Colloid & Surface Phenomena Loition
advertisement

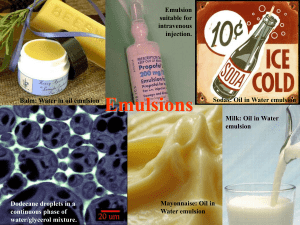
Colloid & Surface Phenomena Loition Jason Ashbery Jonathan Danner Haohao Huang Leigh Vorreuter I. Product Design Considerations • Customer Needs • • • • • • • • • Heals dry skin Prevents dry skin Non-greasy Fast absorbing Non-irritating Non-scented or Scented Contains sun screen Prevent further aging of the skin Long lasting Product Design Considerations • Different Types of Lotion • For Dry Skin • For Extra Dry Skin • For Sensative Skin • Manufacturers • • • • • Bath & Body Works Suave Keri Bristol Meyer Squibb Clairol Product Design Considerations • Product Specifications • • • • • • • • Shelf life Duration Consistency Viscous properties Fragrance Color Absorption Delivery systems of alpha hydroxide, sunscreen, moisturizing agents II. Components and Composition Common Components Present in Different Brands of Moisturing Lotion* Suave Bath & Body Bristol The Andrew Works Meyers Jergens Co. Body Benefits Water X X X X X Glycerin X X X X X (Tetra, Tri, or Di-) sodium EDTA X X X Dimethicone X X X Carbomer X X X X X Tocopheryl Acetate (Vitamin E) Aloe gel X X Petrolatum X X Glyceryl Stearate X Sodium Hydroxide X DM DM Hydantoin X Benzyl Alcohol X Propylparaben X Mineral Oil X X X X X X X X X X X Magnesium Aluminum Silicate X X X Methylparaben X X X X Isopropyl palmitate X X X Cetyl Alcohol X X Cetearyl Alcohol X X Ceteareth-20 X X * Components present in only 1 of the 5 lotions are not listed here. Approximate Composition of a Lotion Patented by The Andrew Jergens Company (U.S. Patent# 6,017,548) Chart # Components Approx. % Weight 1 Water 93.2 2 Glycerin 2.4 3 Dimethyl Distearyl Ammonium Chloride 4 Petrolatum 0.8 5 Lactic Acid 0.6 6 Isopropyl palmitate 0.6 7 Cetyl Alcohol 0.5 8 Glycolic Acid 0.4 9 Dimethicone 0.3 10 Ammonium Hydroxide 0.2 11 Methylparaben 0.02 12 Propylparaben 0.008 1 Approximate Percent Weights 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 III. Colloids and Surface Interactions • Functions of colloids in Moisturizing Lotion • • • • • Diluent Humectant Smoothing aid Emollient Surfactant KERI FRAGRANCE FREE LOTION Component Basic Function Water diluent Glycerin humectant Dimethicone * emollient, smoothing aid Petrolatum * occlusive emollient Disodium EDTA chelating agent Carbomer * thickening agent, emulsifying agent Quaternium-15 * cationic surfactant, cationic emulsifier Cetyl Alcohol * emollient, emulsion modifier, coupling agent Tocopheryl Acetate (Vitamin E) * nutrient Steareth-2 * emulsifier, wetting agent Aloe gel nutrient Benzyl Alcohol antimicrobial Laureth-23 * emulsifier, wetting agent Magnesium Aluminum Silicate thickening agent Sodium Hydroxide alkalizer, pH adjuster * = "colloidal" sized molecules Liquid/ Liquid Emulsion • An emulsion is formed when a mixture of two immiscible liquids are separated by a surfactant molecule. • Oil-in-Water (O/W) • Water-in-Oil (W/O) O/W and W/O Emulsion Phase Inversion of Emulsion • Inversion from W/O to O/W • Variables which lead to phase inversion • Temperature – Ethoxylate emulsifiers • Surfactant composition – Hydrophilic emulsifier concentration • Water concentration – Andrew Jergens Co. Effect of Amphiphiles on Delivery to the Skin • Cationic Surfactants • Effect of Temperature and Salt on micelle stability • Effect of Temperature on delivery • Pemulen® Polymeric emulsifiers • Triggered release mechanism upon contact with electrical charge of skin Traditional Surfactant Emulsion Pemulen ® Polymeric Emulsifiers IV. Product Attributes • Shelf Life – Emulsion stability is what determines the product’s shelf like – If the emulsion becomes unstable the lotion will separate – Adjusting the hyrophilic and lipophile balance of the emulsifier achieves the emulsions stability – The emulsions are thermodynamically unstable due to its positive interfacial energy – When the emulsion tries to reach it thermodynamic equilibrium it causes the emulsion to break up back to its component phase Product Attributes • Shelf Life – The delay of the component break up can be accomplished by adding specific mixed emulsions compiled of non-ionic and ionic surfactants and combined with fatty amphiphiles • Examples can be found in Table 3 – Previously blended emulsifying wax into the the formulation can also help prevent the decay of the emulsions • Examples can be found in Table 4 Product Attributes Table 3 Fatty amphiphiles Cetostearyl alcohol Cetyl alcohol Stearyl alcohol Glyceryl monostearate Stearic acid Phosphatidylcholine Surfactants Sodium lauryl sulphate Cetrimide Cetomacrogol 1000 PEG 1000 monostearate Triethanolamine stearate Sodium stearate Table 4 Emulsifying wax Component Emulsifying wax BP Cetostearyl alcohol, sodium lauryl sulphate Emulsifying wax USNF Cetyl alcohol, polysorbate Cationic emulsifying was BPC Cetostearyl alcohol, cetrimide Glyceryl monostearate S.E. Glyceryl monostearate, sodium stearate Cetomacrogol emulsifying wax BPC Cetostearyl alcohol, cetomacrogol 1000 Polawax Cetyl alcohol, non-ionic surfactant Product Attributes • Shelf Life – The gel network theory of emulsion stability is why both emulsifiers and mixed wax help the shelf life period – The emulsifiers stabilize the oil droplets by the formation of an interfacial film Product Attributes • Consistency – It is related to swelling properties and concentration of the α-crystalline gel phase – When the α-crystalline form is in presence of very small quantities of ionic surfactants and a fatty aclohol and is dispersed in water the amount of swelling increases – This leads to the swelling of the α-crystalline gel phase – The water is in between the bilayers of the gel phase and when it swells the volume ratio of dispersed phase to the free continuous phase water increases Product Attributes • Evaporation and Absorption – When lotion is rubbed into the skin water evaporates and the oil droplets coalesce • Coalescence occurs when the interfacial energy between substrates and adatoms is small – The clusters can detach themselves from any given location on the surface and diffuse as entities over the surface – The clusters behave more like liquid than solid crystallites Product Attributes • Evaporation and Absorption – After the application of the lotion the composition changes as the water and other other volatiles solvents evaporate – A film stays on the skin as a protector and the nutrients are absorbed – Absorption capacity increases with decreasing viscosity Product Attributes • Viscosity – Emulsion size and concentration determines the viscous properties – At the same shear stress and droplet concentrations the viscosity of concentrated emulsions containing smaller droplets was significantly greater – This suggests that electrostatic repulsion plays an important role in determining the rheology of concentrated emulsions Product Attributes • Viscosity – The droplets become closely packed causing the emulsions to be come rigid at lower concentrations for smaller droplets because of their effective volume fraction is greater – This explains why low emulsifier concentrations are good for structured lotions – Lotions are not suppose to be very thick and viscous Product Attributes • Fragrance – Fragrances are applied by collodial systems like emulsions – The lipid part of the stratum corneum is organized in lamellar structures – The lamellar liquid crystals in lotions contain the fragrance molecules – The similarity of the configuration of the crystals in lotion compared to the stratum corneum is why it easy for the fragrance to be absorbed into the skin – The location of the interlayer spacings and the geometrical characteristics play a big role on where the location of the fragrance is Product Attributes • Improvements made to the skin – Liposomes have positive effects on the appearance of the skin – Improve cutaneous hydration, skin structure, depths of wrinkles – Liposomes are spherical vesicles that have an aqueous cavity at their center – They are used to carry water-soluble molecules and hydrophobic molecules – Liposomes have been evaluated as delivery systems for drugs, vitamins and cosmetic materials Product Attributes • Delivery Systems – Particulate systems are very small particles that range from micrometers to millimeter – These particles deliver essential active ingredients such as amino acids, plant extracts, minerals, vitamins, antioxidants, and UV protectants – They also prolong the time during which the ingredient remains on the skin V. HAOHAO VI. Manufacturing Process • The objective is to disperse one liquid within another in an extremely fine form to make certain that separation due to settling either does not occur or takes place very slowly. • Does not normally involve any extraction or chemical reaction. A Few Parameters that may influence liquid-liquid emulsion formation • Shear rate • Sufficient stabilizers need to be present to maintain the smallest droplet size produced for long periods of time. • Blend time and standard deviation of circulation time. • These along with many other parameters make it difficult to specify a mixing process based on desired droplet size. Most predictions are based on existing data. Pilot Scale Manufacturing Process (US Patent# 6,017,548) Federal Rules and Regulations • CGMP’s – Primary objective is to ensure that manufacturers provide consumers with safe and effective products. • Parts 210 and 211 apply to manufacturing of drugs and finished pharmaceuticals. • Part 210 contains a basic overview and some definitions that are used in Part 211. Part 211 • Gives a description of responsibilities of the quality control unit. • States that proper training procedures must be in place. • Buildings and Facility requirements • Cleaning requirements- Rooms and Equipment • Proper labeling and storage of materials • Batch Records Marketing Considerations • • • • Packaging aesthetics Fragrance Color of Lotion Shelf Location