Analysis of Medical Data - Florida State University College of Medicine

Analysis of Medical Data
Research Perspective
Nancy B. Clark. M.Ed.
Director of Medical Informatics Education
FSU College of Medicine
Spring 2004 http://www.med.fsu.edu/informatics
Objectives
Review statistical concepts to be on Step 1.
Determine what data exist relative to a clinical question or formal hypothesis
use IT to locate existing data sources identify and locate existing data sets
Within institution
Outside institution
Analyze, interpret and report findings
Select and use appropriate computer software: Excel,
SPSS
Use software to perform simple statistical analysis and portray results graphically
Interpret reports
Prerequisite Skills
(Step 1 USMLE)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Fundamental concepts of measurement
Scales of measurement
Distribution, central tendency, variability, probability
Disease prevalence and incidence
Disease outcomes (eg, fatality rates)
Associations (correlation or covariance)
Health impact (eg, risk differences and ratios)
Sensitivity, specificity, predictive values
More Prerequisite Skills
(Step 1 USMLE)
Fundamental concepts of hypothesis testing and statistical inference
Confidence intervals
Statistical significance and type I error
Statistical power and type II error
More Step 1 Topics
Fundamental concepts of study design
Types of experimental studies (eg, clinical trials, community intervention trials)
Types of observational studies (eg, cohort, casecontrol, cross-sectional, case series, community surveys)
Sampling and sample size
Subject selection and exposure allocation (eg, randomization, stratification, self- - selection, systematic assignment)
Outcome assessment
Internal and external validity
Scales of Measure
Nominal – qualitative classification of equal value: gender, race, color, city
Ordinal - qualitative classification which can be rank ordered: socioeconomic status of families
Interval - Numerical or quantitative data: can be rank ordered and sizes compared : temperature
Ratio - interval data with absolute zero value: time or space
Distribution, Central Tendency…
Mean
…Variability, Probability…
Mean
Median
Mode
Standard deviation
Statistical Significance p < .01
Confidence Interval
Statistical Significance
Type I and Type II errors
Null Hypothesis = H o
H o
True H o
False
Reject H o
Type I error Correct decision
Do Not Reject H o
Correct decision Type II error
Statistics Online Textbook
The Statistics Homepage
http://www.statsoftinc.com/textbook/stathome
.html
Disease Prevalence and Incidence
Prevalence
probability of disease in entire population at any point in time
2% of the population has diabetes
Incidence
probability that patient without disease develops disease during interval
0.2% or 2 per 1000 new cases per year
Sensitivity, Specificity
sensitivity = a / (a+c) specificity = d / (b+d)
Test is positive
Test is negative
Patients with disease
Patients without disease a c b d
Predictive Value
Positive predictive value = a / ( a+b)
Negative predictive value = d / (c+d)
Post-test probability of disease given positive test = a / (a+b)
Test is positive
Post-test probability of disease given negative test = c / (c+d)
Test is negative
Patients with disease
Patients without disease a b c d
Good Resource Sen, Spc, PV
An Introduction to Information Mastery
http://www.poems.msu.edu/InfoMastery/defa ult.htm
Diagnosis
Sensitivity and specificity
Predictive values
Likelihood ratios
InfoRetriever
Calculators: Epidemiology, Diagnostic test
Fundamental Concepts of Study Design
Good Resource
Epidemiology for the Uninitiated
BMJ
Online Textbook
http://bmj.com/collections/epidem/epid.shtml
Finding Health Statistics
Types of Health Statistics Questions
Fact lookups
Research
Presentations
Social and Policy indicators
Strategies for Finding Health Stats
Use Portal
Start at Internet site
Start with book or article
Internet Portals of Health Stats
Lists of links that provide starting points for browsing or searching
Keyword search in portal vs Google
General idea what you want
The Related Health Services Research Web
Sites http://www.nlm.nih.gov/nichsr/hsrsites.html
The NCHS portal: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/
Other Statistical Web Sites
CDC Data and Statistics http://www.cdc.gov/scientific.htm
FedStats Home Page http://www.fedstats.gov/
Compare these two
U Michigan’s Statistical Resources on the
WEB – HEALTH
What type of stats
Lexis-Nexis Statistical Universe
Subscription resource
Searches stat data
Subject List
Limit search
Reports or tables
http://web.lexisnexis.com/statuniv?B1=Connect+to+Statistic al+Universe
MMWR
Morbidity – illness
Mortality – death
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/
Disease Trends
Tables - searchable
Health Care Data
Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project
HCUPnet
Hospital discharges
Ambulatory service
Costs
Amount of care
By diagnosis and procedure
Surveys of hosp, physicians, nursing homes
Health Consequences
Costs to society, individuals
Cost from care
Costs of illness
Impact on infrastructure
HCFA=>CMS Health Accounts
http://www.cms.hhs.gov/statistics/nhe/default.
asp
State and International Data
Floridahealthstat.com - Where Florida Health
Data Resides
DOH Epidemiology
KFF State Health Facts Online
United Nations Statistics Division
World Health Organization Research Tools
Individual Datasets
EMR
Billing
CDCS
Customized data collection tools
Data Analysis
Selecting the Appropriate Software
Spreadsheet
Numerical (interval or ratio) data
Sums
Averages
Standard deviations
Simple charts and graphs
Statistical Software
Nominal or Ordinal data
Comparisons of two+ groups
Frequency tables
Complicated charts and graphs
Normal curves
Class intervals
Statistical significance
Spreadsheets
Excel
Pocket Excel
Data Tables
Field names at top
Each row is a record (sample)
Sorting whole table
By one column
By more than one column
Sorting individual sections
Descriptive Statistics
Distribution
frequency distribution
Histogram
Central tendency
Mean
Median
mode
Dispersion
Range
Standard deviation
Variance
N
Not P (inferential stats)
Central Tendency
Mean
=AVERAGE(b2:b1500)
Median
=MEDIAN(A2:A7)
Mode
=MODE(A2:A7)
N
=COUNT(A2:A1500)
=COUNTBLANK(A2:B5)
Dispersion
Range
=MAX(A2:A60)- MIN(A2:A60)
Standard deviation
=STDEV(A2:A110)
Variance
=VAR(A2:A110)
Distribution
Frequency distribution
Not easy – use SPSS
FREQUENCY(data_array,bins_array)
Use help
Histogram
Bar chart of frequency table
Hands on experience
Analyze data in examples2.xls
Statistical Software
Intro to SPSS
Statistical Software
SPSS
Provided by request/justification
Lab Computers
Start => Programs => SPSS for Windows =>
SPSS 11.0 for Windows
Start Screen
Don’t show this dialog in the future.
OK
Open Breast Cancer Survival
Data View
Views
Variables
View
File Information
Utilities Menu
File Info…
Output window
Descriptive Statistics
Analyze Menu
Descriptive Statistics
Frequencies
Select Age ►
Click Statistic s button
In Central Tendency
Mean, Median, Mode
In Dispersion
Standard Deviation, variance
In Percentile Values
Quartiles
Continue
OK
Graphing
Graphs Menu
Pie…
Summary for Groups of cases
Lymph Nodes ►
OK
Histogram with Normal Curve
Graphs Menu
Histogram..
Select Age ►
Check Display Normal
Curve
OK
Simple Correlation Analysis
Age and Tumor Size
Analyze Menu
Correlate…
Bivariate
Select Age ►
Select Pathological Tumor Size ►
Check Pearson and Spearman – Two tailed
OK
Is there a correlation? Negative or Positive?
Is it statistically significant?
Save Output
Save on All Users drive
Under Nancy.clark
SPSS Output Files
Name it your name: ie, KerryBachista.spo
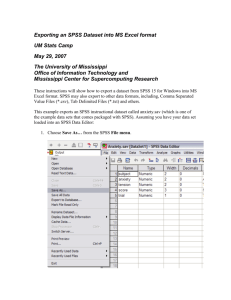
Importing Data
From Excel, SAS, dBase, etc.
Variable names first row
File Menu, Open
Data…
Files of Type
Excel
Tutorial, Samples
Demo.exe
Type in Labels
Pick Type of variable
Enter Value Labels
Etc.
SPSS Tutorials
In the Help Menu
On Informatics Web page
Books:
Statistics for Social & Health Research (Sage)
Argyrous, George
Statistics Applied to Clinical Trials (Klawer
Academic Publishers)
Cleophas, Ton J., et al
Objectives
Determine what data exist relative to a clinical question or formal hypothesis
use IT to locate existing data sources
identify and locate existing data sets
Within institution
Outside institution
Analyze, interpret and report findings
Select appropriate computer software: Excel, SPSS
Use software to perform simple statistical analysis and portray results graphically
Interpret reports