AAAAAAA-3
advertisement
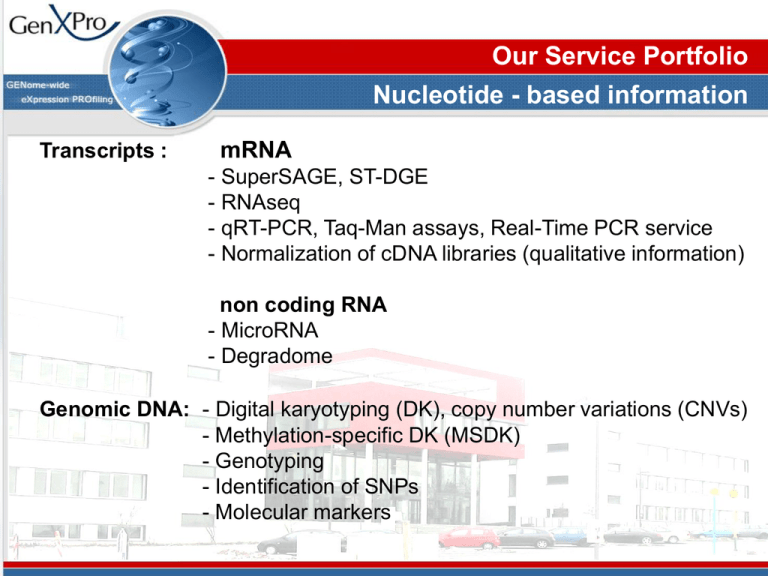
Our Service Portfolio Nucleotide - based information Transcripts : mRNA - SuperSAGE, ST-DGE - RNAseq - qRT-PCR, Taq-Man assays, Real-Time PCR service - Normalization of cDNA libraries (qualitative information) non coding RNA - MicroRNA - Degradome Genomic DNA: - Digital karyotyping (DK), copy number variations (CNVs) - Methylation-specific DK (MSDK) - Genotyping - Identification of SNPs - Molecular markers Transcriptome Analysis & Gene Discovery SuperTag Digital Gene Expression Profiling (ST-DGE) A patented, improved version of SuperSAGE, applying deep sequencing and a bias-free PCR technology for optimal tag-to-gene annotation and transcript quantification. ST-DGE - SuperSAGE became better How it works SuperTag Digital Gene Expression (STDGE) profiling: What gene is expressed and how often? Anchoring Enzyme Tagging Enzyme 5’ 3’ cDNA 5’ 3’ cDNA 5’ 3’ cDNA 5’ 3’ cDNA Streptavidin-Beads AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ Sequencing of Millions of 26 bp SuperTags Counting, BLAST, Statistics Digital Gene Expression Profiling Principle What Gene is expressed and how often ? Streptavidin-Beads 1.Digestion with Anchoring Enzyme 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ cDNA cDNA cDNA cDNA AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ Digital Gene Expression Profiling Principle What Gene is expressed and how often ? Streptavidin-Beads 1.Digestion with Anchoring Enzyme 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ cDNA cDNA cDNA cDNA AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ Digital Gene Expression Profiling Principle What Gene is expressed and how often ? Streptavidin-Beads 1.Digestion with Anchoring Enzyme 2. First Linker Ligation Linker 1 cDNA 3. Digestion with Tagging Enzyme 4. Recovery of Linker-Tags Linker 1 Linker 1 Linker 1 cDNA cDNA cDNA AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ Highly specific 26bp “SuperTags“ Digital Gene Expression Profiling Principle What Gene is expressed and how often ? Streptavidin-Beads 1.Digestion with Anchoring Enzyme 2. First Linker Ligation Linker 1 Linker 2 Linker 1 Linker 2 Linker 1 Linker 2 Linker 1 Linker 2 3. Digestion with Tagging Enzyme 4. Recovery of Linker-Tags 5. Second Linker Ligation 5. PCR AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ Digital Gene Expression Profiling Principle What Gene is expressed and how often ? Streptavidin-Beads 1.Digestion with Anchoring Enzyme 2. First Linker Ligation Linker 1 Linker 1 Linker 1 AAAAAAA-3’ Linker 2 TTTTTTT-5’ Linker 2 Linker 2 Linker Linker1 1 Linker 1 Linker Linker2 2 Linker 2 3. Digestion with Tagging Enzyme 4. Recovery of Linker-Tags 5. Second Linker Ligation 5. PCR 6. 2nd-Generation Sequencing 7. Counting of Tags, Bioinformatics AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ Sequencing of Millions of Tags Linker 1 Linker 2 Linker 1 Linker 2 Linker 1 Linker 2 Linker 1 Linker 1 Linker 1 AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ AAAAAAA-3’ Linker 2 TTTTTTT-5’ Linker 2 Linker 2 Counting, BLAST SuperTag Digital Gene Expression Profiling Quality Quality of digital gene expression data depends on: 1. Quality of the Tag (what gene is expressed?) 2. Quantity of the Tags (how often is the gene expressed?) Tag-Quality The Tagging Enzyme determines Quality of Tags: LongSAGE, other DGE platforms 18-21 bp MmeI: 5’- GGGACNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN -3’ 3’- CCCTGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN -5’ SuperSAGE, SuperTag-DGE EcoP15I : 26-27 bp (=SuperTAG) 5’-CAGCAGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN 3’-GTCGTCNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN -3’ -5’ Tag Quality What gene? SuperTags allow unequivocal identification of the corresponding gene Enzyme Plattform Tag-Size e-value BsmFI-Tag SAGE 14 bp 105 MmeI-Tag LongSAGE, other platforms 18-20 bp 0,34 EcoP15I-Tag SuperSAGE, ST-DGE 26-27 bp 0,00001 Tag Quality Advantages of the SuperTAG 21 bp versus 26 bp 18-20bp (MmeI, LongSAGE) 26 bp (Ecop15I, SuperTAG) BLAST-Hit , Mus musculus, Score = 52 ?! CATGGTGGCTCACAACCATC CATAAC Immunoglobulin kappa chain complex CATGGTGGCTCACAACCATC CGTAAT Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 10 ?! CATGGTGGCTCACAACCATC TGTAGA Homeodomain leucine zipper-encoding gene ?! CATGGTGGCTCACAACCATC TGTATC Mannose phosphate isomerase 1, transcript variant 4 ?! Only the 26 bp tag can differentiate between the transcripts ! Problem of PCR-introduced BIAS Certain tags are preferentially amplified during PCR biased quantification The Solution: GenXPro’s bias-proof adapters (patent pending) secure quantification Downstream applications & Advantages of the SuperTAG 26 bp SuperTAGs can: • directly be used as highly specific primer for PCR 3‘- and 5‘- RACE, RCA, in vitro PCR, qRT-PCR: new genes & non-model organisms can be analyzed. • serve as specific probes: identification of genomic or cDNA clones • be directly spotted on a microarray for HT analysis1 • be used for the simultaneous analysis of two or more organisms (pathogen/host)2 1. Matsumura et al. (2006) Nature Methods 3:469-474 2. Matsumura et al. (2003) PNAS 100: 15718-15723 RNA-Seq vs. ST-DGE (deepSuperSAGE) Mean transcript size : 2 500 bp AAAAAAA-3’ TTTTTTT-5’ 5’cDNA 3’ RNA-Seq SuperTag size: 26 bp STDGE For the same depth of analysis, RNA-Seq requires 20-100 times more sequencing !! *Asmann et. al 2009 Normalization of cDNA libraries Transcript frequencies in human pancreas Frequencies of transcript species Most of the transcript species are expressed at low levels (below 10 copies per million). Total transcript distribution Frequent transcripts make up 50 % of all transcripts: To get the info of rare transcripts, these 50% need to be sequenced as well... Digital Gene Expression vs. Microarrays Major Advantages of SuperTAG-DGE versus Microarrays • No false positives, no cross hybridisation • Open architecture platform: any gene detected, novel genes, unexpected transcripts, antisense transcripts • Reliable quantification of the transcriptome: counts vs. semi-quantitative light signal intensities • Higher dynamic range: unlimited vs. log2<3 • Rare transcripts are exactly quantified • Simultaneous analysis of more than one organisms: parasite-host Digital Gene Expression vs. Microarrays SuperTAG-DGE includes rare Transcripts About 80–95% of all mRNA species are present in five or fewer copies per cell. These rare transcripts make up 35–50% of all the mRNAs. SuperSAGE-Analysis: Transcript Frequencies Example: 4.455.653 Tags from Mouse Spleen (Mus musculus)* 101-1000 0,41% 6-20 17% 1000-10.000 0,16% 21-100 8% >10.000 0,01% More than 75 % rare transcripts: Only this part 1 is visible for 43% microarrays This information is lost on microarrays ! 2-5, 32% >18.000 different transcripts excluding the singletons * >13.000 Singletons with distinct matches to the NCBI-DB ST-DGE A Genome-Wide TaqMan Assay Similar expression tendency in TaqMan assays and ST-DGE Log2 foldchange Taqman assays vs. ST-DGE* Log2 foldchange SuperSAGE Log2 foldchange Taqman 5 3 2 1 -1 -2 -3 -4 Invariably expressed house keeping gene Aurora-Kinase A -6 -7 -8 *in developing chicken embryo gonads SuperTAG vs. Micro-arrays Comparable data: Exact number for every transcript vs. semiquantitative values (Microarrays, RT-PCR) microRNAs and the degradome microRNA mRNA-ends AAAAAAA-3’ AAAAAAA-3’ mRNA AAAAAAA-3’ AAAAAAA-3’ Next-Gen-Sequencing, counting, BLAST Digital Karyotyping (DK) Methylation-specific Digital Karyotyping (MS-DK) Quantification of short fragments of genomic DNA to identify chromosomal changes, amplifications, deletions, and the presence of foreign DNA sequences. 1. First enzyme digestion (methylation-sensitive) 5‘ 3‘ 2. 5‘ 3‘ DNA First linker ligation, binding to matrix Biotin 3‘ 5‘ Digital Karyotyping (DK) Methylation-specificDigital Karyotyping (DK) 3. Second enzyme digestion (methylation-insensitive) 5‘ 3‘ 4. Biotin Second linker ligation, EcoP15I digestion 5‘ 3‘ SuperTag 26bp Biotin Sequencing Counting, Annotation Thank you for your attention www.genxpro.de