Fossils
advertisement
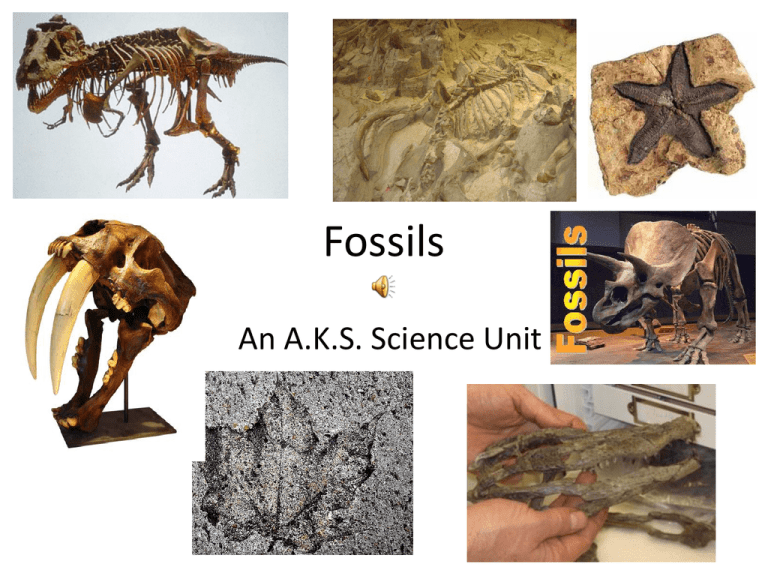
Fossils An A.K.S. Science Unit KWL What could this be? Riddle: What is old and tells us the story of life on Earth billions of years ago? Answer Fossils Fossils Facts • Fossils are the remnants of past life on Earth • Traces of prehistoric animals and plants (hard skeletons, shells of animals, and woody plant material) are preserved in sedimentary rock, amber and ice • A fossil is the imprint or remains of something that lived long ago • Fossils have also been found in amber (hardened tree sap) • Tree sap is a sticky liquid that can harden like glue • When an insect gets stuck in the tree sap, it may become a fossil in amber Amber Frayer • Frayer “ Fossils” • Use pgs. C-22 and C-23 • Include a “Summary” Imprints Imprint Facts • Imprints are shallow prints or marks in solid rock • Living things made the imprints • Imprints are made when living things press on the material that will later turn into rock Molds Mold Facts • A mold is an empty space in rock where something once was or lived • Shells often leave fossils called molds • Shell molds form after shells are buried in sand or mud • As water seeps in, it washes away the shells Cast Cast Facts • A cast is a fossil made inside a mold • A cast can form when minerals seep into a mold • As the minerals harden, they form a copy of the mold’s shape Inverted Triangle Graphic • Create an “Inverted” triangle graphic • Compare and contrast: Imprints, Molds, and Cast • Include a “Summary” • Don’t forget the “Middle” Are they related? Fossils tell us about the past • Fossils help us learn about what Earth was like long ago • Fossils tell us about plants and animals that lived in the past • Fossils can also tell us about the how Earth has changed Venn Diagram Compare and contrast the “elephant” and the “woolly mammoth” What is going on in this picture? What do you know about these words? • Excavate • Archaeological dig • Decompose • Fourth or bottom layer Fossil Fuels Fossil Fuel Facts • A fuel is a material that is burned for its energy • Fossil fuels formed from the remains of plants and animals from long ago • Examples of fossil fuels include: oil, gasoline, coal, and natural gas, Why might we run out of coal in the future? Frayer diagram Frayer “Fossil Fuels” Include a “Summary” Writing Connection • Write a three paragraph “Informational” story about fossils • Include an Introduction, body, and conclusion • Remember to elaborate • Use all 6+1 traits of writing • Brainstorm • Revise and Edit (conventions) Fill out the “L” side of your KWL Science Experiment C.R.C.T. Prep Fossils are usually found in which type of rock? A. Igneous B. Sedimentary C. Metamorphic D. Craggy What is the least number of years it takes for a fossil to form? A. 10 years B. 100 years C. 1,000 years D. 10,000 years Which part of an animal is least likely to be preserved as a fossil? A. Bone B. Tooth C. Skin D. Claw Fossils may also be found in ____________. A. amber B. tar deposits C. frozen earth D. all of the above The body of an animal is more likely to become fossilized if it______________. A. is left on the surface on the ground B. does not contain hard body parts such as bones C. is buried deeply in the ground D. fossilization is equally likely with all of the above A trace fossil is ___________________. A. part of the original organism that has been preserved B. a mark left behind by a living organism C. a hollow print left by the outside of an organism D. a very small part of a fossil A woolly mammoth found frozen in a glacier is an example of a __________. A. body fossil B. trace fossil C. mold fossil D. cast fossil During an archaeological dig, you excavate through four layers of rock that contain fossils. Where are the oldest fossils located? A. in the first, or top, layer B. in the second layer C. in the third layer D. in the fourth, or bottom, layer Why do hard parts of an organism help fossils to form? A. hard parts are less likely to decompose B. hard parts are less likely to be eaten C. hard parts are less likely to be broken D. all of the above An archaeologist is a person who studies_____. A. Remains of the past B. Living things C. Stars and planets D. Rocks What conditions help preserve a fossil? A. Exposure to air and water B. Rapid burn C. The presence of scavengers D. None of the above Which part of a animal is most likely to be preserved in a fossil? A. Lung B. Eye C. Blood D. Tooth Song Time Sung To: "Are you Sleeping" Stomping Dinos, Stomping Dino Where are you, Where are you We never got to meet you Never can we greet you We miss you, We miss you. Sung to: "Where oh where did my little dog go“ Oh, where, oh where did the dinosaurs go? Oh, where, oh where can they be? They were much too big to just disappear. It sure is puzzling to me! The Dinosaur Zoo Allosaurus, Stegosaurus, Brontosaurus too, All went out for dinner At the dinosaur zoo. Along called the waiter Called Tyrannosaurus Rex Gobbled up the table Because they wouldn't pay their cheques. The Dinosaur Song Dinosaurs lived long ago, Long ago, long ago. Dinosaurs lived long ago, And now they are extinct. Tyronnosaurus was a carnivore, carnivore, carnivore. Tyronnosaurus was a carnivore, And he ate only meat. Apatosaurus was a herbivore, Herbivore, herbivore. Apatosaurus was a herbivore, And he ate only plants. Dino-Pokey (to the tune of "The Hokey Pokey") You put your claws in, You take your claws out, You put your claws in, And you scratch 'em all about. You do the dino pokey, And you turn yourself around. That's what it's all about! Additional Verses: feet in feet out stomp them all about teeth in teeth out chomp them all about tail in tail out wag it all about I'm Bringing Home a Baby Dinosaur (to the tune of "Baby Bumble Bee") I'm bringing home a baby dinosaur, Won't my mommy fall right through the floor, I'm bringing home a baby dinosaur, Tromp! Tromp! Tromp! ROAR! ROAR! I'm bringing home a baby dinosaur, Won't my mommy hide behind the door I'm bringing home a baby dinosaur Ouch! Oh no! I'm squashed! (to the tune of "Do Wah Ditty") Here he comes just a stomping with his feet singing, "Dino ditty, ditty dum, ditty do." Searching all round for something good to eat singing, "Dino ditty, ditty dum ditty do." He's huge, (He's huge), He's strong, (He's strong.) He's huge, he's strong, won't be hungry very long. "Dino ditty, ditty dum , ditty do." "Dino ditty, ditty dum, ditty do."









