Overview
advertisement

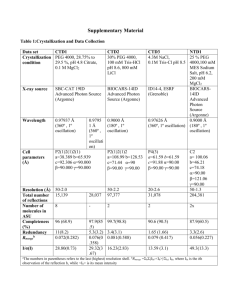
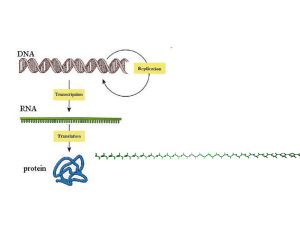
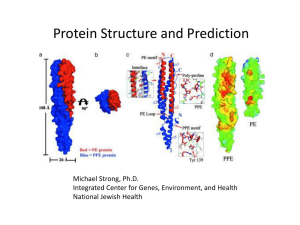
Tutorials for protein data bank and swiss PDB viewer 2010/04/19 Prof. Jinn-Moon Yang Yen-Fu Chen and Kai-Cheng Hsu http://gemdock.life.nctu.edu.tw/dock/download/20100419_spv.ppt http://gemdock.life.nctu.edu.tw/dock/download/20100419_spv.pdf http://ppt.cc/cnqT (ppt) http://ppt.cc/WWxd (pdf) Contents Introduction of protein structures Using thymidine kinase as an example Download and install Tutorial Download protein structures from PDB Basic Operation Advance Operation Resources for tutorial http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFE3CAHNkZg&feat ure=related Introduction of protein structures Proteins present in all biological organisms Polymers of amino acids (20 L-α-amino acids) Nanoparticles Perform particular biochemical functions Transcription and translation stemcells.nih.go: Early Development Cell regulation and catalysis reactions Nature: Mattson, M. Nature. 422, 385-387 (2003) Introduction of protein structures To enable to perform protein’s biological function, protein fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by noncovalent interactions Hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, van der Waals forces and hydrophobic packing 3D protein structures are necessary for understanding the functions of protein at molecular level Protein structure: from amino acid to quaternary structure Adapted from Protein Structure in Wikipedia Hemoglobin: oxy-deoxy states Adapted from structural biology Wikipedia Noncovalent interactions for protein structure and function Ionic bond A bond formed by the attraction between two oppositely charged ions Hydrogen bond An attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, like N,O, and F Potential energy of Na and Cl Potential energy of Na and Cl Noncovalent interactions for protein structure and function van der Waals force Attractive or repulsive force between molecules Hydrophobic interaction The physical property of a molecule (known as a hydrophobe) that is repelled from a mass of water An example of van der Waals force: Gecko climbs on the glass An example of hydrophobic interaction: Water drops on hydrophobic surface Protein structure database: Protein data bank (PDB) Techniques for determining atomic structures X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy and electron microscopy PDB contains information about experimentallydetermined structures of biological marcomoleculeas (proteins, and DNA/RNA) Proteins (1kim) X-ray NMR DNAs/RNAs (2k7e) EM http://www.pdb.org/ Biological complexes (1zrc) Search protein structures in PDB PDB provides search by protein name, ligand, or structrue related keywords Search example: thymidine kinase (TK) • Function: DNA synthesis • Therapeutic: Anticancer and antivirus drug target Example: X-ray structures of virus’ thymidine kinase with substrates/inhibitors Protein name Source spices Experimental method has ligands Search result of “X-ray structures of virus’ thymidine kinase with substrates/inhibitors” 23 structures for these keywords PDB ID of this structure TK of virus TK with ligand (substrate) X-ray structure Structure and related data (1kim) Related data of this structure The title of this structure The citation of this structure Visualization of biological assembly Structure and ligand data (1kim) Ligand in this structure Structure and sequence data (1kim) Related data of this structure Sequence ID of 1kim in UniProtKB Structure classification ID of 1kim Advance inspection for protein structure: download structure from PDB 1. Save the data on your PC 2. Open the file on a structure viewer program (swiss PDBviewer, pymol, and etc.) Classification of Drug Development Unknown O O High-Throughput Screening (HTS) O O Similar compounds Structure-based Drug Design (SBDD) O O O query Known Protein (receptor) Structure Compound similarity search SBDD or de novo design O Known Compound structure DDT 2002 Unknown Discovering new leads SBDD HTS Yellow: virtual screening (SBDD) Blue: high-throughput screening (HTS) • • • • There are more than 5 H-bond donors. The molecular weight is over 500. The LogP is over 5. There are more than 10 H-bond acceptors. Curr. opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 439 Drugs derived from structure-based approaches Drug Discovery Today, 10, 895, 2005 Drug Discovery Today, 10, 895, 2005 Tutorial for Swiss PDB viewer Download and install Download Swiss PdbViewer http://spdbv.vital-it.ch/download.html Download user guide http://spdbv.vital-it.ch/SwissPdbViewerManualv3.7.pdf Tutorial video (English) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nYT5qwtfNew&fe ature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yFE3CAHNkZg Download page General Terms Main chain Residue Arginine Chain Secondary Structure (Ribbon) Side chain Gray: C atom Blue: N atom Red: O atom Atom radius A protein may have multiple chains Install and execute swiss pdb viewer Workspace Layer info Main window Viewer Control panel Move & Rotate Center Zoom Translate Rotate Open control panel control panel Load PDB1 Load PDB2 Display or hide residues -for some residues Press left button of mouse Display or hide residues -for all residues Press right button of mouse Display or hide side chains of residues Display or hide residue labels GLU111 Display or hide atom radius Render in solid 3D Show secondary structures -Display or hide ribbons Bond length 1 angstrom (A) or 1 × 10−10 meters 1.52A ?A Bond length ?A Bond length Hydrogen bond length ?A Hydrogen bonds of helix Hydrogen bond of helix Hydrogen bonds of helix Helix Hydrogen bonds of sheet Sheet Residue 50~55 201~207 323~328 Number of helix ? From residue 46~146 Change color Visualization of biological assembly -color by chain Change color by chain -act on Ribbons Show residue properties -Change color by Type Type Negative Positive Polar Hydrophobic Reisdue ASP GLU HIS LYS ARG SER TYR ASN THR GLN CYS MET PHE ALA TRP LEU ILE PRO VAL GLY Show structure flexibility Change color by B-factor A low B-factor meaning that the position of the atom has been determined with accuracy High B-factor Low B-factor Other color types default atom colors Root mean square between 2 molecules Secondary Structure Selected residues Relative accessibility Thymidine kinase • Function: DNA synthesis • Therapeutic: Anticancer and antivirus drug target Analyze protein-ligand interactions -Select ligands (or residues) Press left button of mouse to select the ligand (THM, thymidine) of 1kim Identify binding site -Show protein (ribbon) and ligand (stick) Select residues in the binding site -Neighbors of selected residues Center selected residues H-bonds of the binding site -Compute H-bonds H-bonds between protein and ligand -Show H-bonds of selection H-bonds between TK and THM -Show residues from selection Show residue label Press right button of mouse 1. Q125 recognize the thymine moiety 2. Activity was decreased by over 90% if Q125 mutated (Biochemistry, 2000. 39: p. 4105-4111) van der Waal forces -Stacking interactions M128 and Y172 sandwich the thymine moiety Stabilize the binding of substrate (JBC, 1999. 274: p. 31967-31973) Observe the protein surface -Compute Surface Surface preference Show ligand in the surface Discard surface Comparison of multiple structures -Import PDB PDB code: 3vtk Another structure of thymidine kinase Open layer info Show or hide 1kim 3vtk Superimpose two molecules Results of superimposition RMS: 0.63 Ǻ Measure the structure similarity Comparison of binding sites -Neighbors of selected residues Comparison of ligands 3vtk: inhibitor (Green) 1kim: substrate(CPK) Save files Homework Keyword 1. Capture a picture of N1 neuraminidase (ribbon) and its ligand (stick) 2. Capture a picture of H-bonds between protein and ligand E-mail pikihsu@gmail.com Mail title: 學號姓名_HW2