Science - Explore the Possibilities
advertisement

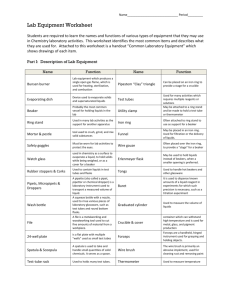
What is Science? •We see various natural phenomena in our daily life. Natural Phenomena are things that happen in nature. Lightning Rainbow Melting of Ice The Fall of the Ball Growth of a Baby into Adult •We want to know why and how all these things happen. We search for an answers. Thus, the study of science gives us answers. •Science is the systematic study of nature and how it affects us and the environment. •The information produced from the study of science is known as scientific knowledge. •Scientific knowledge develops as new scientific discoveries are discovered every day. •Using scientific knowledge, we invent many useful devices such as light bulbs, telephones and computers. The application of scientific knowledge for the use of mankind is called technology. •We use technology almost every aspect of life thus making science part of our every day life. Importance of Science •Science plays important roles in our daily life. a. Science helps us to understand ourselves. Knowing how our body works, helps us to take better care of our health. b. Science also helps us to understand our environment. This helps us to improve the quality of our environment and conserve it for our future generation. c. Science makes our life more comfortable. We invent various machines to help us to work faster and more efficiently. Use and benefits of science in daily life In Homes •Facilities such as electricity and tap water make life easier and more comfortable. •Various appliances such as washing machine, microwave oven and vacuum help us to do our housework faster. Communication •Communication is easier and faster with the use of television, telephone, mobile phone, facsimile and computer. •Global communication is now possible with the use of communication satellites, e-mail and the internet. Transportation •Transportation is easier, faster and more comfortable. •Modern public transports such as commuter trains and light rail transit reduce congestion in cities. •The design of better roads and highways increases the safety of users. Construction •Buildings and structures are now built with strong materials such as steel, concrete and reinforced glass. •Powerful machinery such as cranes, tractors and bulldozers are usually used in construction works. Agriculture •Machines are used to carry out heavy and difficult tasks such as ploughing and harvesting. •Plant breeding, new agricultural techniques, fertilizers and insecticides contribute greatly in increasing the world’s agricultural products. Medicine •More diseases can now be cured with the discoveries of new drugs, vaccines, antibiotics and the invention of better surgery techniques and equipment. •Diseases can be diagnosed and detected earlier with various tests and devices such as X-ray machine and ultrasound scanning device. Careers in science • Science offers various career opportunities according to one’s area of interest. a. Doctor – a person has been trained in and practices medicinal science. b. Veterinarian – an animal doctor. c. Pharmacist – a person who dispenses medical drugs and advise their uses. d. Engineer – a skilled person who designs, builds or maintains engines, buildings, bridges or roads. e. Architect – a person who design buildings and advises on their construction. f. Chemist – a person trained in chemistry. •Science is divided into a number of areas of study: a. Biology – the study of life. b. Physics – the study of matter, energy, force and motion. c. Chemistry – the study of composition and chemical properties of substance. d. Astronomy – the study of planets and stars in the Earth. e. Geology – the study of rocks, minerals and the structure of the universe. f. Meteorology – the study of weather and climate. g. Biochemistry – the study of chemical process in living organisms. Science Laboratory •The place where a scientist works is called laboratory. •Students carry out scientific investigations or experiments during science lessons in science laboratories. •There are rules and safety precautions that must be followed by the students in order to avoid accidents. Rules and Safety Precautions Never enter the laboratory unless a teacher is present. Do not eat, drink, or taste chemicals. Always follow the teacher’s instructions. Never touch chemicals with your bare hands. Use a spatula. Read a label on a reagent bottle before using its content. Turn off the Bunsen burner after use. Do not pour back any unused chemical into its bottle. Do not throw solid wastes into the sink. Wash and keep all apparatus after use. Do not run or play in the laboratory. Do not test anything without the teacher’s permission. Report any breakages to the teacher. Keep the bench clean and tidy. •We need to use apparatus to carry out experiments Test tube To hold a small amounts of liquid or chemical. Boiling tube For heating small amounts of liquid. Beaker Conical Flask Flat – Bottomed Flask To hold bigger amounts of liquids or chemicals. Measuring cylinder To measure volume of liquids. Pipette To measure a fixed volume of liquids. Burette To measure small volumes of liquid accurately. Retort stand To hold or support apparatus. Filter funnel Used together with a filter paper to filter mixtures of solids and liquids. Bunsen burner To provide a flame for heating. Tripod stand To support apparatus during heating. Wire gauze To support apparatus and ensure even heating. Evaporating dish To hold liquids for evaporating. Crucible To hold solids for strong heating. Test tube holder To hold a test tube during heating. Spatula To transfer small amounts of liquids. a. A Bunsen burner is used in the laboratory to heat substance. b. The Bunsen burner has an air – hole. The air – hole can be opened or closed by turning the collar. c. When the air – hole is opened, the Bunsen burner gives a blue flame. This is called a non – luminous flame. The flame is very hot because the gas is burned completely. d. When the air – hole is closed. The burner gives a yellow flame. This flame is easier to see and it is called luminous flame. This flame is less hot and produce a lot of black soot because the gas is not burned completely. The parts of Bunsen burner e. The correct way to light up a Bunsen burner is as follows: •Close the air – hole by turning the collar. •Hold a lighted match or a lighter at the top of the barrel. •Turn on the gas slowly. A yellow or luminous flame will be obtained. •Open the air – hole to obtain a blue or non – luminous flame. f. To avoid accidents when using a Bunseen burner, the following precautions should be taken. •Use a lighter or a match to light up a Bunsen burner instead of a burning paper. •We must light up the match before turning on the gas. •When heating a test tube, hold the test tube at an angle of 45 degrees. Use a test – tube holder and do not point the mouth of the test tube to yourself of your friends. •Do not heat flammable substances like alcohol directly. •When not using the Bunsen burner temporarily, close the air – hole to obtain the yellow flame because this flame is easily seen. Remember to turn off the gas after using the burner. The correct way to hold a test tube during heating. •Some substances in the laboratory are hazardous or dangerous. •Hazard warning symbols are placed on labels of bottles or containers of hazardous substances to show the danger of the substances. •As young scientists, you must be able to recognize the symbols and know how to handle the substances properly. Symbols Danger of substances Examples Handling techniques Explosive •Easily explodes when mixed with other substance •Sodium, potassium •Concentrated acids and alkalis •Keep in paraffin •Avoid contact with water •Keep away from other substances including water. Flammable or inflammable •Easily catches fire and burns •Organic solvents such as ethanol, petrol or kerosene •Mercury, chloroform, •Causes death or lead, benzene, harm to the body bromine, sodium cyanide, if absorbed through the skin, hydrogen sulphide swallowed or inhaled. Toxic / poisonous •Keep away from fire or heat sources. •Do not inhale, touch or taste the substances. •Keep in a locked cupboard. •Concentrated acids and •Causes damage alkalis, to the skin or bromine, eyes upon hydrogen peroxide. contact Corrosive Irritant / harmful •Irritates causes (itchiness and rashes) skin, eyes and respiratory system •Ammonia solution, chloroform, dilute acids and alkalis •Avoid contact with skin or eyes. •Spill on body parts should be washed away quickly under running water •Spill on body parts should be washes with a lot of water. Radioactive •Gives out radiation that can cause cancer or destroy bodily tissues. •Uranium, plutonium, radium. •Keep in special lead containers. See you next time!!