Chapter 2 - landman

The Biological Basis of
Behavior chapter 2
Neurons: The Messengers chapter 2
Neurons vary in size and shape
All are specialized to receive and transmit information
Myelinated neuron (Fig. 2-1) chapter 2
Three Types of Neurons
Sensory (afferent) neurons:
Carry messages from sense organs to the spinal cord or brain
Motor (efferent) neurons:
Carry messages from the spinal cord or brain to the muscles and glands
Interneurons (association neurons):
Carry messages from one neuron to another chapter 2
Glial Cells
The nervous system also contains glial cells, or glia, which:
Hold neurons in place, provide nourishment, and remove waste
Prevent harmful substances from passing from the bloodstream into the brain
Form the myelin sheath chapter 2
The Neural Impulse (Fig. 2-2) chapter 2
The Synapse chapter 2
Major Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine
Dopamine
Serotonin
Norepinephrine
Endorphins chapter 2
Neural Plasticity
The brain has the ability to be changed by experience.
Rosenzweig (1984) chapter 2
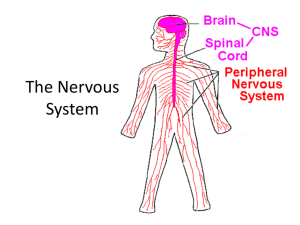
The Central Nervous System
The nervous system has two parts:
The central nervous system (CNS)
• the brain and spinal cord chapter 2
The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
• linking all of the body's parts to the CNS
The Brain chapter 2
Four Lobes of Cerebral Cortex chapter 2
The Limbic System
The structures listed below are often considered to constitute the limbic system. This system is involved in olfaction, emotions, learning, and memory. The limbic system was introduced as a concept by Paul MacLean in 1952 and was long considered the seat of the emotions. Though some of the structures included in this system are in fact involved in some emotional responses, we now know that it does not correspond exactly to any of the multiple emotional systems in the brain.
chapter 2
Hemispheric Specialization
Cerebrum has two separate cerebral hemispheres
Connected by the corpus callosum
Split-brain research chapter 2
Two Cerebral Hemispheres chapter 2
Processing of speech and language Language chapter 2
Tools for Studying the Brain
Microelectrode techniques
Macroelectrode techniques
Structural imaging
Computerized Axial Tomography scanning (CT)
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Functional imaging
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
Magnetic Source Imaging (MSI)
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scanning chapter 2
The Spinal Cord chapter 2
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) contains two types of neurons: afferent neurons efferent neurons chapter 2
The PNS is divided into two subsystems
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system
Autonomic Nervous System chapter 2
The Endocrine System
Endocrine Glands:
Tissues that produce and release hormones
Hormones:
Chemical substances released by glands that help regulate bodily activities chapter 2
Endocrine Glands
Pituitary gland
Pineal gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroids
Pancreas
Adrenal glands
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Gonads chapter 2
Genes, Evolution, and Behavior
Behavioral Genetics
What is the relationship between heredity and behavior?
chapter 2
Evolutionary Psychology
What are the origins of behavior, and what adaptive value do they provide?
Genetics
Genes
Chromosomes
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) chapter 2
Patterns of Inheritance
Dominant genes, recessive genes
Polygenic inheritance
Genotypes and phenotypes chapter 2
Behavior Genetics
A variety of methods are used to study the contribution of genes
Animal behavior genetics
• Strain studies
• Selection studies
Human behavior genetics
• Family studies
• Twin studies
• Adoption studies chapter 2
Average Risk of Schizophrenia Among Biological Relatives of
Average risk of schizophrenia among biological relatives (Fig. 2-19) chapter 2
Social Implications
New challenges have arisen as a result of our better understanding of genes.
chapter 2
Modern prenatal screening
Over-simplified reporting of genetic technologies in mass media
Evolutionary Psychology
Examining adaptive value of behaviors from an evolutionary perspective
Common applications
Language
Mate selection
Criticisms chapter 2