSH “……………” Bones and kidneys Stimulated by elevated Ca2+ Decreases blood Ca2+ Bone, kidneys, intestine Stimulated by low blood Ca2+ levels; PTH effects are enhanced by calcitriol and opposed by calcitonin Controls Ca2+ balance in the blood in bone to release Ca and phosphates into blood; in kidneys to enhance reabsorption of Ca; in the intestine to increase absorption of Ca; causes conversion of Vit. D into its active form, calcitriol NE (norepinephrine) noraadrenaline AKA catecholamines Adrenal medulla (nervous tissue SNS) Most cells Blood vessels, liver, heart Stimulated by activated sympathetic preganglionic fibers (Ach release) Increase cardiac activity, blood pressure, glycogen breakdown, blood glucose levels; release of lipids by adipose tissue; more potent for vasoconstriction and BP Epinephrine AKA catecholamines Adrenal medulla Most cells, blood vessels, liver, heart Stimulated by activated sympathetic preganglionic fibers (Ach release) Increase cardiac activity, blood pressure, glycogen breakdown, blood glucose levels; release of lipids by adipose tissue; more potent for heart and metabolic activities. Aldosterone Most potent 95% of (mineralocorticoids) Adrenal cortex (glandular tissue; majority of gland) Kidneys Increase renal absorption of Na+ and water and accelerate urinary loss of K+; crave salty foods Cortisol Most important (glucocorticoids) Adrenal cortex Most body cells Androgens (Gonadocorticoids) AKA Sex hormones Testosterone is most important Adrenal cortex General; no effect on sexual characteristics Glucagon Secreted by alpha cells of the pancreas Liver, adipose tissues Insulin Secreted by beta cells of the pancreas Most cells Testosterone & Testes Testes; Stimulated by ACTH Stimulated by low blood glucose concentration; inhibited by GHIH like hormone from delta cells Stimulated by high blood glucose concentrations; inhibited by GHIH like hormones Stimulated by LH Stimulated by FSH Inhibin Anterior pituitary Estrogen Uterus Progesterone Uterus (regulates period, pregnancy) Increase blood sugar; keeps blood glucose levels constant; very active responding to stress; anti-inflammatory; enhance epi’s vasoconstrictive effects to increase BP; diseases Cushing’s disease and Addison’s disease Seem to be related to the female’s sex drive Promotes glycogenolysis; gluconeogenesis from lactic acid, fats & AA; elevates blood glucose concentrations Lowers blood sugar; affects protein and fat metabolism; enhances transport of glucose Sperm maturation; secondary sex characteristics and sex drive; necessary for sperm production; maintains sex organs in their functional state; Inhibin inhibits FSH release Maturation of reproductive organs; appearance of secondary sex characteristics; breast development and cyclic changes Ovaries Relaxin pelvis, cervix (dilates cervix and birth canal) Inhibin anterior pituitary (inhibits FSH release) Thymosins Thymus Lymphocytes and other cells of the immune response Inhibited by sex hormones Development of the T lymphocytes; coordinate and regulate immune response ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) Gastrin; secretin; serotonin Estrogen, progesterone, hCH, hCS Erythropoietin, Heart Kidney, adrenal cortex Reduces BP; blood volume, and blood Na concentration Gastrointestinal tract Placenta Stomach, liver, pancreas Uterus, ovary, mammary gland Stimulates local acting digestive hormones Kidneys Bone marrow Signals production of RBC; powerful vasoconstrictor Maintains pregnancy Renin Cholecalciferol Leptin Skin Adipose tissue Precursor of Vit. D Sensation of satiety (fullness) Reduces insulin sensitivity Resistin