Slide 1
advertisement

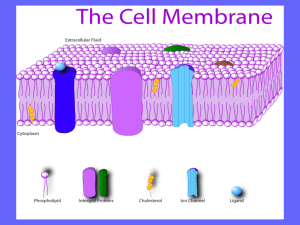
7.2 The Plasma Membrane Chapter 7 A View of the Cell Pages 175 - 178 Homeostasis – Maintaining a Balance • Cells must keep the proper concentration of nutrients and water and eliminate wastes. • The plasma membrane is selectively permeable – it will allow some things to pass through, while blocking other things. • A cell's contents would be the same as its surrounds, were it not for selective permeability. Structure of the Plasma Membrane • Because cells have a watery environment both inside and outside, the polar ends of the phospholipids in the plasma membrane form double layers • The double layer of the plasma membrane is called a lipid bilayer Structure of the Plasma Membrane • Lipid bilayer – two sheets of lipids (phospholipids). – Found around the cell, the nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria, and chloroplasts. – Embedded with proteins and strengthened with cholesterol molecules. What is a Phospholipid? • A phospholipid is like a fat molecule but has – one less fatty acid group – a phosphate portion. What’s a Phospholipid? – Polar (water-soluble) heads face out and the nonpolar fatty acids hang inside. Hydrophobic / Hydrophillic • Hydrophobic = “afraid of water” • Non-polar side • This is the part that is like the fats – how does water act with oil? • Hydrophillic = “water loving” • Polar side • This is the side that is in contact with the watery environments. Membrane Proteins • Determine what particles can pass through the membrane – like doors • Serve as enzymes (may speed reactions). • Act as markers that are recognized by chemicals and molecules from the inside and the outside of the cell (the immune system) – like a house number. Carbohydrate sticking out Fluid Mosaic Model • Because the phospholipid molecules and some proteins are free to move, the plasma membrane is said to be a fluid mosaic. • The fluid mosaic model describes a structure with polar layers on the outside and nonpolar layer on the inside. Fluid Mosaic Model • Which of the following pictures below most likely approximate the motion phospholipids make in a plasma membrane? All of these things are true for plasma membranes: • Folded membranes increase surface area for efficiency. • Endoplasmic reticulum is made up of folded membranes. • Ribosomes are sometimes attached to folded membranes. Carbohydrate chains Membrane protein Polar head of phospholipid Non-polar tails of phospholipid Cholesterol • What structure is analogous to a sewage system? • Membrane protein • Where are you least likely to find water? • Between the non-polar tails of the phospholipids • What would happen to the plasma membrane if part D is completely removed? • It would collapse on itself Diseases of the plasma membrane Decreased movement of molecules entering the cell might be a result of a disease that causes a thickened plasma membrane. Cystic Fibrosis is a disease of the plasma membrane Diseases of the plasma membrane • Cystic Fibrosis, incurable hereditary disorder that causes the body to secrete an abnormally thick, sticky mucus that clogs the pancreas and the lungs, leading to problems with breathing and digestion, infection, and ultimately, death. Diseases of the plasma membrane • One of the most common fatal genetic disorders in the United States, cystic fibrosis occurs in about one in every 3,900 babies. Diseases of the plasma membrane • Cystic fibrosis is caused by a defect in the gene responsible for making a protein that controls the flow of chloride ions into and out of certain cells through the membrane.