ppt - Discover Earth Science
advertisement
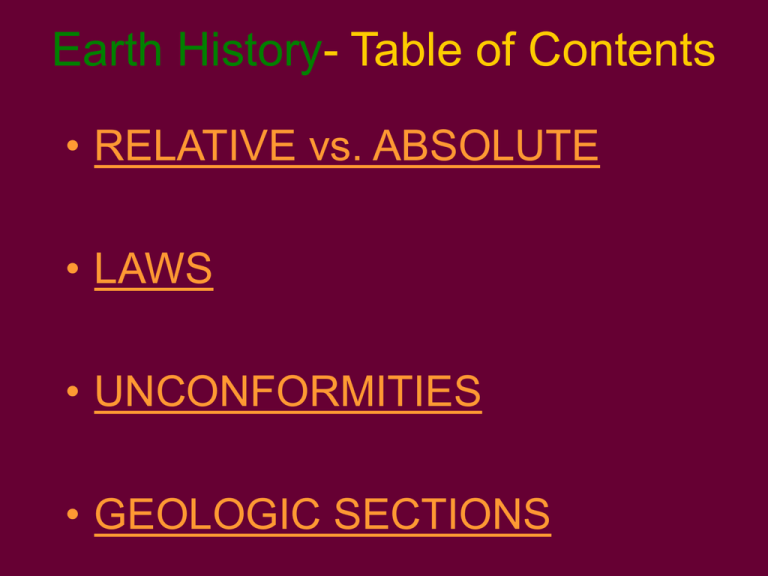
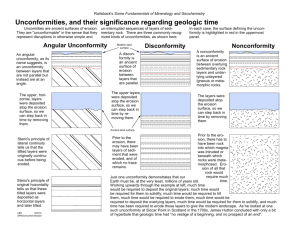
Earth History- Table of Contents • RELATIVE vs. ABSOLUTE • LAWS • UNCONFORMITIES • GEOLOGIC SECTIONS Who’s got the TIME? • RELATIVE: order/sequence known, but not the actual date of occurrence. • ABSOLUTE: actual date known. If 2 dates are known, then the RATE OF CHANGE can be known- such as Mountain Building. First Things First…or… “How’d that get there?” • In the 17th C., Nicolas Steno made an important observation: "Sediments are usually deposited in horizontal layers." He called this “ORIGINAL HORIZONTALITY” Finding Relative Time The LAW of... • SUPERPOSITION: a sedimentary sequence will be OLDEST on BOTTOM (if undisturbed). • CROSS-CUTTING: a body of igneous rock is younger than rock it has intruded (cut across). • INCLUDED FRAGMENTS: pieces of rock found IN another rock must be OLDER (formed first). Superpositionyoungest to oldest IGNEOUS INTRUSION: • occurs when magma squeezes into or between layers of pre-existing rock. Cross Cutting Included Fragments AND… an UNCOMFORMITY UNCOMFORMITYa buried surface of erosion separating two rock masses. This represents a gap in geologic time... ….outlined below... ….a look at the Grand Canyon and 3 types of unconformities... Oh, and what’s this? 2 1 3 Angular unconformity- An unconformity in which the beds below the unconformity dip at a different angle than the beds above it. “SEQUENCE” of events… 1. The lower sediments were deposited as horizontal layers in a body of water. 2. These sediments were then raised above water level and tilted during a tectonic event (what type of boundary?). 3. Streams & other forces of erosion carved a nearly horizontal surface across the tilted beds. STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 STEPS 4-6 “SEQUENCE” of events… 4. The land surface subsided (or the water level raised), submerging the erosion surface. 5. A new series of sediments deposited in horizontal layers on the erosion surface. 6. The complicated sequence of tilted and horizontal rocks was again uplifted, exposing them to erosion and producing the outcrop we see today. Disconformity • An unconformity in which the beds above the unconformity are parallel to the beds below the unconformity, though layers are “missing”. Nonconformity • An unconformity that separates profoundly different rock types, such as sedimentary rocks from metamorphic rocks. Practice: what happened here? S T R E S S • Stress is a force that is capable of greatly deforming rocks, and may result in folding or faulting of rock – Faults are CRACKS or FRACTURES in rocks caused by stress… – Folds are “bends” in rock layers • Stress comes in three varieties: – TENSION – COMPRESSION – SHEAR TENSION BEFORE STRESS AFTER STRESS Tension lengthens materials, causing them to thin -- example= RIFTS/Mid-Ocean Ridges …RESULTS NORMAL faults… HANGING WALL (‘HANGS’ ON) FOOT WALL (‘STICKS’ OUT) This example of tension results in a structure called a GRABEN… COMPRESSION BEFORE STRESS AFTER STRESS Compression shortens materials, causing them to thicken. …RESULTS REVERSE or THRUST faults…”upslope” HANGING WALL FOOT WALL This type of compression results in a structure called a HORST. SHEAR STRESS Shear stress is caused by side by side movement – example= TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES! …RESULTS