Continental drift
advertisement

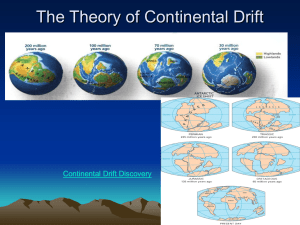
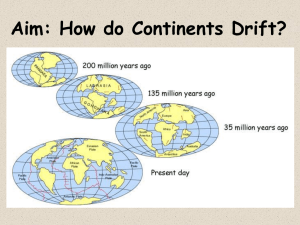
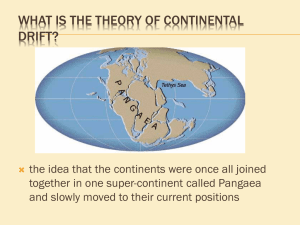
Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics Section 9.1 Continental Drift Continental drift • As people have studied maps , they were impressed by the similarity of the continental shorelines on either side of the Atlantic Ocean. • In 1915, Alfred Wegener, a German scientist, proposed his hypothesis of continental drift. • His hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single continent. • He called this super continent Pangaea, meaning all land. • Surrounding Pangaea was a huge ocean, Panthalassa, meaning “all seas.” • Wegener also hypothesized that about 200 million years ago Pangaea began breaking up into smaller continents. • These continents then drifted to their present positions. Continental drift Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis stated that all the continents once joined together to form A. Two major supercontinents. B. Two major supercontinents and three smaller continents. C. One major supercontinent. D. Three major supercontinents. The supercontinent in the continental drift hypothesis was called A. B. C. D. Panthalassa. Pangaea. Mesosaurus. Africa. What hypothesis states that the continents were once joined to form a single supercontinent? A. B. C. D. Plate tectonics Continental drift Seafloor spreading Paleomagnetism Continental drift Evidence to support continental drift 1. The Continental Puzzle: • When looking at maps of the time Wegener thought that the continents might have been joined when he noticed the similarities between coastlines on opposite sides of the South Atlantic Ocean. • His opponents correctly argued that erosion continually changes shorelines over time. CONTINENTAL DRIFT Continental drift 2. Matching Fossils: • If the continents had once been joined, Wegener reasoned, research should uncover fossils of the same plants and animals in areas that had been adjoining parts of Pangaea. • Wegener knew that identical fossil remains of Mesosauras, a small, extinct land reptile that lived 270 million years ago, had already been found in both eastern South America and western Africa. • Wegener knew that it was impossible for these reptiles to have swum across the Atlantic. • His opponents thought that there were land bridges that might have connected the continents at some earlier time. – Ex: Bering Straight between Asia and North America • There was no evidence that suggested that South America and Africa were connected by a land bridge. • Wegener thus concluded that South America and Africa must have been joined at one time. Continental drift Continental drift 3. Rock Types and Structures: • The clear picture in the continental drift puzzle is one of matching rock types and mountain belts. • Rock evidence for continental drift exists in the form of several mountain belts that end at one coastline, only to appear on a landmass across the ocean. – Ex: Appalachian Mountain Belt runs northeastward through the eastern U.S., ending off the coast of Newfoundland. Mountains of the same age with similar rocks and structures are found in the British Isles and Scandinavia. • When these landmasses are fit together the mountain chains form a nearly continuous belt. Continental drift Continental drift 4. Ancient Climates: • Wegener was a meteorologist, so he was interested in obtaining data about ancient climates to support continental drift. • He found glacial deposits showing that between 220 million and 300 million years ago, ice sheets covered large areas of the Southern Hemisphere. • Layers of glacial till were found in southern Africa and South America, as well as in India and Australia. • The land area that shows evidence of this glaciation now lies near the equator in a subtropical or tropical climate. • Large tropical swamps existed during the same time in the Northern Hemisphere with lush vegetation which eventually became the coal fields of the eastern U.S., Europe, and Siberia. Continental drift One kind of evidence that supports Wegener’s hypothesis is that A. The same magnetic directions exist on different continents. B. Major rivers on different continents match. C. Land bridges still exist that connect major continents. D. Fossils of the same organism have been found on different continents. Evidence about ancient climates indicates that A. Glacial ice once covered much of what is now India and Australia. B. Continents in the Northern hemisphere today were once centered over the South Pole. C. Continents in the Southern Hemisphere today were once centered onver the North Pole. D. No continents occupied the Southern Hemisphere. The geographic distribution of the swimming reptile Mesosaurus provides evidence that A. Europe was covered by a shallow sea when Mesosaurus lived. B. A land bridge existed between Australia and India. C. South America and Africa were once joined. D. The Atlantic Ocean was wider when Mesosaurus lived than it is now. Which of the following was not used in support of the continental drift hypothesis? A. B. C. D. Fossil evidence Paleomagnetism Ancient climate Fit of South America and Africa How did opponents of continental drift account for the existence of similar fossils on widely separated continents? A. B. C. D. Parallel evolution Oceanic currents Large ocean rafts Migration across land bridges Continental drift • Wegener’s drift hypothesis faced a great deal of criticism from other scientists. • One objection was that Wegener could not describe a mechanism that was capable of moving the continents across the globe. • Wegener proposed that the tidal influence of the Moon was strong enough to give the continents a westward motion. • Physicists responded that tidal friction of the size needed to move the continent would stop Earth’s rotation. Continental drift • Wegener also proposed that the larger and smaller continents broke through the oceanic crust, much like ice breakers cut through ice. • There was no evidence to suggest that the ocean floor was weak enough to permit passage of the continents without the ocean floor being broken and deformed in the process. • Most scientists rejected Wegener’s hypothesis, but a few geologists continued to search for additional evidence. Continental drift • With major strides in technology, scientists were able to map the ocean floor. • Extensive data on earthquake activity and Earth’s magnetic field also became available. • By 1968, these findings led to a new theory, known as plate tectonics. • This theory provides the framework for understanding most geologic processes. What was the main reason Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis was rejected? A. He was not well liked by other scientists. B. He could not provide a mechanism for the movement of the continents. C. He could provide only illogical explanations for the movement of the continents. D. His evidence was incorrect. Wegener’s idea that tidal forces might cause continental drift was shown to be impossible when it was A. Determined that Earth’s magnetic field was too strong. B. Shown that the tidal forces needed to move continents would stop Earth’s rotation. C. Determined that Earth’s density was too low. D. Shown that no tides occurred 200 million years ago. Science Journal Label the top of the page with Section 9.1 and the date. Answer in complete sentences. 1. Explain the theory of Continental Drift including the four pieces of evidence.