Mitosis Review Powerpoint
advertisement

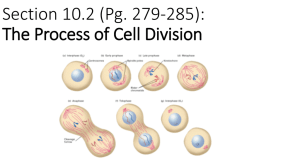
MITOSIS: CELL DIVISION Why do cells divide? Growth Repair Replace dead cells What cells divide often? Skin Stomach lining Red Blood cells Embryo Plant roots Hair Nails What cells rarely/never divide? Nervous System Liver Why do we age? Eventually cells stop being replaced “Apoptosis” Cell death “We die because out cells die.” William R. Clark “C” Terms Chromosomes Long threads of genetic material Found in nucleus Chromatid One side of a duplicated chromosome “C” Terms Centromere Structures that hold sister chromatids together NOTE 2 sister chromatids = 1 duplicated chromosome “C” Terms Chromatin DNA tnagled around a histone (a protein) Condensed chromatin = chromosome Huh? C. Duplicated chromosome A. DNA B. histone Chromatin “C” Terms Centrioles Small protein bodies In cytoplasm Animal cells only Cell Division in a Nutshell Before: Chromosome duplicates = 2 sister chromatids During: Sister chromatids separate After: 2 “daughter” cells Genetically identical Cell Cycle Mitotic phase 10% Interphase 90% Interphase Made up of three phases: G1, S, G2 What happens? Things necessary to divide Interphase G1 Phase Cell Growth 8-10 hours S Phase DNA replication Chromosome replication 6-8 hours G2 Phase More Cell Growth Centriole replication 4-6 hours Mitotic Phase Mitosis Division of nucleus (chromosomes) Occurs after interphase Cytokinesis Division of cytoplasm Creates 2 daughter cells Occurs at the end of mitosis Mitosis Phases Interphase Prophase Prometaphase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Task Draw a diagram of mitosis Label 6 phases & give each a short description Interphase “Resting Phase” Cell NOT dividing Precedes mitosis Prepares cell for division How? Early Prophase Centrioles: Make spindle fibres Move towards opposite plates Chromosomes now visible Late Prophase Centrioles reach poles Nuclear membrane (envelope) & nucleolus start to disappear Metaphase Spindle fibres attach to centromeres Duplicate chromosomes line up at equator Guided by spindle fibers Anaphase Spindle fibers retract Pull sister chromatids apart Towards opposite polls Telophase Chromatin reappears Nuclear membrane & nucleolus reappear Cytokinesis occurs Result Two daughter cells What phases do you see? A C B D Cytokinesis Why would it occur differently in animal and plant cells? Plant cells have a rigid cell wall! Cytokinesis Animal Cells Cell membrane pinches inward Creates cleavagefurrow Think: Pull a string around a balloon Plant Cells Cell Plate forms between two new nuclei Becomes cell wall Cytokinesis Cytokinesis Plant vs. Animal – Another Difference? Centrioles not present in plant cells What makes spindle fibers in plant cells? Form from cytoskeleton Concept Map