Ch 1 Powerpoint
advertisement

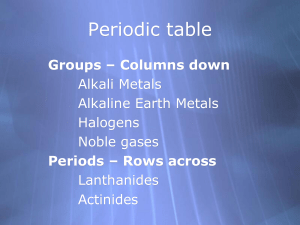
Show the Arrangement of Particles in Solid, Liquid and Gaseous Water Solid Liquid Gas Density of Water / Ice Why does ice float on water? Relate your answer to the kinetic molecular theory of matter. Observe Water Isopropyl Alcohol Oil Add an ice cube with red food coloring to each container. Explain your observations in terms of relative densities, solubilities, and the kinetic molecular theory of matter. Chapter 1 Terms • Sort the terms provided into categories and name each category. • Construct a sentence for each category showing the interrelationships between the terms in the category. • Revise your categories for homework as you read chapter 1. Making Peanut Brittle - Demonstration • Place ½ c corn syrup, 1 c sugar, and 1 c peanuts in a large measuring cup • Microwave for 4 minutes. Stir. • Heat for another 4 minutes. • Stir in 1T butter, 1 t vanilla, and 1 t baking soda • Quickly spread on greased aluminum foil Explain your observations using at 4/13/2015 least 10 terms presented in chapters 51. Electric Current & Tin (II) Chloride • Working with your lab partner, dissolve 1 plastic spoonful of SnCl2 in 50 mL of water. • Place the solution in a petri dish. • Connect alligator clips to one post of a battery and to a wire attached to the side of the petri dish. Connect another set of clips to the other post of the battery and to a second wire in the petri dish. • Record your observations. Explain the chemistry involved. Petri dish with SnCl2 4/13/2015 battery 6 Decomposition of Tin Chloride Electrolysis – Signs of chemical change – Physical properties – Atoms, Compounds and Ions – Determining the Area of an Irregularly Shaped Piece of Cardboard Using graphical analysis (with your graphing calculator), find the area of the irregularly shaped piece of cardboard. What is another variable that is directly proportional to area? Percent Composition of Margarine • Spend five minutes with your partner developing a procedure and discussing the data and calculations Ion Naming • Monoatomic Ions (periodic table) • Transition Metals Polyatomic Ions • Naming Ions when number of oxygen atoms changes: Perchlorate Chlorate Chlorite Hypochlorite Naming Ions When Number of Hydrogen Atoms Changes • • • • • • • Phosphate Hydrogen phosphate Dihydrogen phosphate Carbonate Bicarbonate Sulfate Bisulfate Use your knowledge of the metric system and the use of conversion factors to prove Peter’s math correct or incorrect. •0.5t(5mL/1t)(1 cc/1 mL) = 2.5 cc •Volume – 2 x 3.5 x 3.625 = 25.375 in3 •Density - 1 lb / 25.375 in3 = 0.0394 lb / in3 •0.0394 lb / in3 (453.6g / 1 lb) (1 in3 / 16.387 cm3) = 1.0906 g / cm3 2.5 cc (1.0906g / cc) = 2.7265 g While the math is correct, the sig figs ARE NOT!! TEST TUBE WITH NAIL OBSERVATIONS: EXPLANATIONS????? CuSO4 and NaCl combine: Activity Series: Fe, Cu Iron ions react with oxygen and water: New Concepts: Complex ion ~ Redox Reactions ~ Base Anhydride ~ Isotopes Antimony has two stable isotopes, Sb-121 and Sb-123 with masses of 120.9038 and 122.9043 amu respectively. Calculate the percent abundance of each. Calculation of Weighted Average Atomic Mass Using Percent Abundance of Isotopes of the Element Silver has an atomic mass of 107.9 amu. If 51.84% of Ag exists as Ag-107 (106.9051 amu), what is the identity and atomic mass of the other isotope? Molecules Diatomic – H2, O2, N2, Cl2, Br2, I2, F2 Polyatomic molecules – S8, P4, O3 Allotropes • O, P, S, C exist in different forms • Carbon: • O O2 and O3 (Electricity converts O2 to O3. Ozone is a blue colored gas with a pungent odor. Its name comes from ozein which means “to smell”) • S What is the average mass of one atom of titanium in grams? What is the mass percent of C in chloroform (CHCl3)? Calculating Empirical Formulas In a chemical reaction, 1.000 g of sulfur combines with 3.963 g of copper to give a pure compound. What is the empirical formula of this compound? Calculating Molecular Formulas A compound was analyzed and found to contain 53.50% carbon, 11.19% hydrogen, and 35.51% oxygen by mass. If the molar mass of this compound is 90.12 g/mol, what is the molecular formula of the compound? Review: Isotopes • Uranium has an atomic mass of 238.0289. It consists of two isotopes: uranium-235 with a mass of 235.044 amu and uranium-238 with a mass of 238.051 amu. Calculate the % abundance of the U-235 isotope. Mass Percent • Calculate the mass percent of sulfur is barium sulfate Mass / Moles / Particles • Calculate the number of atoms in 12 grams of iron. Formulas • Determine empirical and molecular formulas for a compound that is 71.65% Cl, 24.27% C, and 4.07% H. The molar mass of the compound is 98.96 g/ mol Coulomb's Law • The force of attraction between ions in an ionic compounds is due to: – The magnitude of charge on the ions – The distance between the ions Smaller ions and ions with greater charge have greater forces of attraction Naming Hydrocarbons: Alkanes: •1 carbon: CH4 – •2 carbons: C2H6 – •3 carbons: C3H8 – •4 carbons: C4H10 – •5 carbons: C5H12 – Naming Hydrocarbons Alkanes, continued: •6 carbons: C6H14 – •7 carbons: C7H16 – •8 carbons: C8H18 – •9 carbons: C9H20 – •10 carbons: C10H22 – Alkenes – Alkynes – Substituted Hydrocarbons Halocarbon – chloroform Carboxylic acid – acetic acid Ester – methyl acetate Aldehyde – formaldehyde Ketones – acetone Alcohols – ethyl alcohol propyl alcohol isopropyl alcohol Amines - methyl amine Naming Molecules CO CO2 N 2O N 2O 5 N 2O 3 Radioactivity • Alpha particles: • Beta Particles: • Gamma Rays: U-235 loses 1 alpha particle. What element is formed? What is its atomic mass and number? Co-60 loses 1 beta particle. What element is formed? What is its atomic mass and number? Radioactive Decay Series • U-238 undergoes a series of 14 reactions to form lead-206. The first four reactions are alpha, beta, beta, and alpha decay, in that order. Write the equations for these first four steps. Stability of Atomic Nuclei • Only 2 stable isotopes (H, He) have more p than n • Up to Ca, stable isotopes may have equal numbers of p and n or one or two more n than p • Beyond Ca, stable isotopes must have a ratio of n:p that is greater than one • Beyond Bi, (83p, 126n) there are no stable isotopes, heavier nuclei cannot be held together • Elements with even atomic numbers have more stable isotopes than those with odd atomic numbers What Holds a Nucleus Together? • The mass of 1 p = 1.0073 amu and the mass of 1 n = 1.0087 amu. Therefore an alpha particle (2p, 2n) has an expected mass of 4.0320 amu. • The actual mass of an alpha particle = 4.0015 amu. The difference, 0.0305 amu, is called nuclear mass defect. • Mass defect can be converted into energy units using E=mc2 • This amount of energy is released when the nucleus is formed and is called nuclear binding energy. Peanut Brittle and Chapter 1: Physical Properties: State Changes: Heat Energy: Chemical Changes: Mixture Types: