Assiut university researches Role of MRI in evaluation of sport
advertisement

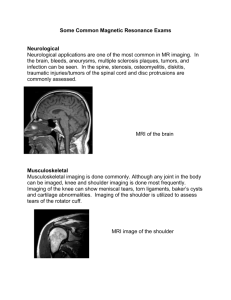
Assiut university researches Role of MRI in evaluation of sport injuries in knee joint دور ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى ف ى ت ق ي يم اإل صاب ات ال ري ا ض يه ال خا صه ب م ف صل ال رك به Aml Atef Ahmed Abd-Elrahman أمل عاطف أحمد ع بدال رحمن Abd Elkareem Hassan Abd Allah, Mohamed Zidan Mohamed, Abu Elhassan Hassib Mohamed أب و ال ح سن ح س يب محمد، محمد زي دان محمد،ع بدال كري م ح سن ع بدهللا Abstract: Sports-related knee injuries are common, with contact sports and sports involving twisting movements being the most frequent causes. Sports injuries may affect any of the knee structures, including ligaments, menisci, bones, and cartilage and peri-articular soft tissues. However, relatively few injuries involve isolated structures, with complexInjuries affecting multiple structures being much more common: dislocation, ligaments sprains and cartilage tears. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has an enormous impact on musculoskeletal imaging and the knee is the most frequently visualized. MRI of the knee is most commonly indicated in patients with suspected injuries of the menisci and cruciate ligaments. Plain radiographs have little value unless injury is due to direct impact. Orthopaedic surgeons commonly examine patients with knee pain; however, precisely diagnosing an intra-articular cause of pain is difficult. MRI of the knee is used to diagnose disorders of the knee because the high soft tissue resolution allows precise imaging of intra-articular structures. MRI of the menisci has proven useful for more than 10 years. MRI has become a practical tool for the evaluation of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries, with its high levels of accuracy and sensitivity reported in the literature. Intra-articular knee lesions are associated with significant morbidity and frequently need surgical treatment and rest. Although common, their correct diagnosis still is a challenge. Clinical tests may be confusing, and delay in diagnosis can result in socioeconomic problems and sometimes a worse prognosis. Therefore, complementary diagnostic tools are often necessary, mainly when suspecting multiple lesions. MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) of the knee provides detailed images of structures within the knee joint, including bones, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, muscles and blood vessels, from many angles. MRI is a non invasive medical test that helps physicians diagnose and treat medical conditions. MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio frequency pulses and a computer to produce detailed pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and virtually all other internal body structures. The images can then be examined on a computer monitor, transmitted electronically, printed or copied to a CD. MRI does not use ionizing radiation (x-rays). Benefits of MRI is: a noninvasive imaging technique that does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation, MRI has proven valuable in diagnosing a broad range of conditions, including muscular and bone abnormalities, MRI can help determine which patients with knee injuries require surgery, MRI may help diagnose a bone fracture when x-rays and other tests are inconclusive, MRI enables the discovery of abnormalities that might be obscured by bone with other imaging methods and MRI provides a noninvasive alternative to x-ray, angiography and CT for diagnosing problems of the blood vessels. Risks of MRI: the MRI examination poses almost no risk to the average patient when appropriate safety guidelines are followed, If sedation is used, there are risks of excessive sedation. The technologist or nurse monitors your vital signs to minimize this risk, although the strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or cause problems during an MRI exam, There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if contrast material is injected. Such reactions usually are mild and easily controlled by medication. If you experience allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance, Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is currently a recognized, but rare, complication of MRI believed to be caused by the injection of high doses of gadolinium contrast material in patients with very poor kidney function and Manufacturers of intravenous contrast indicate mothers should not breastfeed their babies for 24-48 hours after contrast medium is given. However, both the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the European Society of Urogenital Radiology note that the available data suggest that it is safe to continue breastfeeding after receiving intravenous contrast. MRI and MR arthrography are the most commonly used imaging techniques for evaluating the articular cartilage of the knee joint in clinical practice. Despite significant improvements in MRI technology over the past decade, a major limitation of currently available sequences is their inability to consistently detect superficial degenerative and post traumatic cartilage lesions that may progress to more advanced osteoarthritis. The relatively low sensitivity of these sequences is mainly attributed to their suboptimal spatial resolution. However, additional factors, such as partial volume averaging, suboptimal tissue contrast, and inability to evaluate articular cartilage in multiple planes, also play important roles in limiting the sensitivity. In the future, the use of high-field-strength scanners, multichannel coils, and more SNR-efficient sequences may allow images of the knee joint to be obtained with even higher spatial resolution and greater tissue contrast in clinically feasible scanning times. These sequences may further improve clinical cartilage imaging and will allow better identification of patients with knee pain who may benefit from early medical and surgical intervention. :ال م لخص ن أك ثر اإل صاب ات ت ع ت بر إ صاب ات ال رك بة مع األل عاب ال ري ا ض ية م ش يوعا ف هى ت حدث ل لري ا ض ين وك ذل ك ل أل شخاص ال عادي ين ال ذي ن ال وي ع ت بر م ف صل ال رك بة من أك ثر ال م ناطق عر ضة.ي مار سون ال ري ا ضة ل هذه اإل صاب ات ح يث أن ه ي ح توى ع لى أرب طة وغ ضاري ف سري عة ال تأث ر ألى حرك ات خاط ئة وال تى ت حدث عامة أث ناء ممار سة ال ري ا ضة أو .ي ع ت بر ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى من أهم ح تى ب دون ها ال و سائ ل ال م س تخدمه ل ت شخ يص إ صاب ات م ف صل ال رك بة ل ما ل ه دور ال غ ضاري ف, ف عال ف ى ت و ض يح أى من أجزاء م ف صل ال رك بة من أرب طة ال هالل ية ,ال عظام واألن سجة ال رخوة حول ال م ف صل .عادة ما ي فح صون ل رك بة ول كن جراحى ال عظام ال مر ضى ال ذي ن ي عان ون من األم ا الي س تط ي عون ت حدي د أ س باب األل م اذا ك ان ت ب س بب إ صاب ات داخل ال م ف صل وه نا ي أت ى دور ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى .وق د ث بت أهم ية ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى م نذ أك ثر من 01س نوات ف ى ال عدي د من األب حاث ال ع لم ية خا صة ف ى ت ق ي يم إ صاب ات ال رب اط ف ى و ا صاب ات ال غ ضاري ف ال هالل ية و ال ص ل ي بى األمامى و ال خل ارت شاح ال رك بة ح يث أن ه ي حظى ب م س توي ات عال ية من ال دق ة وال ح سا س ية .عادة ما ت ح تاج اإل صاب ات داخل ال رك بة ال ى ال تدخل ال جراحى وال راحة ال سري ري ة ول كن مازال ال ت شخ يص ال صح يح ل إل صاب ه ي ة ي م ثل ت حدي ا ك ب يرا .وي ع ت بر ال تأخر ف يه ي ؤدى إل ى م شاك ل إج تماع وإق ت صادي ة .ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى هو ف حص ط بى غ ير م تداخل وي ساعد األط باء ف ى ت شخ يص وع الج اإل صاب ات ال خا صة ب م ف صل ال رك بة ك ما أن ه ي حدد اذا ك ان ال م صاب ي ح تاج إل ى ت دخل جراحى أم ال .ي وف ر ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى إت احة ال صور ل م ف صل ي م كن ن قل هذه ال صور ع بر شا شات ال رك بة من عدة زواي ا مخ ت ل فة و ال حا سوب وي م كن إر سال ها إل ك ترون يا أو ط ب عها ع لى أق راص م ض غوطة. ال هدف من ال عمل • :معرف ة أ ش كال اإل صاب ات ال ري ا ض ية ال مخ ت ل فة ال خا صة ب م ف صل ال رك بة ب وا سطة ال ت صوي ر ب ال رن ين ال م غ ناط ي سى. صيخشت ىف ىسيطانغملا نينرلاب ريوصتلا رودو ةيمهأ نايب • ت حدي د طرق ال عالج ف ى اإل صاب ات ال ري ا ض ية ال خا صة ب م ف صل و ال رك بة.