Linkage mapping
advertisement

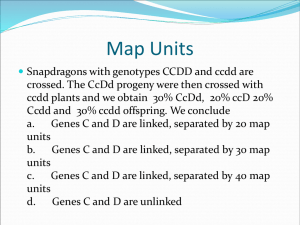
Linkage mapping Genetic recombination ▫ describes any process that produces new combinations of alleles P generation AABB aabb P gametes AB ab F1 AaBb generation Possible F1 gametes: A·B a·b A·b a·B parental combinations non-parental combinations For unlinked genes, recombination occurs by independent assortment. For linked genes, recombination occurs by crossing over. Recombination frequency (RF) • is the probability that a single recombination event will take place between two loci Recombination frequency Genes Relative location unlinked different chromosomes 50% (0.50) linked same chromosome < 50% • RF can be expressed as a decimal or percentage Linkage map • represents the positions of genes, relative to each other ▫ places genes on a chromosome, based on their recombination frequencies • it is not an actual physical map of a chromosome ▫ doesn’t ID the specific chromosome on which a gene is located ▫ doesn’t ID the specific location of the gene Constructing a linkage map Rationale: • the farther apart two loci are on a chromosome, the more likely they are to undergo recombination ▫ greater RF = greater distance Distances on a linkage map are measured in genetic map units (m.u.) 1 m.u. = RF of 1% (0.01) Example 1: • If A and B are found to have a RF of 5%, they are separated by 5 m.u. 5 m.u. A B Example 2: A and B have an RF of 5% A and C have an RF of 3% Based on the above info, two possible linkage maps exist: 5 m.u. 3 m.u. C A B 3 m.u. A 2 m.u. C B The RF for B and C will be 8% The RF for B and C will be 2% ...not enough info to know which one Example 3. L and M have an RF of 15% L and N have an RF of 20% a.) Construct two possible linkage maps for L,M, and N that could produce these RF’s. On each of these maps, indicate the map distance between M and N. b.) If M and N are found to have a recombination frequency of 4%, indicate which map is correct. RF = # of recombinant (non-parental) alleles total # of alleles Example 4. Two true-breeding parental plants (AABB and aabb) are crossed. The F1 offspring produce gametes in proportions indicated in the table. Calculate the RF for A and B. Are loci A and B linked? F1 gametes Frequency A·B 250 a·b 250 A·b 250 a·B 250 Total 1000 Non-parental combinations: 250 + 250 = 500 RF = 500/1000 = 0.5 (50%) Loci for A and B are unlinked. They are located on different chromosomes. Example 5. Two true-breeding parental plants (CCDD and ccdd) are crossed. The F1 offspring produce gametes in proportions indicated in the table. Calculate the RF for genes C and D. Are loci C and D linked? F1 gametes Frequency C·D 350 c·d 350 C·d 150 c·D 150 Total 1000 Non-parental combinations: 150 + 150 = 300 RF = 300/1000 = 0.3 (30%) Loci for C and D are linked. They are located on the same chromosome. Example 6. Produce linkage maps: a) for loci A and B (Example 4) b) for loci C and D (Example 5) Example 7. Two parents (CCvv and ccVV) are crossed. The F1 generation is entirely hybrid CcVv. The F1 generation produces the following gametes: CV (179), cv (174), Cv (477), cV (473). Determine if loci C and V are linked by calculating their recombination frequency. If they are linked, construct a linkage map and indicate map distance. Given: parental genotypes: CCvv and ccVV parental gametes: Cv and cV F1 gametes: CV (179), cv (174), Cv (477), cV (473) Non-parental RF = 353/1303 combinations: 179 + 174 = 353 = 0.27 (27%) Since the recombination frequency for C and V is 27%, they are separated by 27 map units. 27 m.u. C V RF < 50% Loci C and V are linked. In reality: can’t “see” the gametes produced ....next best thing: Perform a test cross to determine which allelic combinations were passed on in the gametes. If JJKK is crossed with jjkk, and the offspring is test-crossed to jjkk, offspring arising from parental gametes will be JjKk or jjkk offspring arising from recombinant gametes will be Jjkk or jjKk ...score the phenotypic proportions to determine the number of recombination events that occurred. Example 8. CCDD is crossed to ccdd. The offspring is testcrossed to ccdd. The following genotypes are obtained in the test-cross progeny: Ccdd and ccDd Frequency CcDd 909 Ccdd 235 ccDd 241 ccdd 915 recombinant a) Which of these offspring are the products of recombinant gametes? Genotype Total 2300 b) Calculate the RF for C and D. Non-parental combinations: 235 + 241 = 476 RF = 476/2300 = 0.21 (21%) Example 9. If AABB is crossed to aabb , and the F1 is then testcrossed, what percentage of the testcross progeny will be aabb if the two genes are: a) unlinked b) completely linked (no crossing-over at all) c) 10 m.u. apart d) 24 m.u apart Summary • Linkage maps represent the positions of genes on a chromosome, relative to each other. • Unlinked genes have RF values of 50%. Linked genes have RF values < 50%. • The greater the distance between genes, the more likely it is that a crossing over event will occur. • When constructing a linkage map, 1 m.u. = RF 1%