DNA vs. RNA
advertisement
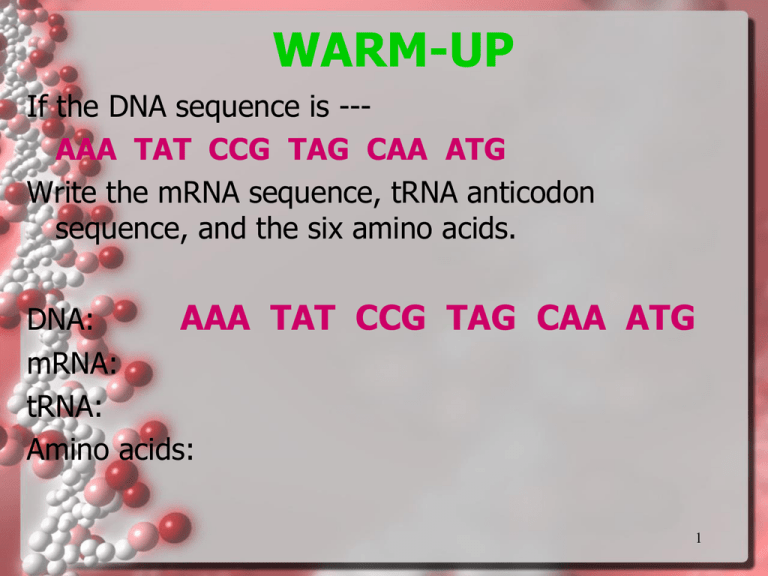
WARM-UP If the DNA sequence is --AAA TAT CCG TAG CAA ATG Write the mRNA sequence, tRNA anticodon sequence, and the six amino acids. DNA: AAA TAT CCG TAG CAA ATG mRNA: tRNA: Amino acids: 1 Review Chromosomes v. Genes v. DNA • Chromosomes contain genetic information • Genes are sections of chromosomes • Segments of genes are called DNA DNA and RNA are examples of what major macromolecule? Nucleic Acids What are the other 3 macromolecules? -Lipids -Carbohydrates -Proteins 3 What does DNA stand for? Deoxy-ribo-nucleic acid • DNA is often called the blueprint of life • DNA contains the instructions for what traits (eye/hair color, etc.) are inherited from generation to generation • Where is it found? Nucleus 4 DNA Structure • Composed of sub-units called Nucleotides • Nucleotides can be broken down into 3 parts 1. Phosphate Group 2. Deoxyribose Sugar (5 carbon sugar) 3. Nitrogenous Base • Cytosine (C) • Guanine (G) • Adenine (A) • Thymine (T) 1. Phosphate 3. Nitrogenous Base 2. Deoxyribose Sugar (A, T, G, C) 5 The Shape of DNA • The basic shape is like a twisted ladder or zipper. – This is called a double helix, which means it is double stranded “Rungs of ladder” Nitrogenous Base (C,G, A or T) “Legs of ladder” Phosphate & Sugar Backbone 6 One Strand of DNA • One strand of DNA is a polymer of nucleotides. • One strand of DNA has many millions of nucleotides. nucleotide phosphate deoxyribose bases 7 Nucleotides O O -P O O O O -P O O One deoxyribose together with its phosphate and base make a nucleotide. O O -P O O Phosphate Nitrogenous base O C C C O Deoxyribose 8 5 DNA O 3 3 P 5 O O C G 1 P 5 3 2 4 4 P 5 P 2 3 1 O T A 3 O 3 5 O 5 P P9 Double Stranded DNA • Remember, DNA has 2 strands that fit together like a zipper. • The teeth are the nitrogenous bases but why do they stick together? 10 Chargaff’s Rule • They stick together because of hydrogen bonds of the nitrogenous bases • Adenine always pairs with Thymine –A T • Cytosine always pairs with Guanine T A –C G G C 11 DNA by the Numbers • Each cell has about 2 m of DNA. • The average human has 75 trillion cells. • The average human has enough DNA to go from the earth to the sun more than 400 times. • DNA has a diameter of only 0.000000002 m. The earth is 150 billion m or 93 million miles from the sun. 12 What about RNA? Stands for: Ribo-nucleic acid • Structure similar to DNA but different – Nucleotides divided into 3 parts 1. Phosphate Group 2. Ribose Sugar 3. Nitrogenous Base – – – – Adenine (A) Uracil (U) (Replaces Thymine) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) – Single stranded 13 How are DNA and RNA related? • DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis – The reading and expression of genes is from DNA to RNA to protein – DNA -> RNA -> Protein = Central Dogma of Biology 14 DNA Structure • Rosalind Franklin took diffraction x-ray photographs of DNA crystals • In the 1950’s, Watson & Crick built the first model of DNA using Franklin’s x-rays 15 DNA Nucleotide Phosphate Group O O=P-O O 5 CH2 O N C1 C4 Sugar (deoxyribose) C3 C2 Nitrogenous base (A, G, C, or T) 16 Pentose Sugar • Carbons are numbered clockwise 1’ to 5’ 5 CH2 O C1 C4 Sugar (deoxyribose) C3 C2 17 Antiparallel Strands • One strand of DNA goes from 5’ to 3’ (sugars) • The other strand is opposite in direction going 3’ to 5’ (sugars) 18 Nitrogenous Bases • Double ring PURINES Adenine (A) Guanine (G) A or G • Single ring PYRIMIDINES Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) T or C 19 Base-Pairings • Purines only pair with Pyrimidines • Three hydrogen bonds required to bond Guanine & Cytosine 3 H-bonds G C 20 •Two hydrogen bonds are required to bond Adenine & Thymine T A 21 DNA Replication 22 3 Questions about DNA Replication 1. What is DNA Replication? the process where DNA make a copy of itself 2. Why does DNA need to copy? Simple: Cells divide for an organism to grow or reproduce, every new cell needs a copy of its DNA or instructions to know how to be a cell. 23 3 Questions about DNA Replication 3. When does DNA replication occur? – It occurs right before the cell divides – During the S Phase of interphase of the cell cycle 24 Synthesis Phase (S phase) • S Phase during interphase of the cell cycle S DNA replication takes place in the S phase. phase G1 interphase G2 Mitosis -prophase -metaphase -anaphase -telophase 25 DNA Replication is Semiconservative • The two strands of the parental molecule separate, and each acts as a template for a new complementary strand • In other words: when DNA makes a copy, one half of the OLD strand is always kept in the NEW strand. – This helps reduce the number of COPY errors. • New DNA consists of 1 PARENTAL (original) and 1 NEW strand of DNA DNA Template Parental DNA New DNA 26 Semiconservative Replication 27 Question: • What would be the complementary DNA strand for the following DNA sequence? DNA 5’-CGTATG-3’ 28 Answer: DNA 5’-GCGTATG-3’ DNA 3’-CGCATAC-5’ 29 1. What is the complimentary mRNA sequence to DNA sequence A-T-T-G-C-A? A. T-A-A-C-G-T C. U-A-A-C-G-T B. U-A-A-C-G-U D. T-A-A-G-C-U 2. What causes the two sides of the double helix of DNA to stay joined together? A. joining of phosphate molecules C. joining of base pairs B. joining of sugar molecules D. joining of RNA 3. What the three main parts of a nucleotide of DNA? (Choose all that Apply) A. phosphate group C. deoxyribose sugar B. ribose sugar D. nitrogenous base 4. The process whereby DNA unzips and makes a strand of mRNA is called? A. replication C. translation B. transcription D. complementation 5. When does DNA replication occur? A. During transcription C. During translation B. During mitosis D. During the S phase of interphase 6. Determine the amino acids sequence from this mRNA sequence: AUG CCC GGA UUA UAG (Use amino acid chart on board) A. Met Pro Gly Leu Stop C. Met Leu Pro Gly Stop 31 B. Stop Leu Pro Gly Met D. Met Pro Cys Gly Stop Lesson Closure 3 things you learned in class today 2 questions you have about the lesson 1 real-life connection MIND MAPS Create a map using all of the following terms Be sure to link them together DNA Nucleotide Transcription Translation Uracil Ribose sugar Amino acid Nucleus Double Helix RNA Thymine chromosome nucleic acid deoxyribose sugar mRNA Unzipping Protein 33






