ubiquinol oxidase
advertisement

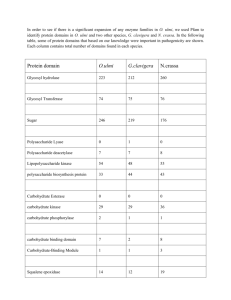
Exploring the Structure and Function of Cytochrome bo3 Ubiquinol Oxidase from Escherichia coli Lai Lai Yap Department of Biochemistry Heme-Copper Oxidase Superfamily • catalyze reduction of oxygen to water, and utilizes free energy produced to pump protons across membrane • transmembrane proton and voltage gradient thus generated is converted to useful energy forms (eg. ATP by ATP synthase) Heme-Copper Oxidase Superfamily • 2 main groups (based on electron-donating substrate) : cytochrome c oxidase (eg. mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase) and ubiquinol oxidase (eg. cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase) • membership based on presence of subunit homologous to subunit I of mammalian cytochrome c oxidase • subunit I: – largest subunit – binuclear center (where O2 binds and is reduced to water) consisting of a heme and copper (CuB) – a second heme (which facilitates transfer of electrons to binuclear center) Respiratory Chains of E. coli Substrates eg. NADH, succinate D e h y d r o g e n a s e s Cytochrome bo3 O2 Low O2 affinity Quinone Cytochrome bd High O2 affinity O2 Cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase • • • • a terminal oxidase in the aerobic respiratory chain of Escherichia coli member of the heme-copper oxidase superfamily consists of four subunits catalyzes two-electron oxidation of ubiquinol-8 (Q8H2) at periplasmic side of cytoplasmic membrane and four-electron reduction of oxygen to water at cytoplasmic side • also functions as a proton pump by translocating protons across the cytoplasmic membrane to establish an electrochemical proton gradient • possible mechanism: ubiquinone bound at the high affinity site (QH) acts as cofactor and mediates electron transfer from ubiquinol substrate (at the low-affinity QL site) to heme b • reduced heme b then provides electrons to the binuclear center for the reduction of oxygen to water Electron and proton transfer in cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase 2H+ periplasm QL 2e- 2e- QH 2e- Heme o3 CuB QH2 Heme b II 2e- III IV I cytoplasm 2H+ translocation H2 O ½ O2 + 2H+ Spherical rendering structure of ubiquinol oxidase ubiquinol binding site Subunit I Subunit II Subunit III Subunit IV P C Structure of ubiquinol oxidase ubiquinol binding site Subunit I Subunit II Subunit III Subunit IV P C Redox metal centers of ubiquinol oxidase (in subunit I) His334 His333 His106 His284 His419 CuB His421 Heme b Heme o3 Rainbow rendering of ubiquinol oxidase and cytochrome c oxidase Cytochrome c binding site Cytochrome c oxidase Ubiquinol binding site Ubiquinol oxidase Superposition of ubiquinol oxidase and cytochrome c oxidase Ubiquinol oxidase Cytochrome c oxidase Proton transfer pathways • D- and K-channels in subunit I • channels form polar cavities that originate on the cytoplasmic side, leading to the binuclear center for proton pumping and water formation • D-channel : uptake of both chemical and pumped protons • K-channel : load enzyme with protons at some earlier catalytic steps D- and K-channels of ubiquinol oxidase H+ out H421 H334 H106 H333 T149 H284 E286 S145 N142 T201 Y288 T204 T359 N124 K362 S299 S315 T211 D135 D-channel K-channel D-channel K-channel 2H+ periplasm QL 2e- 2e- QH 2e- Heme o3 CuB QH2 Heme b II 2e- III IV I cytoplasm 2H+ translocation H2 O ½ O2 + 2H+ Structure of ubiquinol oxidase ubiquinol binding site Subunit I Subunit II Subunit III Subunit IV P C Ubiquinol oxidase with modeled ubiquinone (at ubiquinol binding site) Ubiquinone binding site of ubiquinol oxidase with modeled ubiquinone H98 M78 I102 M79 D75 Q101 L160 R71 ubiquinone Electron and proton transfer in cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase 2H+ periplasm QL 2e- 2e- QH 2e- Heme o3 CuB QH2 Heme b II 2e- III IV I cytoplasm 2H+ translocation H2 O ½ O2 + 2H+ Membrane normal view of subunit I with modeled ubiquinone possible electron path from ubiquinone to binuclear center CuB H419 heme o3 H421 heme b M79 H106 I102 ubiquinone