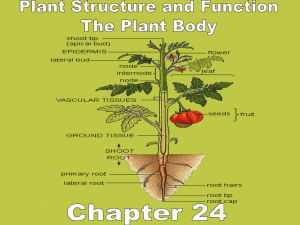
PowerPoint Presentation - Modeling the Organism: The Cell in
advertisement
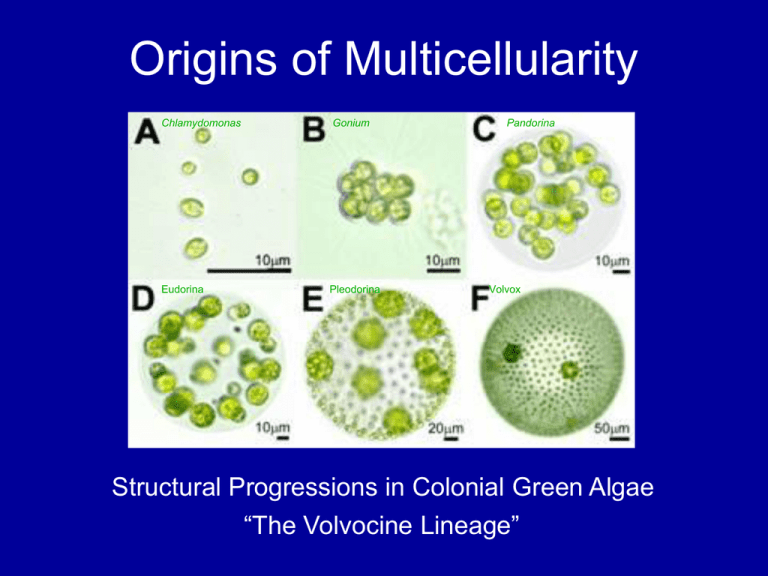
Origins of Multicellularity Chlamydomonas Gonium Eudorina Pleodorina Pandorina Volvox Structural Progressions in Colonial Green Algae “The Volvocine Lineage” Alternation of Generations Evolutionary Emphasis on the Diploid Soma mitosis Diploid (2n) Phase Fertilization 2n sori Meiosis Ferns Haploid (n) Phase 2n n Mosses mitosis n Arabidopsis thaliana The Thale or Mouse-Eared Cress The Arabidopsis Life Cycle Embryo (2n) Ovule (n) Pollen (n) flowering rosette growth Nuclear Genome 5 chromosomes 125Mb (10x yeast) 14% transposable elements 25,500 genes (4.5x yeast) 11,000 gene families +79 (chloroplast) +58 (mitochondrion) COGs in the Genomics Wheel ca 2000 Transformation by Agrobacterium the Crown Gall Bacterium imbibition, vernalization -> radicle outgrowth Germination Shoot apex hypocotyl (note apical Photomorphogenesis (hook opening, cotyledon greening) Root hairs Root apex elongation hook) Photomorphogenesis Cryptochromes and Phytochromes Three Primary Tissues •Dermal Epidermis •Ground General Tissue •Vascular Xylem Phloem Enhancer trap GUS construct Topless-1 embryos make an apical root Plant Embryogenesis Shaping the Plant Cell Cellulose Synthase Complexes Microtubules Overlay Meristems Tunica L3 Radial Zones Layers Organization of Shoot Meristems L1/L2/L3 chimeras Embryo/Seedling Mutants Apical-basal mutations (b-e) Radial symmetry mutations (f,g) Organogenesis mutations (h-j) Axial Mutants Cross section of root Root Structure QuickTime™ and a Video decompressor are needed to see this picture. video Root Hairs microtubules gl1 ttg No Leaf Hairs WT But Lots of Roots! Epidermal Fates WT has 8 files of root hairs GL2::GUS expressed in N cells Root Hair Specification ( ) Day length and Temperature FL-T leaf phloem apex Florigen is the protein encoded by the FL-T locus; it is produced in the leaves and moves through the plant to the meristems to transmits the flowering response through the plant The Flowering Stimulus FL-C Conversion to a Floral Meristem Vegetative meristem Floral meristem identity genes (Lfy, Ap1, Cal; Tfl) Floral meristem Mapping genes (define boundaries) (Su) Floral organ identity (homeotic) genes (whorl identity) Sepals (Ap2) Petals (Ap2, Ap3, Pi) Stamens (Ap3, Pi, Ag) Carpels (Ag) stigma, carpels The ABC Model of Floral Whorl Identity B (Ap3, Pi) A (Ap2) Sepals ap2 C (Ag) Petals pi Stamens Carpels ag A Few Questions for Thought •Explain the evolutionary origins of multicellular organisms. What are the benefits and costs of multicellularity? •Compare and contrast plant and animal (drawing upon your own general knowledge) body plans. •Describe how a new plant is formed during development (from fertilization through germination). •What are meristems, and why are they important in plant biology? •What are the three primary tissues of the plant body? •What is the difference between a shoot and a root meristem? Between a vegetative and a floral meristem? •How are organ identities in determined in the flower? What are the role(s) of homeotic genes in this process?