Unit 11 Review Activity 12-13
advertisement

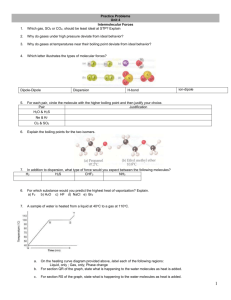
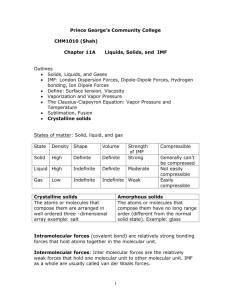
Unit 11 Review Activity MM 12-13 1. Which of the following can exhibit dipole-dipole attractions between its molecules? CO2, SO2, H2, IF, HBr, CCl4 • SO2, IF, and HBr • All are polar molecules 2. Which of the following substances exhibit hydrogen bonding in their liquid and solid states? CH3NH2, CH3F, PH3, HCOOH •CH3NH2 and HCOOH 3. Predict which substance will have the higher BP. TiO2 or TiCl4 • TiO2 has a larger BP due to the higher charge on Oxygen 4. Predict which substance will have the higher BP. LiF or MgF2 • MgF2 has a higher BP because of the higher charge of magnesium 5. List the 3 types of IMF in order of increasing strength. • Dispersion, dipole, and hydrogen bonding 6. Which type of IMFs are common to the pair? Xe and CH3OH •London dispersion 7. Which type of IMFs are common to the pair? NH3 and HF •Hydrogen bonding 8. Which of the following atoms would you expect to be most polarizable? O, S, Se, Te • Te – has the most electrons 9. Explain what happens to the boiling point of noble gases as you move down the group. • BP increases because the atom increases in size due to increasing number of electrons which increases polarizability 10. Rationalize the difference in boiling points between the pair. Br2 (59C) and ICl (97C) • ICl is polar so the most prominent IMF is dipoledipole while the prominent IMF in Br2 is dispersion force. 11. What is the relationship between IMF and viscosity? •As IMF becomes stronger, viscosity increases 12. State the phase changes that are exothermic. • Freezing, condensing, deposition and Larry 13. Explain why the heat of fusion for any substance is generally lower than the heat of vaporization. • With heat of fusion only some IMF are being broken, with heat of vaporization all the IMF are broken. 14. Identify the states of matter in sections A, B and C. • A = Solid • B = Liquid • C = Gas 15. Name the “points” on the graph. Star, triangle, square and T • Triangle = normal mp • Square = normal bp • T = triple point • Star = critical point 16. Covalent bonding happens in both molecular and covalent network solids. Why do these two kinds of solids differ so greatly in their hardness and melting points. • Covalent- network solids are extremely strong forces due to the lattice structure of the molecules. Comparatively the covalent solid’s IMF bonds are weak. 17. A white substance melts with some decomposition at 730C. As a solid, it is a nonconductor of electricity, but it dissolves in water to form a conducting solution. Which type of solid is it? •Ionic 18. Suppose you have 2 colorless molecular liquids, one boiling at -84C, the other at 34C, and both at atmospheric pressure. True or False The higher boiling liquid has greater total IMF than the other. •True 19. Suppose you have 2 colorless molecular liquids, one boiling at -84C, the other at 34C, and both at atmospheric pressure. True or False The lower boiling liquid must consist of nonpolar molecules. •False – has less total IMF 20. As the IMF attraction between molecules increases in magnitude, will vapor pressure increase or decrease? • IMF increases then VP decreases 21. As the IMF attraction between molecules increases in magnitude, will heat of vaporization increase or decrease? •IMF increases and heat of vaporization increases 23. A flask of water is connected to a vacuum pump. A few moments after the pump is turned on, the water begins to boil. After a few minutes, the water begins to freeze. Explain why these processes occur. • The pump reduces the pressure in the flask above the water when atmospheric pressure = vapor pressure. Water boils, boiling is endothermic, and the temperature drops if the system is not able to absorb heat from the surroundings fast enough. As the temp of water decreases, the water freezes.