Chapter 21 Review
advertisement

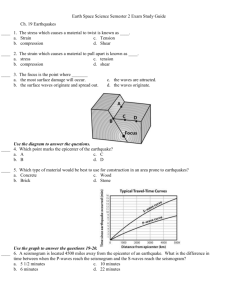
Chapter 21 Review Fossils and the Rock Record The oldest rock layer in an undisturbed rock sequence occurs 1. at the bottom of the sequence 2. below the sedimentary rock layer 3. below the unconformity 4. at the top of the sequence 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 15 ... se q of t p th e to th e lo w at be 16 he on fo rm ity un c im se d th e lo w be 14 en ta th e. .. of tto m bo th e at 1 r.. . 0% 0% 0% 0% 17 18 19 20 The amount of time it takes for one-half of the original amount of an isotope to decay is known as its 1. 2. 3. 4. correlation half-life period radioactivity 0% c 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 n tio a l re or 14 0% h ife f-l l a 0% rio pe 0% d ra 15 16 17 18 di iv ct a o ity 19 20 Evolution is the process by which organisms 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 16 ... be hi nd ev i er ve pr es e m e le av co be 15 de nc d in es an g ch o tt ap ad 14 b. .. ir . . th e d gr in nd ge s di 1 t.. . . 0% 0% 0% 0% ta 1. digest and grind their food 2. adapt to changes in their environments 3. become preserved by mineral replacement 4. leave behind evidence of their existence 17 18 19 20 On the geologic time scale, the smallest unit of time is called a(n) 0% 0% h n 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 oc ep pe eo er 0% d 0% rio era eon period epoch a 1. 2. 3. 4. 18 19 20 When part of the rock record is destroyed, the erosional gap that forms is a(n) 0% co 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 tio n su un 1 0% rp os i y ke in 0% pe be d io n 0% nf or m ity inclusion key bed unconformity superposition cl us 1. 2. 3. 4. 17 18 19 20 Which of the following is used to determine the absolute age of a rock? 1. 2. 3. 4. relative-age dating correlation permineralization radiometric dating 0% re 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 ti la -a ve ge 15 t da g in c 0% la re or n tio pe 16 0% 17 rm e in ra a liz n tio ra 18 di ric et om 19 0% da g tin 20 Index fossils are useful to geologists if the fossils 1. have lived over a short period of time 2. are not easily recognized 3. are not widely distributed geographically 4. are scarce h 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 0% 0% 0% 0% e av ed liv e ov ra a 15 re o sh .. a te o n 16 s ily re ar e .. g. co tw no 17 e id ly d 18 . ib tr is .. ar 19 e s e rc a c 20 What are fossil insects preserved in hardened tree sap called? 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 ga 14 15 16 0% be r s 0% am pr ol ite fo s e tr ac 1 0% st ro lit hs 0% co trace fossils gastroliths coprolites amber si ls 1. 2. 3. 4. 17 18 19 20 Molds, casts, coprolites, and petrified wood are all example of 1. fossils 2. radioactive isotopes 3. unconformities 4. disconformities 0% f si os ra 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 di 15 ls c oa e tiv i 0% e op t so 16 s un c 0% e iti m r fo on 17 s s di 18 co 0% iti m r o nf 19 es 20 The Phanerozoic Eon includes the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 17 Er as ic oz o en C Te 16 0% ch s ry Pe r si c ra s Ju 15 0% Ep o ds Pe r io oz o en C 1 0% io ds 0% rt ia Cenozoic Periods Jurassic Periods Tertiary Epochs Cenozoic Eras ic 1. 2. 3. 4. 18 19 20 The Archean and Proterozoic are examples of 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 as 0% er hs oc pe 1 0% ds 0% rio ns 0% ep eons periods epochs eras eo 1. 2. 3. 4. 17 18 19 20 Which of the following is marked by the appearance of organisms with hard parts? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 ... of th e oz o eg i nn i ng of th e Me s Pr ec nd eb ee th th th ee eb nd eg i nn i of th e ng of th e a. .. ... ic 0% 0% 0% 0% th 1. the beginning of the Cenozoic 2. the end of the Precambrian 3. the end of the Mesozoic 4. the beginning of the Cretaceous 17 18 19 20 Which of the following lists the units of geologic time in order from shortest to longest? era, eon, period, epoch epoch, eon, period, era eon, era, period, epoch epoch, period, era, eon 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 15 n er a, er io d, oc h, p er a, ep n, eo 16 eo ch d, e pe rio ,p er io on h, e oc ep 14 po d, e po ,p er io on a, e er 1 ra ch 0% 0% 0% 0% d, e 1. 2. 3. 4. 17 18 19 20 An example of a fossil with original preservation includes a(n) 1. insect imbedded in amber 2. coprolite 3. dinosaur footprint 4. mold of a fish skeleton 0% 0% 0% 0% in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 ct se im d be d de in ... co ite ol r p d a os in ur in pr t o fo m 15 16 17 d ol 18 o t fa fis h e el sk 19 n to 20 An example of a fossil with altered hard parts includes 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 d wo o d n. .. tr i fie pe ca ti a sa be r- t o ot he d ga st ... a hu m an a 1 ro lit h 0% 0% 0% 0% m um m ifi ed 1. a mummified human body 2. a gastrolith 3. a saber-toothed cat in tar 4. petrified wood 16 17 18 19 20 An example of a trace fossil includes a ud si on cr ac tra il or m 0% ra in d ro p im pr es st 0% k 0% w of a cl am 0% m cast of a clam worm trail mud crack raindrop impression ca 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Which correctly orders units of geologic time, from most general to most specific? 1. 2. 3. 4. eon, era, period, epoch era, epoch, eon, period period, era, eon, epoch epoch, eon, period, era 0% 0% 0% 0% eo 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 n 14 ra ,e io er p , d, er 15 o ep a, ch o ep o ,e h c n, rio pe pe 16 ri d ,e od 17 ra o ,e n, ep o ep ch e h, oc 18 o ri pe , n 19 ,e od ra 20 What is the correct label for “C” on the diagram? 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 0% ce le o Pa rm 17 ne ia n 0% ic zo le o Pa le o Pa 1 0% ne 0% Pe Paleogene Paleozoic Permian Paleocene ge 1. 2. 3. 4. 18 19 20 The shaded area of which graph represents the percentage of geologic time that is part of the Precambrian? 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 A B C D 12 13 14 15 0% 0% A B 16 17 0% 0% C 18 D 19 20 The principle of superposition can be used to determine 1. the actual age of these rock layers 2. the relative densities of these rock layers 3. the actual temperatures of these rock layers 4. the relative age of these rock layers th 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 0% 0% 0% 0% e a u ct al ag e o f th 17 th e es ... t la re e iv d en th 18 e ti si e a s u ct .. al t p em th 19 u at er e ... t la re e iv ag e o 20 f th . e. What classification of unconformity occurs when sedimentary rock overlies igneous rock? un c nf or m ity 0% an gu la r co ity on fo rm no di 0% rm ity 0% nc sc on fo rm ity 0% on fo 1. disconformity 2. nonconformity 3. angular unconformity 4. conformity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 What characteristic of radioactive decay makes it useful for determining the absolute age of samples? 1. occurs at a constant rate 2. changes based on temperature 3. speeds up under high pressure 4. slows down in very dense samples 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 ry . ve in ow n ow sd un de 17 sl up ds ee sp 16 .. h. .. rh ig t.. . on ed ge s an ch oc cu rs a ta ba s co ns ta nt . .. 0% 0% 0% 0% 18 19 20 Using the graph, determine the halflife of thorium-232. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 ar s ye bi ll io n ye io n bi ll io n bi ll 14 16 0% ar s 0% 35 2 ye ar s ye n 7 1 0% ar s 0% 28 7 billion years 14 billion years 28 billion years 35 billion years bi lli o 1. 2. 3. 4. 17 18 19 20 Radiocarbon dating can be used to determine the age of what type of materials? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 15 flo w s 0% va or ga n or ga in g liv 14 ni c is m k ro c us ne o ig 13 0% la 0% s 0% m at er ia ls 1. igneous rock 2. living organisms 3. organic materials 4. lava flows 16 17 18 19 20 The shaded area of which of these graphs best represents the percentage of marine organisms that became extinct at the end of the Paleozoic? 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 B 0% 17 18 0% 0% 19 D 0% C A B C D A 1. 2. 3. 4. 20 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 en re s en ms p re s nis Or ga ms p nis Or ga 19 t .. . td ... t .. . en re s ms p nis Or ga Or ga nis ms p re s en t .. . Why are fossils of organism’s from the Phanerozoic eon much more likely to be found than fossils of organisms from any other eon? 1. Organisms present during the Phanerozoic eon had only soft body parts. 2. Organisms present during the Phanerozoic eon were all microscopic. 3. Organisms present during the Phanerozoic eon had hard body parts. 0% 0% 0% 0% 4. Organisms present during the Phanerozoic eon are the most ancient life forms. 20 Present time is part of the Mesozoic era. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa 15 16 17 e ls 18 19 20 Eons are longer units of time than Eras. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa 15 16 17 e ls 18 19 20 The Precambrian consists of the three earliest eons of geologic time. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 Fa 16 17 e ls 18 19 20 The star on the time line indicates the beginning of the Precambrian. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 18 19 20 Mammals and dinosaurs both emerged during the Paleozoic Era. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 16 Fa 17 18 e ls 19 20 According to the principle of superposition, the youngest rock layers are closest to the surface. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 Fa 16 17 e ls 18 19 20 Intrusions are younger than the rocks they cut across. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 15 16 17 18 19 20 An unconformity between two sedimentary layers is classified as a disconformity. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 15 16 17 18 19 20 A geologist who needed to correlate two rock formations in different areas could use a key bed for this work. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 Fa 16 17 18 e ls 19 20 After one half life, the ratio of parent atoms to daughter atoms in a sample is 1:2. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 15 16 17 18 19 20 The radioactive decay scale divides the history of Earth into time units that help geologists analyze the rock record. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 15 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 16 17 18 19 20 The remains of once living plants or animals are called varves. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 14 Fa 15 16 17 e ls 18 19 20 The principle of uniformitarianism states that sedimentary rocks are deposited in horizontal layers. 1. True 2. False 0% 0% ue Tr 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 Fa 14 15 e ls 16 17 18 19 20 Dendrochronology is the science of comparing annual growth rings in trees to date changes in Earth's environments and past events. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 13 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Key beds are time markers that can be used to correlate rock layers across large areas. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 11 12 Fa ls e Tr ue 0% 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20