The relationship between PAI-1 Polymorphism with recurrent
advertisement
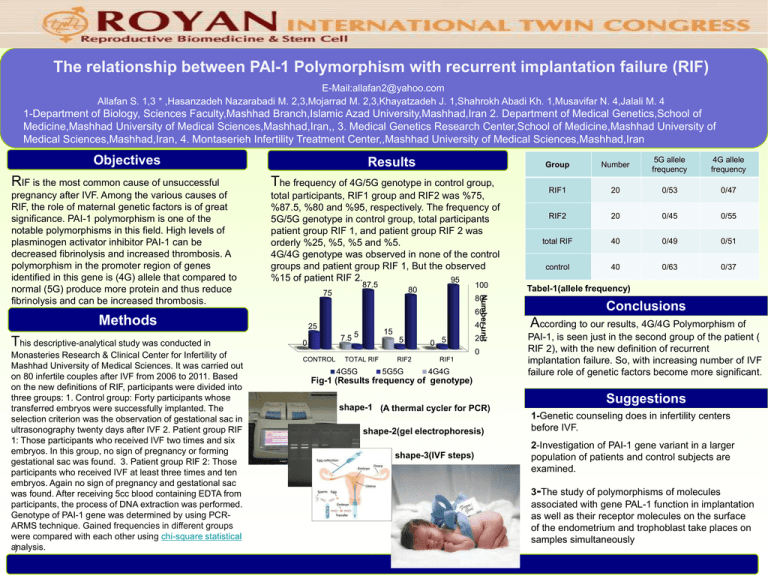
The relationship between PAI-1 Polymorphism with recurrent implantation failure (RIF) E-Mail:allafan2@yahoo.com Allafan S. 1,3 * ,Hasanzadeh Nazarabadi M. 2,3,Mojarrad M. 2,3,Khayatzadeh J. 1,Shahrokh Abadi Kh. 1,Musavifar N. 4,Jalali M. 4 1-Department of Biology, Sciences Faculty,Mashhad Branch,Islamic Azad University,Mashhad,Iran 2. Department of Medical Genetics,School of Medicine,Mashhad University of Medical Sciences,Mashhad,Iran,, 3. Medical Genetics Research Center,School of Medicine,Mashhad University of Medical Sciences,Mashhad,Iran, 4. Montaserieh Infertility Treatment Center,,Mashhad University of Medical Sciences,Mashhad,Iran Objectives Results RIF is the most common cause of unsuccessful The frequency of 4G/5G genotype in control group, pregnancy after IVF. Among the various causes of RIF, the role of maternal genetic factors is of great significance. PAI-1 polymorphism is one of the notable polymorphisms in this field. High levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor PAI-1 can be decreased fibrinolysis and increased thrombosis. A polymorphism in the promoter region of genes identified in this gene is (4G) allele that compared to normal (5G) produce more protein and thus reduce fibrinolysis and can be increased thrombosis. total participants, RIF1 group and RIF2 was %75, %87.5, %80 and %95, respectively. The frequency of 5G/5G genotype in control group, total participants patient group RIF 1, and patient group RIF 2 was orderly %25, %5, %5 and %5. 4G/4G genotype was observed in none of the control groups and patient group RIF 1, But the observed %15 of patient RIF 2. 95 87.5 Monasteries Research & Clinical Center for Infertility of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences. It was carried out on 80 infertile couples after IVF from 2006 to 2011. Based on the new definitions of RIF, participants were divided into three groups: 1. Control group: Forty participants whose transferred embryos were successfully implanted. The selection criterion was the observation of gestational sac in ultrasonography twenty days after IVF 2. Patient group RIF 1: Those participants who received IVF two times and six embryos. In this group, no sign of pregnancy or forming gestational sac was found. 3. Patient group RIF 2: Those participants who received IVF at least three times and ten embryos. Again no sign of pregnancy and gestational sac was found. After receiving 5cc blood containing EDTA from participants, the process of DNA extraction was performed. Genotype of PAI-1 gene was determined by using PCRARMS technique. Gained frequencies in different groups were compared with each other using chi-square statistical analysis. ) Number unit 75 80 60 Methods This descriptive-analytical study was conducted in 100 80 25 15 7.5 5 0 40 5 0 5 20 0 CONTROL TOTAL RIF 4G5G RIF2 5G5G RIF1 4G4G Fig-1 (Results frequency of genotype) shape-1 (A thermal cycler for PCR) shape-2(gel electrophoresis) shape-3(IVF steps) Group Number 5G allele frequency 4G allele frequency RIF1 20 0/53 0/47 RIF2 20 0/45 0/55 total RIF 40 0/49 0/51 control 40 0/63 0/37 Tabel-1(allele frequency) Conclusions According to our results, 4G/4G Polymorphism of PAI-1, is seen just in the second group of the patient ) RIF 2), with the new definition of recurrent implantation failure. So, with increasing number of IVF failure role of genetic factors become more significant. Suggestions 1-Genetic counseling does in infertility centers before IVF. 2-Investigation of PAI-1 gene variant in a larger population of patients and control subjects are examined. 3-The study of polymorphisms of molecules associated with gene PAL-1 function in implantation as well as their receptor molecules on the surface of the endometrium and trophoblast take places on samples simultaneously .