Independent Assortment
advertisement

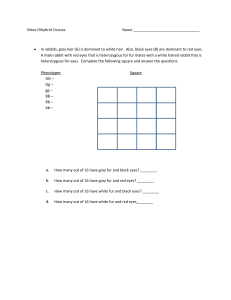
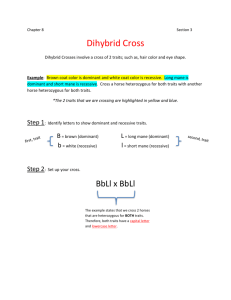
Dihybrid Crosses (two traits) Independent Assortment: When looking at the inheritance of more than one trait, like ears and fur color on a rabbit, if the traits are not on the same chromosome, they will not always stay together. They can sort independently of one another. (see page 495) When working with Dihybrid Crosses we use the FOIL method Example of a Dihybrid Genotype Bb CC First BC Outside Inside Last BC bC bC In mice, running is dominant to waltzing, and black coat color is dominant to white. Use a punnet square to predict the results of a cross between a heterozygous running, white mouse and a waltzing, heterozygous black mouse. *First we need to FOIL out the genotypes ____ ____, ____ ____ X ____ ____, ____ ____ F: F: O: O: I: I: L: L: Now we can do our Punnet Square Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: In rabbits, black fur (B) is dominant to white fur (b) and long hair (L) dominates short hair (l). What is the chance of getting a black, short-haired rabbit from a cross between a rabbit that is heterozygous for both traits and a rabbit that is white and heterozygous for long hair? ____ ____, ____ ____ X ____ ____, ____ ____ F: F: O: O: I: I: L: L: Now do the Punnet Square Genotypic Ratio: Phenotypic Ratio: