PHYSICS OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS
advertisement

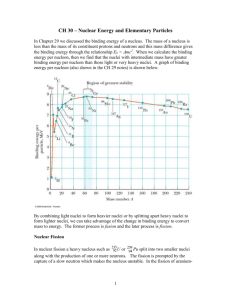
PHYSICS OF NUCLEAR WEAPONS Nuclear Binding Energy Nuclear Stability Weapon Types • Fission “Little Boy” “Fat Man” Weapon Size Nuclear Weapons & States The Fission Reaction 200 MeV/240 ≈ 0.8 MeV/nucleon ≈ 1,000,000 X Echemical Weapon Types • Fusion Two-Stage Thermonuclear The Fusion Reaction 17.6 MeV/5 ≈ 3.5 MeV/nucleon ≈ 5 X Efission Comparison of Fission & Fusion Nuclear Fission Definition: Natural occurrence of the process: Byproducts of the reaction: Conditions: Energy Requirement: Nuclear Fusion Fission is the splitting of a large atom into Fusion is the fusing of two or more lighter two or more smaller ones. atoms into a larger one. Fission reaction does not normally occur in nature. Fusion occurs in stars, such as the sun. Few radioactive particles are produced by Fission produces many highly radioactive fusion reaction, but if a fission "trigger" is particles. used, radioactive particles will result from that. Critical mass of the substance and highspeed neutrons are required. High density, high temperature environment is required. Extremely high energy is required to bring Takes little energy to split two atoms in a two or more protons close enough that fission reaction. nuclear forces overcome their electrostatic repulsion. Energy Released: The energy released by fission is a million times greater than that released in chemical reactions; but lower than the energy released by nuclear fusion. The energy released by fusion is three to four times greater than the energy released by fission. Nuclear weapon: One class of nuclear weapon is a fission bomb, also known as an atomic bomb or atom bomb. One class of nuclear weapon is the hydrogen bomb, which uses a fission reaction to "trigger" a fusion reaction. Paths to Fissionable Material Nuclear Fuel - Uranium • Ore → Yellow Cake → Enriched Uranium Deposits Uranium Deposits Uranium Enrichment Slightly Enriched (SEU): 0.9%-2.0% Used in Heavy-Water Reactors (HWR) Low-Enriched (LEU): 2%-20% 3%-5% used in Light-Water Reactors (LWR) 12%-19.75% used in Research Reactors Highly Enriched (HEU): >20% ≥ 85% used in weapons primaries ≥ 20% ‘weapons-usable’ in implosion designs 40%-80% used in secondary of two-stage ≥ 20% used in fast neutron reactors 50%-90% used in naval reactors 26.5% in commercial fast reactors Critical Mass Critical Masses Isotope or Mixture Critical Mass Half Life (kg) (years) Decay Heat (watts/kg) U-233 16 160,000 0.28 U-235 Np-237 Pu-238 Pu-239 Pu-240 Pu-241 48 59 10 10 37 13 700,000,000 2,100,000 88 24,000 6,600 14 Pu-242 Am-241 89 57 380,000 430 Neutron Production From Spontaneous Fission (per kg-sec) 1.2 Main Gamma Energies (MeV) 2.6 from Tl208 Properties of Nuclear-Explosive Nuclides 0.00006TABLE A-10.36 0.19 0.021 0.14 0.087 560 2,700,000 0.100 2.0 22 0.41 7.0 1,000,000 0.10 6.4 49 0.66 from Am241 0.12 1,700,000 0.045 110 1,500 0.66 Comparison of Energy Content • • • • • • • • • Fission of U-233: 17.8 kt/kg Fission of U-235: 17.6 kt/kg Fission of Pu-239: 17.3 kt/kg Fusion of pure deuterium: 82.2 kt/kg Fusion of tritium and deuterium (50/50): 80.4 kt/kg Fusion of lithium-6 deuteride: 64.0 kt/kg Fusion of lithium-7 deuteride: Total conversion of matter to energy: 21.47 Mt/kg Fission of 1.11 g U-235: 1 megawatt-day (thermal) Broader comparison of Energy Densities Enrichment Process Uranium • • • Isotopic Masses and Abundances • • 235U 235U 238U 238U Abundance = 0.720% Abundance = 99.274% Mass = 235.04393 (UF6, 349.03433) Mass = 238.05079 (UF6, 352.04119) • m238/ m235 = 1.0086 • m238/ m235 = 1.0043 → v235/ v238 = 1.0043 UF6 Enrichment Methods • Electromagnetic (Calutron) (≤ 15% enrichment) Enrichment Methods • Gaseous Diffusion Enrichment Timeline Enrichment Methods • Thermal Diffusion Enrichment Methods • Gas Centrifuge Centrifuges • Materials: Aluminum → Maraging Steel → Carbon Fiber Composite • 100,000 rpm (balanced, magnetic bearings) • STUXNET Enrichment Methods • LASER Techniques (AVLIS/MLIS) Method Comparison Resources • • • • • • • • • IAEA/INFCIS The Atomic Archive World Nuclear Association Nuclear Chemistry Federation of American Scientists Nuclear Pathways ALSOS Digital Library Nuclear Safeguards Education Portal World Information Service on Energy (WISE) Uranium Project