Chapter 24 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins

CHE 242
Unit VIII
The Structure, Properties,
Reactions and Mechanisms of
Carboxylic Acids and Their
Derivatives
CHAPTER TWENTY-FOUR
Terrence P. Sherlock
Burlington County College
2004
Structure of Proteins
Chapter 24
=>
2
Stereochemistry of
-Amino Acids
Chapter 24 3
=>
Essential Amino Acids
• Arginine (Arg)
• Threonine (Thr)
• Lysine (Lys)
• Valine (Val)
• Phenylalanine (Phe)
• Tryptophan (Trp)
• Methionine (Met)
• Histidine (His)
• Leucine (Leu)
• Isoleucine (Ile)
=>
4 Chapter 24
Complete Proteins
• Provide all the essential amino acids.
• Examples: those in meat, fish, milk, eggs.
• Plant proteins are generally incomplete.
• Vegetarians should eat many different kinds of plants, or supplement diet with milk or eggs.
=>
Chapter 24 5
Rare Amino Acids
• 4-Hydroxyproline, 5-hydroxylysine found in collagen.
• D -Glutamic acid in cell walls of bacteria
• D -Serine in earthworms
•
-Aminobutyric acid, a neurotransmitter
•
-Alanine, constituent of the vitamin pantothenic acid.
Chapter 24
=>
6
Zwitterion
• Amino acid exists as a dipolar ion.
• -COOH loses H + , -NH
2 gains H + .
• Actual structure depends on pH.
Chapter 24 => 7
Properties of Amino Acids
• High melting points, over 200
C
• More soluble in water than in ether.
• Larger dipole moments than simple acids or simple amines.
• Less acidic than most carboxylic acids, less basic than most amines.
O
+ _
H
3
N CH C O p K a
= 10
R p K b
= 12
Chapter 24 8
=>
Structure and pH
Chapter 24
=>
9
Isoelectric Point
• pH at which amino acids exist as the zwitterion (neutral).
• Depends on structure of the side chain.
• Acidic amino acids, isoelectric pH ~3.
• Basic amino acids, isoelectric pH ~9.
• Neutral amino acids, isoelectric pH is slightly acidic, 5-6.
Chapter 24
=>
10
Electrophoresis
Chapter 24
=>
11
Reaction with Ninhydrin
• Used to visualize spots or bands of amino acids separated by chromatography or electrophoresis.
• Deep purple color formed with traces of any amino acid. =>
Chapter 24 12
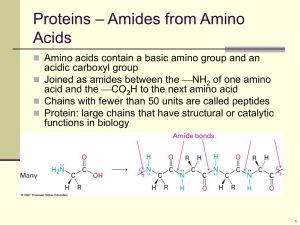
Structure of Peptide
• The peptide bond is an amide bond.
• Amides are very stable and neutral.
Chapter 24 13
=>
Peptide Bond Formation
• The amino group of one molecule condenses with the acid group of another.
• Polypeptides usually have molecular weight less than 5000.
• Protein molecular weight 6000-40,000,000.
=>
Chapter 24 14
Classification of Proteins
• Simple: hydrolyze to amino acids only.
• Conjugated: bonded to a nonprotein group, such as sugar, nucleic acid, or lipid.
• Fibrous: long, stringy filaments, insoluble in water, function as structure.
• Globular: folded into spherical shape, function as enzymes, hormones, or transport proteins.
Chapter 24
=>
15
Levels of
Protein Structure
• Primary: the sequence of the amino acids in the chain and the disulfide links.
• Secondary: structure formed by hydrogen bonding. Examples are
helix and pleated sheet.
• Tertiary: complete 3-D conformation.
• Quaternary: association of two or more peptide chains to form protein. =>
Chapter 24 16
Alpha Helix
Each carbonyl oxygen can hydrogen bond with an N-H hydrogen on the next turn of the coil.
Chapter 24
=>
17
Pleated Sheet
Each carbonyl oxygen hydrogen bonds with an N-H hydrogen on an adjacent peptide chain.
Chapter 24
=>
18
Summary of Structure
Chapter 24
=>
19
Denaturation
• Disruption of the normal structure of a protein, such that it loses biological activity.
• Usually caused by heat or changes in pH.
• Usually irreversible. A cooked egg cannot be “uncooked.”
=>
Chapter 24 20
Chapter 24 21
POWER POINT IMAGES FROM
“ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, 5 TH EDITION”
L.G. WADE
ALL MATERIALS USED WITH PERMISSION OF AUTHOR
PRESENTATION ADAPTED FOR BURLINGTON COUNTY COLLEGE
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY COURSE
BY:
ANNALICIA POEHLER STEFANIE LAYMAN CALY MARTIN
Chapter 24 22