Geologic History - Mrs. Plante Science
advertisement
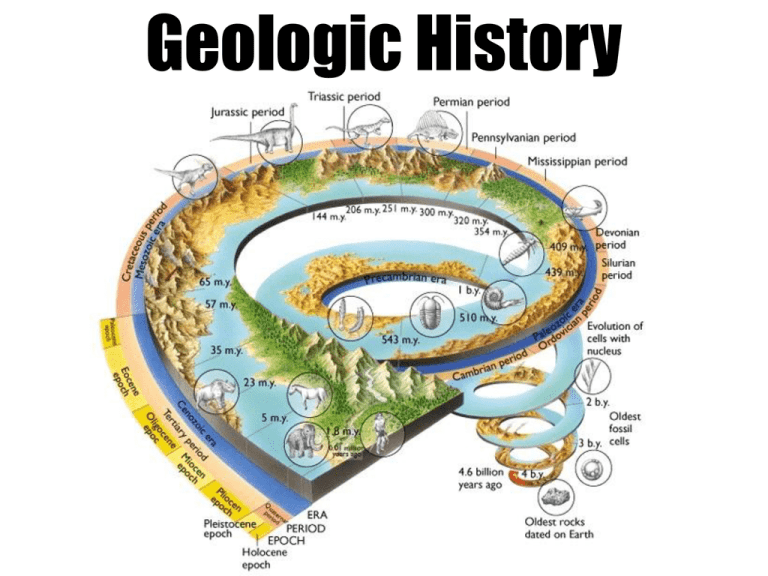
Geologic History Fossils and the Past • A fossil is the preserved remains or evidence of life. In megalodon sharks, only the teeth are found as fossils, dating 10 to 70 millions years old. Wooly Mammoth Teeth Wooly Mammoth Tusk Soft-bodied organisms, such as jellyfish, are usually not preserved very well as fossils. Most fossils form when organisms are buried in sediments. • Sediments often harden and change into rock. When this happens, organisms may be trapped in the rock. Most fossils are found in sedimentary rocks. Burgess Shale • Mud and creatures from the shallow sea floors at the top of the cliff was periodically swept over the edge, falling to deeper water where the creatures were buried and preserved as fossils. Unusually some of the fossils are preserved as carbon films which means that the fossils are formed from the original creatures themselves, rather than the more usual replacement by minerals. Marine fossils in Limestone (sedimentary) Fossils in Sandstone (Sedimentary) Crinoid Fossils are almost never found in igneous rocks because magma is found deep within Earth where no living things exist, and lava at the surface of Earth burns organisms before fossils can form. This site in Nebraska is home to hundreds of skeletons of extinct rhinos, camels, threetoed horses, and other vertebrates that were killed and buried by ash from a huge volcanic eruption some 12 million years ago. Pompeii, Italy Fossils are rarely found in metamorphic rocks because the heat, pressure and/or chemical activity that causes a rock to change, also detroys or damages the fossils. A distorted and stretched trilobite fossil in metamorphic slate. Interpreting Fossils • Fossils indicate that many different kinds of life forms have existed at different times in Earth’s history. Trilobites lived from about 520 to 250 million years ago, and are now extinct. Eurypterids are the NYS fossil, and lived 400 million years ago. When fossils are arranged according to age, they show that certain living things have changed or evolved over time. 488 – 444 mya 444 – 416 mya 444 – 416 mya 416 – 359 mya The Geologic Time Scale • The geologic time scale divides earth’s history into sections of time. • Divided into: – Eons – Eras – Periods – Epochs • The boundaries between geologic time intervals represent major changes on earth which include major extinctions • Geologic time began when earth first formed about 4.6 billion years ago Pages 8 and 9 ESRT The Geologic Time Scale • Precambrian: a “super” eon composed of the earliest Archean and Proterozoic eons • 88% of all geologic time • Fossils in precambrian rocks are rare Flora and fauna of the Precambrian sea Precambrianaged rocks in North America Uniformity of Process • “The present is the key to the past.” • Present observations help geologists interpret the past AND make predictions about the future.