Heredity PPT
advertisement
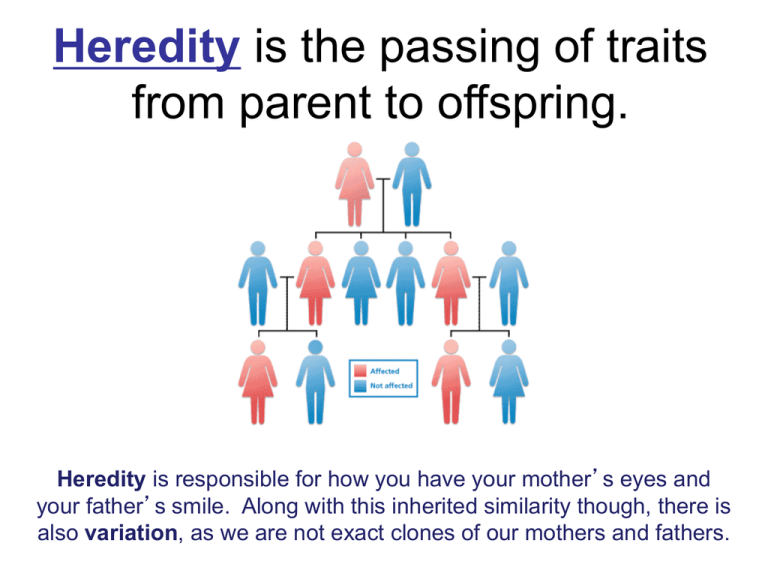
Heredity is the passing of traits from parent to offspring. Heredity is responsible for how you have your mother’s eyes and your father’s smile. Along with this inherited similarity though, there is also variation, as we are not exact clones of our mothers and fathers. Offspring are the new organisms produced by one or more parents. (children, babies, young) The study of heredity in biology is called genetics. The Father of Genetics Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk who studied mathematics and science but became a gardener in a monastery. • Mendel thought there might be a connection between the color of a pea plant flower and the type of seed the plant produced. • He began to experiment with garden peas in 1856. • Mendel made careful use of experimental design to study pea plants and had the first recorded study of how traits pass from one generation to the next. Reproduction Reproduction - biological process by which new "offspring" (individual organisms) are produced from their "parents". *It is the process by which an organism produces others of its same kind. Types of Reproduction • Asexual - one parent • Sexual - two parents Asexual Reproduction: a type of reproduction in which a new organism is produced from one parent and has the same DNA or genetic material as the parent. Yeast cells dividing (budding) Spider plant offspring Asexual Reproduction • Requires only one parent • Offspring have 100% the same chromosomes as the parent. – In other words, the offspring are exact “clones” of the parent. – Mitosis – Movie Asexual Reproduction Advantages: • Animals that remain in one particular place and are unable to look for mates would need to reproduce asexually. • Numerous offspring can be produced without "costing" the parent a great amount of energy or time. This type of reproduction is also faster. • Environments that are stable and experience very little change are the best places for organisms that reproduce asexually. Disadvantages: • Lack of genetic variation - all of the organisms are genetically identical and therefore share the same weaknesses. • If the stable environment changes, the consequences could be deadly to all of the individuals. *Animals are not the only organisms that reproduce asexually. Yeasts, plants, and bacteria are capable of asexual reproduction as well. Sexual reproduction: a type of reproduction in which two cells, usually an egg and a sperm, join to form a new organism with its own genetic identity. Animal Plant Sexual Reproduction Advantage: • Allows genetic variation within a species which assists with the species survival Disadvantages: • Requires 2 parents • Reproduction is slower Sexual Reproduction • All the members of the Animal Kingdom – Fish – Mammals – Amphibians – Birds – Reptiles – Insects – Crustaceans Sexual Reproduction • Examples of organisms that reproduce sexually – Chickens – Iguanas – Lobsters – Sharks – Humans – Butterflies – Sunflowers – Roses Sexual Reproduction • Happens 2 ways – Internally (inside) • The egg is fertilized by sperm inside the female – Mammals, birds, reptiles, insects, spiders – Externally (outside) • The egg is fertilized by sperm outside the female • The female lays the eggs and then the male fertilizes them. – Fish and some amphibians – Plants and fungi (pollen and spores) Asexual Reproduction Examples Asexual Reproduction • Examples of organisms that reproduce asexually – Hydra – Sea Star – Strawberry – Eubacteria – Euglena – Paramecium – Yeast Types of Asexual Reproduction • Fragmentation Fragmentation is where a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals. Ex. Planaria Types of Asexual Reproduction • Vegetative Propagation (Plant cuttings) • http://leavingbio.net/VEGETATIVEPROPAGATION.htm Vegetative reproduction is a type of asexual reproduction in plants where new parts grow from parts of the parent plant. It has long been used in horticulture and agriculture. Ex. Spider Plant Types of Asexual Reproduction • Binary Fission – Bacteria – Protists Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction where every organelle is copied and the organism divides in two. Types of Asexual Reproduction • Budding • Movie Budding is where a new individual develops from an outgrowth of a parent, splits off, and lives independently. Types of Asexual Reproduction • Regeneration Regeneration occurs when a body part has broken off and the organism grows a new one. Ex. Lizard Tail *The ability to restore lost or damaged tissues, organs or limbs









