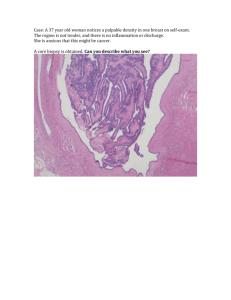
Epithelial and membrane transport
advertisement

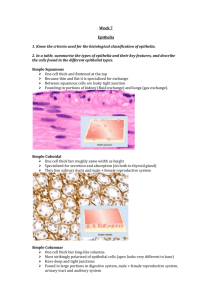
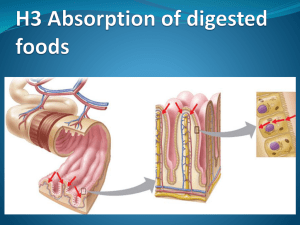
Epithelial and membrane transport G Ogweno Types of epithelial tissues • Surface linning • Glandular • Cell shape: squamaous, cuboidal, columnar • Layers: simple, stratified, pseudostratified • Examples: skin, intestine, respiratory,uroepithelium Epithelial polarity • Apical surface: microvilli absorptive,cilia motile • Lateral junctional complexes • Basal:basal lamina, basement membrane, basal infoldings for ion transport, hemidesmosomes for fixation • Distribution of enzymes, transporters, Antigen detection, signal transduction Epithelial junctional complexesTight • Also called zonula occludens • Integral membrane proteins- occludins, claudins • Determines permeability characteristics& cell migration • On apical side-continuous belt, divides into apical and basal domains (fencing) • Prevents Para cellular transport and binds cells together; barrier; gating • Common intestinal and skin Epithelial junctions:adhering • • • • Also zonula adherens Belt just below tight junctions Cell-cell contact by CAMs Cytoskeleton-actin Epithelial junctions:Gap • • • • 2 nm gap between adjacent cells Hollow cylindrical structures-connexons Form channels-Interecellular Point of electrical coupling :low -resistance communication, • may be gated-responsive to physiological stimuli • Nexus in smooth muscles;intercalated disc in cardiac muscles Epithelial junctions:desmosomes • Also called spot, macula adherens, button like between adjacent cells • Intermediate filaments-tonofilaments cytoskeleton of adjacent cells • Gap between of 25-30 nm • Provide structural support to physical stress • Prevent shearing forces e.g epidermis Functions of epithelia • • • • Body barrier e.g microorganisms Prevents water loss/dessication Maintenance of internal environment Regulated vectorial transport Types of capillaries • Type 1: continuous-10-15 nm clefts, much tighter in BBB.found pulmonary,brain,testis • Type 2:fenestrated-thin fenestrated.small intestine, exocrine glands,muscles • Type 3: discontinuous-large gaps, can pass cells, sinusoids e.g liver, bone marrow Epithelial vectorial transport • • • • • • • • • • Function of membrane transport protein polarity Apical- absorption or reabsorption; basolateral-secretion Create ionic gradients Both Transcellular(tight) and paracellular (leaky) transport depending on epithelium Are specific for ions-cations vs anions Transport proteins(channels,carriers&pumps) and kekyness determine direction and type of solutes transport Active transport is transcellular while paracelluler is passive Na+/K+ ATPase exclusively basolateral except in choroid plexus apical K+ through channels recycled Inwardly directed Na+ gradient driving force for apical Na+ channels, secondary active transport for other solutes e.g Na+glucose.Na-H+ exchanger Epithelial membrane solute transporters • Placed either on apical or basolateral membranes control absorption or secretion • Na+: basolateral Na+/K+ ATPase pumps out, creates inward gradient,Cl- paracellular • K+: apical channel eflux;basal Na+/K+ • Glucose:apical secondary active transport(SGLT), basal carrier exit(Glut) • Cl-: secondary active uptake basal Na+/K+/Clcontransporter, passive cl-apical exit through channels e.g CFTR;Na+ paracellularly into lumen Transepithelial water movement • Passive, driven by osmotic pressure gradient • Transepithelial(transcelluler): aquaporins • Paracelluler(junctional):follows NaCl gradient(secretion/reabsorption)& solvent drag • Some eipthelia have high solute-transport and low water permeability • Hydraulic conductivity varies • Isotonic movement occurs due to constitutive expression of aquaporins and localized interepithelial osmotic gradient Regulation of epithelial transport • Controlled by Neural/hormonal signals • Neural:enteric&sympathetic • Hormonal: Aldosterone • Paracrine:gastric histamine for HCl Mechanisms: 1. Gene expression:Synthesis/degradation of specific transporters 2. Change in activity of membrane transporters/post-translational modification of pre-existing transport proteins(channel gating) 3. Recruitment/Retrieval of transporters from membrane by endocytosis or insertion into membrane from intracelluler vesicular pool 4. Change in paracellular(leak) pathway 5. Luminal supply of transported species