Preparation of Aspirin (PowerPoint)
advertisement

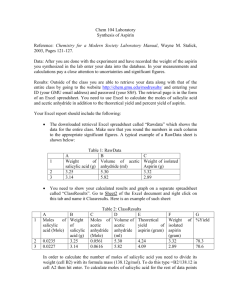
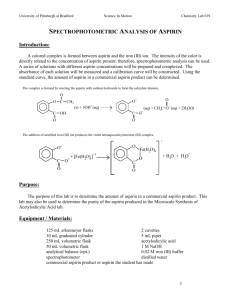
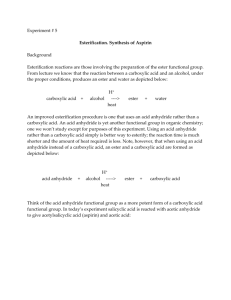
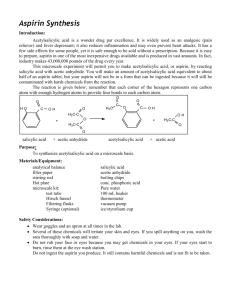
Intro to Chemistry Chem1020 Lab Preparation of Aspirin Chemistry Department Minneapolis Community & Technical College 1 Overview • Part I Introduction • Part II Synthesis of aspirin • Part III Separation of aspirin • Part IV Testing of aspirin • Part V Calculation 2 Part I. Introduction • In this experiment you will learn how to use a chemical reaction to make new substances such as aspirin: Salicylic acid + Acetic anhydride Aspirin + Acetic acid • You will also learn how to separate the desired product from other substances, which is as important as the synthesis itself. • During the following week, you will evaluate the quantity and purity of the aspirin product. • Stoichiometric calculation, a topic covered in Chapter 8.4 in the textbook, will be performed on this reaction. 3 Part II. Preparation ~ 1.5 g salicylic acid ~ 2 mL acetic anhydride • Use the provided graduated • Use the attached spatula for cylinder to measure. transferring. • Weigh it on a diagonally-folded and zeroed weighing paper. • Record its exact mass. An Erlenmeyer flask 4 drops phosphoric acid • It serves as a catalyst, which speeds up reaction without changing its own composition. • Use the provided pipette dropper. 4 Part II. Precautions! • For any chemicals, always put the cap back onto its container after each use, even if someone will be using it right after you. • Salicylic acid is a fluffy solid. Be careful not to make a mess at the weighing station. In case of spilling, alert the instructor immediately. • Both acetic anhydride and phosphoric acid are corrosive and reactive. o Keep them inside the fume hood. o Be careful not to get it onto your skin. o In case of spilling, alert the instructor immediately. 5 Part II. Preparation (Heating is done in fume hood) 1. Clamp and tilt the Erlenmeyer flask allowing the solid to mix with the liquid inside the flask. 2. Lower the flask into a waterbath which sits above a hot plate. Insert a thermometer into the water-bath (not the flask) to monitor temperature. Turn on the heating knob (the right one) of the hot plate all the way to “high”. Setup side view 6 Part II. Preparation 3. When the temperature reaches 80 ºC, turn off the hot plate. . 4. Swirl the flask gently to let all solids dissolve. If you have to take the flask out of the water bath to shake, put it back as soon as all solids dissolve. Keep it in the water bath for 5 minutes. 5. Take the flask out of the water bath and let it cool down undisturbed (meaning no shaking or stirring). Eventually most of the liquid will crystallize, generating a white, crystalline cake at the bottom of the flask. That solid, should be mainly the aspirin product. 6. Add enough ice-cold water into the flask and use a glass stirring rod to break up the solid chunks. Ice-cold distilled water 7 Part III. Separation Now the solid aspirin is mixed with other substances: unreacted reactants, phosphoric acid catalyst, acetic acid – the other product. To separate aspirin from them, vacuum filtration will be used. Buchner funnel Setup side view Setup front view filtration flask electric pump on/off switch 8 Part III. Separation 1. Determine and record the total mass of a watch glass and a filter paper. Write your name on the edge of the paper. 3. Turn on the pump. Quickly swirl and pour the reaction mixture into the funnel. Use the ice-cold water to rinse out all solid in the flask. 4. Squirt more ice-cold water onto the crystals in the Buchner funnel to wash away other impurities. John D. 2. Put the filter paper into the Buchner funnel. Wet it with ice-cold water so that it fits nicely in the funnel. 5. Use a micro spatula to pick out the filter paper with aspirin, and put them on the watch glass for drying over one week. John D. Ice-cold distilled water 9 Part IV. Testing • Quantity (Done a Week Later) Determine and record the total mass of watch glass, filter paper, and aspirin product • Quality Determine the purity of your product: Your instructor will demonstrate that pure salicylic acid (one of the reactants) and pure commercial aspirin show different colors when mixed with an FeCl3 solution. Use the provided semi-micro spatula to transfer a small amount (match-head size) of your product into the test tube, and add 2 drops of 1% FeCl3 solution. Compare the resulting color to the instructor’s results. Draw a conclusion about the purity of your product. 10 Part V. Sample Calculation Data: a. Msalicylic acid 1.52 g c. Mwatch glass + filter paper + aspirin b. Mwatch glass + filter paper 19.18 g 20.98 g Calculation: a. Actual yield of aspirin = Mwatch glass + filter paper + aspirin - Mwatch glass + filter paper = 20.98 – 19.18 = 1.80 g (2 decimal places) b. Theoretical yield of aspirin Salicylic acid + Acetic anhydride Molecular formulas: C7H6O3 Molar masses: 1.52g S.A. 138.12 g/mol Aspirin + Acetic acid C9H8O4 180.16 g/mol 1mol S.A. 1mol Aspirin 180.16g Aspirin 1.98g Aspirin (3 sig. fig.) 138.12g S.A. 1mol S.A. 1mol Aspirin c. Percent yield Actual yield 1.80g 100% 90.9% (3 sig. fig.) Theoretica l yield 1.98g 11