10-Triacylglycerol
advertisement
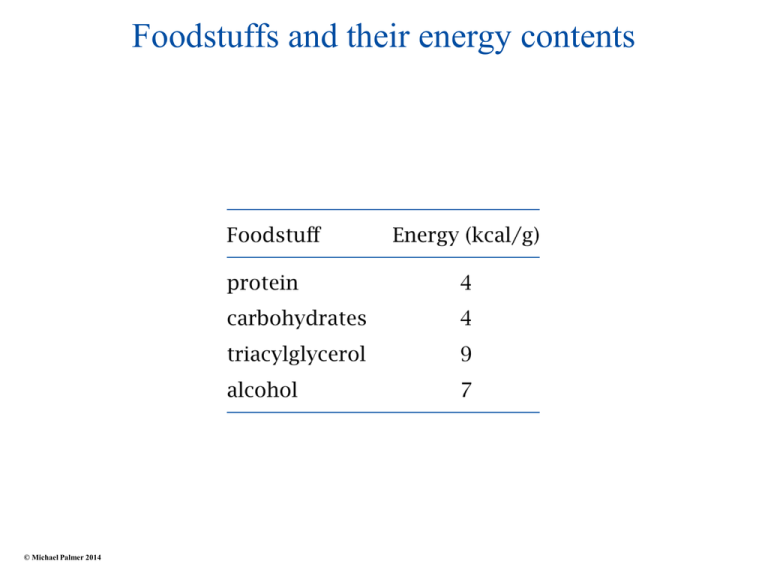
Foodstuffs and their energy contents © Michael Palmer 2014 Carbon pools in carbohydrate and fat metabolism © Michael Palmer 2014 Triacylglycerol and its cleavage products © Michael Palmer 2014 Solubilization of fat by detergents © Michael Palmer 2014 Uptake and re-packaging of digested fat in the small intestine © Michael Palmer 2014 The lymphatics drain excess fluid from the interstitial space © Michael Palmer 2014 Chylomicrons are drained from the intestine through the lymphatics, bypassing the liver © Michael Palmer 2014 Lipoprotein lipase extracts triacylglycerol from chylomicrons © Michael Palmer 2014 Two activated forms of fatty acids © Michael Palmer 2014 Activation of fatty acids and transport to the mitochondrion © Michael Palmer 2014 Reactions in β-oxidation © Michael Palmer 2014 Shared reaction patterns in β-oxidation and TCA cycle © Michael Palmer 2014 The reaction mechanism of thiolase © Michael Palmer 2014 Utilization of propionate © Michael Palmer 2014 Organ relationships in triacylglycerol utilization © Michael Palmer 2014 Brown fat tissue © Michael Palmer 2014 Medium-chain fatty acids ● contain less than 12 carbon atoms ● low content in most foods, but relatively high (10–15%) in palm seed and coconut oil, from which they are industrially prepared ● triglycerides with medium chains are more soluble and more rapidly hydrolyzed by gastric and pancreatic lipase ● not efficiently re-esterified inside intestinal cells; systemic uptake mostly as free fatty acids ● reach mitochondria by diffusion, without prior activation to acyl-CoA and acyl-carnitine Ketone body metabolism © Michael Palmer 2014 Synthesis of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate © Michael Palmer 2014 Decarboxylation of acetoacetate © Michael Palmer 2014 Acetone can serve as a precursor for gluconeogenesis © Michael Palmer 2014 Anticonvulsant effects of acetone and acetol © Michael Palmer 2014 The acetyl-CoA carboxylase reaction © Michael Palmer 2014 The structure of fatty acid synthase © Michael Palmer 2014 Phosphopantetheine acts as a flexible tether in acyl carrier protein © Michael Palmer 2014 Fatty acid synthase reactions (1) © Michael Palmer 2014 Fatty acid synthase reactions (2) © Michael Palmer 2014 Mitochondrial export of acetyl-CoA via citrate © Michael Palmer 2014 Mitochondrial export of acetyl-CoA via acetoacetate © Michael Palmer 2014 Elongation and desaturation of fatty acids ● elongases reside in mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum ● chemistry of elongation similar to β-oxidation in mitochondria, similar to fatty acid synthase in the ER ● desaturases occur in the ER, introduce double bonds at various positions ● double bonds are created at least 9 carbons away from the ω end—ω-3 fatty acids cannot be formed and are therefore essential Cerulenin, an antibiotic that irreversibly inhibits fatty acid synthase © Michael Palmer 2014 Fatty acid synthase inhibition slows tumor growth in mouse experiments © Michael Palmer 2014 The glyoxylate cycle © Michael Palmer 2014 Reactions in the glyoxylate cycle © Michael Palmer 2014