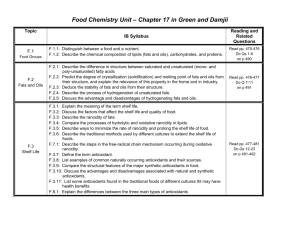
Natural products: fats and oils
advertisement

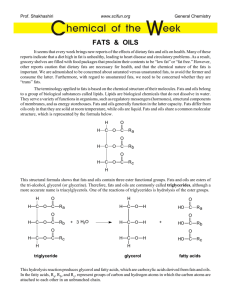
Natural products: fats and oils Intermediate 2 Chemistry Unit 2(e) Key questions • What is the difference between a fat and an oil? • What causes this difference? Classifying fats and oils • According to their origin – Animal e.g. lard – Vegetable e.g. sunflower oil – Marine e.g. cod liver oil Function in the human body • Provide energy • A more concentrated energy source than the same mass of carbohydrate What are fats and oils? • Esters • Their parent alcohol is glycerol • The alkanoic acids are fatty acids Glycerol Fatty acids Key questions • Can you give an example of a situation when fats or oils are broken down? • What type of reaction is involved? • In what ratio will the products be produced? Difference between fats and oils • Fats are solid at room temperature; oils are liquids. • Fats have higher melting points than oils. Structure of fats • Saturated molecules • Regular structure • Tight packing • Stronger forces between molecules Structure of oils • Unsaturated molecules • Irregular structure • Loose packing • Weaker forces between molecules Converting oils into fats • What would need to be done to convert an oil into a fat? – C=C is removed through an addition reaction with hydrogen