File
advertisement
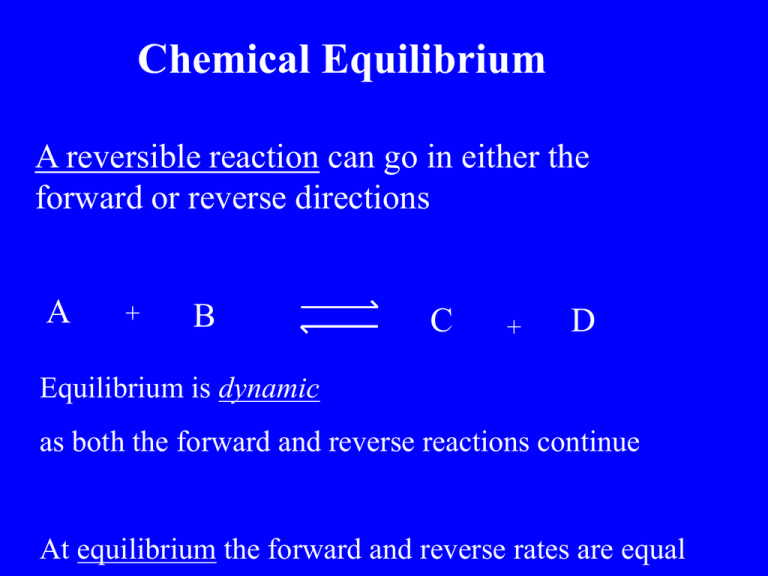
Chemical Equilibrium A reversible reaction can go in either the forward or reverse directions A + B C + D Equilibrium is dynamic as both the forward and reverse reactions continue At equilibrium the forward and reverse rates are equal Le Chateliers Principle If a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system adjusts to relieve the stress CoCl42- + H2O H= + Endothermic ( Cooling) Co(H2O)62+ + 4ClH= - Exothermic (Heating) Le Chatelier’s Principle If a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system adjusts to relieve the stress 2+ Cr O 2 7 - H2O CrO42- + 2H+ Le Chateliers Principle If a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system adjusts to relieve the stress FeCl3 + CNS- Fe(CNS)2- + 3Cl- Le Chatelier’s Principle CoCl42- + Co(H2O)62+ H2O + H= + 4ClH= - Exothermic (Heating) Endothermic ( Cooling) What happens if the red solution is heated ? Heating is a stress Le Chatelier states the opposing reaction occurs The cooling reaction occurs ie the reverse reaction Turning red into blue Haber process Manufacture of ammonia NH3 for the fertilizer industry N2 + 2 NH3 3 H2 2 NH3 Kc = N2 x H2 3 H= - 92.4 Haber process Manufacture of ammonia NH3 for the fertilizer industry N2 + 3 H2 2 NH3 H= - 92.4 Le Chatelier’s principle predicts the yield of NH3 is maximised by 1. Low temperature 2. High pressure Actual temp used is 500oC (as lower temp reduces the rate ) Pressure used is 200 ATM Contact process Manufacture of Sulfuric acid H2SO4 2SO2 + O2 2 SO3 H= - 196 Le Chatelier’s principle predicts the yield of SO3 is maximised by 1. Low temperature 2. High pressure Actual temp used is 450 oC (as low temp reduces the rate ) Pressure used is 1 ATM