The Addicted Synapse
advertisement
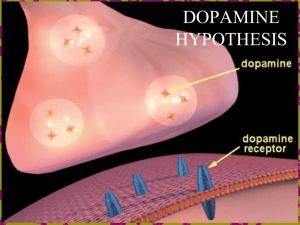
The Addicted Synapse Katie Malanson Objectives, Part 2 • Name the brain structures of the reward pathway. • Describe the connections between the brain structures in the reward pathway • Describe how drugs of abuse alter synaptic transmission. • Describe the molecular biology behind tolerance, dependence, and relapse. • Explain the benefit derived from increased expression of dopamine D2 receptors. Addiction hijacks Natural Reward Pathways Self Stimulation (Percent) Addiction hijacks Natural Reward Pathways Routtenberg 1978 From Mice to Men: Reward Pathway in Humans PFC – Prefrontal Cortex NAc – Nucleus Accumbens VTA – Ventral Tegmental Area PFC NAc VTA PFC NAc VTA Cocaine activates the Reward Pathway Cocaine activates the Reward Pathway The Amygdala is important for the emotional aspects of addiction The Synapse Presynaptic Neuron Ca2+ Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels Postsynaptic Neuron AP Slowly acting receptors – Ion channel is separate from receptor Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ion Channel Ca2+ Neurotransmitter Transporters Neurotransmitter Slow excitation or Slow inhibition Ca2+ Fast acting receptors are ion channels Cl- Ca2+ Cl- Fast excitation Fast inhibition The Synapse Presynaptic Neuron Ca2+ Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels Postsynaptic Neuron AP Slowly acting receptors – Ion channel is separate from receptor Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ion Channel Ca2+ Neurotransmitter Transporters Neurotransmitter Slow excitation or Slow Inhibition Ca2+ Fast acting receptors are ion channels Cl- Ca2+ Cl- Fast excitation Fast inhibition The Dopamine Synapse Presynaptic Neuron Ca2+ AP Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Postsynaptic Neuron Dopamine only has slowly acting receptors with ion channel separate from receptor Ion Channel Dopamine Dopamine Transporters Slow excitation or Slow Inhibition Drugs of abuse alter dopamine signaling between the VTA and the NAc Prefrontal Cortex VTA NAc Dopamine Glutamate Amygdala Effect of Cocaine VTA Presynaptic Neuron 2+ Ca AP Voltage-Gated Ca2+ Channels Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ NAc Postsynaptic Neuron Dopamine only has slowly acting receptors with ion channel separate from receptor Ion Channel Cocaine X Dopamine Transporters Dopamine Slow excitation or Slow Inhibition 1. Cocaine blocks the dopamine transporter. 2. More dopamine is available at the synapse. 3. Postsynaptic signaling through the dopamine receptor is increased. Drugs of abuse alter dopamine signaling between the VTA and the NAc Nicotine Prefrontal Cortex Dopamine VTA NAc Dopamine Glutamate Amygdala Drugs of abuse alter dopamine signaling between the VTA and the NAc Ethanol Prefrontal Cortex Inhibitory neuron Dopamine VTA NAc Dopamine Drugs of abuse alter dopamine signaling between the VTA and the NAc Heroin & other opiates Prefrontal Cortex Inhibitory neuron Dopamine VTA NAc Opiate receptors Heroin & other opiates Conclusion: Drugs of abuse increase dopamine signaling between the VTA and the NAc. Tolerance and Dependence VTA Presynaptic Neuron Ca2+ NAc Postsynaptic Neuron AP Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ca2+ Ion Channel Dopamine Transporters 1. 2. 3. 4. Dopamine Receptors are activated Signaling increases CREB transcription factor is activated Gene transcription increases - Dynorphin Tolerance and Dependence VTA Dynorphin NAc Dopamine The increased Dynorphin is released by the NAc It acts on the VTA to reduce Dopamine release Tolerance, Dependence and Relapse: Drugs of Abuse Alter Gene Expression Drugs of abuse increase dopamine release Transcription factors increase When CREB goes up When Delta FosB goes up Dynorphin decreases Dopamine release from the VTA Cdk5 alters the structure of the NAc neuron Drugs of Abuse alter Synaptic Structure: Potential for Relapse Tolerance, Dependence and Relapse: Drugs of Abuse Alter Gene Expression When CREB goes up When Delta FosB goes up Dynorphin decreases dopamine release from the VTA Cdk5 alters the structure of the NAc neuron: Dopamine signaling increases FAST BUT TRANSIENT SLOW AND SUSTAINED Tolerance, Dependence and Relapse: Drugs of Abuse Alter Gene Expression When CREB goes up When Delta FosB goes up Dynorphin decreases dopamine release from the VTA Cdk5 alters the structure of the NAc neuron: Dopamine signaling increases FAST SLOW AND SUSTAINED TOLERANCE and DEPENDENCE SENSITIVITY and RELAPSE Dopamine Receptors are Not Created Equal Dopamine D1 Receptors D2 Receptors Excitatory effects Inhibitory effects Stimulate Addiction Inhibit Addiction Tolerance and Relapse VTA Presynaptic Neuron Ca2+ NAc Postsynaptic Neuron AP Ca2+ Ca2+ D1 and D2 Dopamine receptors Ca2+ Ca2+ Dopamine Transporters D2 Ion Channel D1 Ion Channel Stimulates addiction Inhibits addiction “Addictive Personality”: Levels of Dopamine D2 Receptor predict how rats will self administer drugs Low Impulsive Area 1 High Impulsive Highly impulsive rats have lower levels of D2 receptor. Area 2 Dalley et al 2007 “Addictive Personality”: Levels of Dopamine D2 Receptor predict how rats will self administer drugs Low Impulsive High Impulsive Area 1 Area 1 Area 2 Area 2 Dalley et al 2007 Conclusion: Lower levels of D2 receptors are associated with impulsive, addictive behaviors DA Receptor Levels Social Stress decreases Dopamine D2 receptors When monkeys are raised together, subordinate monkeys have fewer D2 receptors. Morgan et al 2002 Social Stress decreases Dopamine D2 receptors Dominant Subordinate Cocaine The subordinate monkeys self administered more drugs than their dominant peers. Morgan et al 2002 Drug use also alters Dopamine D2 Receptor Expression in Humans Cocaine Abusers have lower levels of Dopamine D2 receptor. Addiction as a Disease: Drug use inhibits brain activity like heart disease inhibits heart activity. Other influences on the NAc Cortical development Affects the NAc Prefrontal Cortex Hippocampus Learning affects the NAc VTA NAc Amygdala Emotion affects the NAc Maturation of PFC Loss of Grey Matter Due to Synaptic Pruning • The PFC does not reach maturity until mid 20s. • Elimination extra synapses • Myelination of remaining synapses • Drugs of abuse taken during maturation of brain drastically change the maturation process, having long lasting effects. MRI Study of 13 children scanned every 2 years Gogtay et al 2004 Objectives, Part 2 • Name the brain structures of the reward pathway. • Describe the connections between the brain structures in the reward pathway • Describe how drugs of abuse alter synaptic transmission. • Describe the molecular biology behind tolerance, dependence, and relapse. • Explain the benefit derived from increased expression of dopamine D2 receptors.