Rock Cycle Microscopy Powerpoint
advertisement

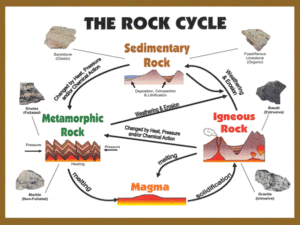
College of Engineering Department of Materials Science and Engineering Rock Cycle Microscopy Vijaya K Rangari,Ph.D Email: rangariv@mytu.tuskegee.edu Ph.334 724 4875 Materials Science and Engineering Tuskegee University How do you see small object ? Why NANO now How do you see NANO ? Electron microscopes Atomic force Microscopy Igneous Rock (Basalt) • Rocks formed by the cooling and solidifying of molten materials. • Igneous rocks can form beneath the Earth's surface, or at its. surface, as lava. • Basalt is a dark-colored, finegrained, igneous rock. • It most commonly forms as an extrusive rock, such as a lava flow. • Earth's Most Abundant Bedrock. Igneous Rock Basalt Sedimentary Rock (Bituminus Coal) • Coal is an organic sedimentary rock that forms from the accumulation and preservation of plant materials, usually in a swamp environment. • Formed when sand, mud and pebbles at the bottom of the rivers, lakes and oceans pile up • Sedimentary rocks are produced by the weathering of pre-existing rocks and the subsequent transportation and deposition of the weathering products. • The sediment is compressed over a long period of time before consolidating into solid layers of rock Sedimentary Rock Bituminus Coal Metamorphic Rock(Slate) Metamorphic rocks that are changed from their original (sedimentary and igneous rocks) form due to changes in temperature, pressure or chemical alteration. Metamorphic rock Slate is a fine-grained, foliated metamorphic rock that is created by the alteration of shale or mudstone by low-grade regional metamorphism. Slate Most slates are gray in color and range in a continuum of shades from light to dark gray. Slate also occurs in shades of green, red, black, purple and brown. Activity on Microscopy of Rocks We will provide three types of rocks a. Sedimentary = pressure and compaction b. Igneous = heat (volcanoes) c. Metamorphic = heat and pressure (regional) Look at the given three different rock samples: 1. With a hand held lens (magnifying glass) and 2. With a microscope Look for the rock with the most different Shapes Size Color Edges Select one type of rock and describe its color, shape, size and anything else you see different from others. Make an assumption about the rock where it come from ? Thanks for your attention Questions and Comments