Topic 3: The Evolution of Life on Earth

Life on Earth
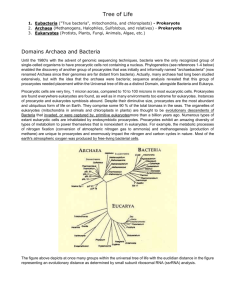
Topic 7: Procaryotic Organisms
Part of the Evolution of Australian Biota Module
Biology in Focus, Preliminary Course
Glenda Childrawi and Stephanie Hollis
DOT Point
Describe technological advances that have increased knowledge of procaryotic organisms
Describe the main features of the environment of an organism from one of the following groups and identify its role in that environment
Archaea
Bacteria uhh.hawaii.edu
Introduction
Procaryotes are singlecelled organisms. They are the smallest, simplest organisms. They are abundant in the air, water, soil, and on most objects.
It’s believed that live as we know it has evolved from these organisms bio.m2osw.com
Technology
Structural methods of classifying procaryotic organisms in the past have been very valuable however, these methods did not always reflect the organisms’ possible evolution. textbookofbacteriology.net
Technology
New technological advances have changed the way procaryotic organisms are now classified, and increased our understanding and knowledge of biological structures, chemical composition and biochemical (genetic) characteristics.
uhsecho.com
Technology
The light microscope has allowed us to identify cells as being unicellular and small with a cell membrane and cell wall. The electron microscope allowed us to see fine details including organelles and DNA.
microscope-microscope.org
Technology
Chemical analysis has allowed us to determine the chemical composition of cytoplasm and membranes. Genetic sequencing has allowed us to determine the number of chromosomes and further explore genetic material.
nhchemicalanalysis.com
Technology
These developments , due to technology, in our knowledge of present day organisms allows for a better understanding of the origins of life and the processes involved in the evolution of living things. nrc-cnrc.gc.ca
Technology
For example, we now know that bacteria have evolved along two main evolutionary lines, classified as kingdoms-Bacteria and Archaea wired.com
Bacteria
Bacteria are an enormously diverse group that share many environments with, or live on and in humans and other animals and plants . These are habitats of moderate temperature with water freely available, low in salt and where sunlight and organic compounds are plentiful.
answersingenesis.org
Bacteria
Oxygen is not so important since many of the bacteria have powerful fermentation capabilities, producing ATP
(energy) under anerobic conditions. The group bacteria contains almost every variety and combination of biochemical energy extraction and carbon-fixation thought to be possible.
science.howstuffworks.com
Bacteria
However, this group also contains some of the most specialised and sensitive cellular organisms known. These are often pathogens that have become highly adapted to particular environments within animal or plant hosts. herryyudha.com
Bacteria
Cyanobacteria resemble algae and plants in that they contain chlorophyll and generate oxygen during photosynthesis. They occur as individual cells or as filamentous aggregates of many individual cells joined end to end. serc.carleton.edu
Bacteria
Cyanobacteria contains pigment called phycobilins which give them a blue-green appearance. They often form dense mats of growth in shallow marine or estuarine environments.
futurity.org
Scientists believe this bacteria is responsible for the oxygen in our atmosphere.
Bacteria
Endospore-forming bacteria are the most resistant form of life known. Endospores form inside the mother cell rather than budding from it. They form under conditions of nutrient depletion or as a result of other environmental signals forewarning difficult times ahead for the bacterium.
www2.raritanval.edu
Bacteria
Endospores appear to have evolved as a resistant, virtually metabolically inactive cell type, increasing the probability of survival under extreme conditions such as cold, heat or desiccation. kswfoodworld.wordpress.com
Bacteria
Bacterial endospores are remarkably resistant to high temperature, high radiation and many chemicals which would rapidly destroy all other living cells. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endospore
Clostridium tetani lives in anerobic environments
Archaea
Archaea are still commonly referred to as archaebacteria, however, this term has been discarded as they are not bacteria.
Archaea are a more specialised group than bacteria and its members are therefore more restricted to the environments they inhabit. microbiologyonline.org.uk
Archaea
Archaea are single-celled, microscopic organisms which do not contain any membrane bound organelles. They do not require sunlight for photosynthesis, nor do they require oxygen. scienceline.org
Archaea
Most live in extreme environments and are called extremophiles , however, some still live in ordinary temperatures, salinities and acid levels.
Thermophiles live in water temperatures greater than 50C
Halophiles live in hypersaline environments greater than 9% and up to 32% salt concentration
Acidophiles live in acidic environments lower than pH 2 and as low as pH 0.9
green-buzz.net
Archaea
By studying these organisms that presently live in extreme conditions on Earth, we are able to infer what the organisms were like that survived during the extreme conditions of early Earth. news.sciencemag.org
Homework
-Students to complete DOT Point 3.5
**Hand out Holiday Research Activity and discuss** green-buzz.net