2014 John Barnard Slides
advertisement

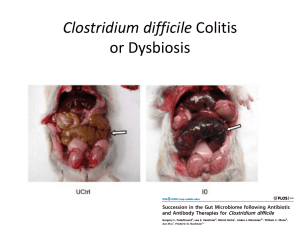
Emerging Trends and Provocative Findings in Basic Science NASPGHAN 2014 John Barnard, MD DISCLOSURE No disclosures relevant to this presentation. • Big Data • Misconduct • CRISPR-Cas9 • Liver stem cells • Microbiome • Genomics Big Data Big data is an allencompassing term for any collection of data sets so large and complex that it becomes difficult to process using traditional data processing applications. volume variety velocity variability PubMed Citations with “Big Data” in Title 200 150 100 50 0 Scholarship in theHepatol Networked Nat Rev Gastroenterol 6:386, 2014 World: Big Data, Little Data, No Data Christine L. Borgman, University of California, Los Angeles Oliver Smithies Lecture, Balliol College, Oxford. Oxford, UK. Jun. 2013. Why Hasn’t ‘Big Data’ Saved Democracy? Large clinical data sets Payer data sets Microbiome data* Image data Will Big Data Legitimize the Field of Motility? EHR data J Fuzzy Science Genomic data*2014? Sensor data Proteomic data By Fred Barbash July 29, 2014 CRISPR-Cas9: Gene Editing • Bacterial immunity against foreign DNA • CRISPRs clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) “RNA guide” • Cas9 • Endonuclease “molecular scissors” CRISPR-Cas9 system is “simple and efficient” And many others “Genome editing has never been easier” Netherlands 2 children with DF508 CFTR mutation Summary The CRISPR/Cas9 system edits the genome in intestinal stem cells organoids and restores CFTR function. Background and Methods adult mice on NTBC Results Results Summary First proof of principle that CRISPR-Cas corrects a genetic disease in vivo Only 1/250 hepatocytes corrected, aided by positive selection by NTBC removal. • One cell embryo injection • Modification of two genes (Rag1 and PPARg) History’s path is unchartable when it is not yet past but present, when we are still standing in the middle of it. Jennifer Couzin-Frankel Science 342:1432, 2013 Implications of CRISPER-Cas9 • Genome editing is easy? • Promising • Correction of single gene disorders is genuinely possible A Comprehensive Review Cell 157, 1324-1338, 2014 Background • Hippo/YAP signaling pathway – highly conserved, complex signaling pathway – brake on cell proliferation/organ size – tumor suppressor signaling – important in regulation of liver size Background YAP ductal cell YAP HIPPO hepatocytes Oval cells (Progenitor cells) AAV-YAP Implications Sci Trans Med 2014; 6:245, 1-21. J Clin Invest 2014 124:3617 Background and Methods • RISK study (CCFA) • Large inception pediatric IBD cohort – N = 1656, over 28 sites – Treatment naïve; Prospective – Ileal host gene expression, microbial abundance and deep phenotyping in 359 subjects (controls, ileocolonic, colon-only and UC) Results Ileocolonic Crohn’s Colon only Crohn’s UC 1281 ileal host genes 1.5 X vs controls 1055 ileal host genes; 82% similar to ileocolonic 232 ileal host genes; 18% similar to ileocolonic Results NL ileum UC colon only Crohn’s ileocolonic Crohn’s Host gene expression and microbial shifts in ileal IBD. Summary • Ileal host gene expression is remarkably similar in patients with ileocolonic Crohn’s disease and colon-only disease • Host gene and microbe profiles identify ileum as primary inductive site for all forms of Crohn’s disease Background and Methods • RISK study, CCFA • N = 447 Crohn’s & 221 controls (28 sites) – Treatment naïve – Prospective • Mucosa-associated and lumenal microbiota 16S rRNA sequencing along with deep phenotyping Results Most prominent microbiome changes are in tissue associated microbiota Antibiotic exposure amplifies dysbiosis Results Of those bacteria increased in Crohn’s – the more dramatic the increase; the higher the PCDAI (and converse) Microbiota Dysbiosis Index (MDI) predicts PCDAI PCDAI Results Sensitivity Biopsy-associated ilieal microbiome is most accurate for disease classification 1 - Specificity Predictive modeling for relapse using microbiome and clinical variables better than clinical variables alone Summary • Microbiome at diagnosis strongly correlates with Crohn’s disease status • Antibiotics aggravate dysbiosis • Mucosa-associated microbiome may be better than lumenal in assessing disease parameters Mice given E coli engineered to produce known anorexogenic lipids Healthy Mice TallyHo Obese Mice Room Source antibiotics biocides Premie Science 2014; 345:1048-1052 Summary • Seven families over 6 weeks – “Home Microbiome Project” – Human and home microbiome (including some pets) • Home microbiome comes from human occupants • Home identifiable knowing human microbiome • Occupant leaving home for even three days begins to redefine home microbiome • … other disturbing observations and implications… Nat Genet 2014; 46:1131-1134 Summary • IBD patients GWAS – 172 with pancreatitis within 3 mos of 6-MP – 2035 IBD no pancreatitis (controls) – 472 IBD on 6-MP – no pancreatitis (replication) • HLA DQA1 HLA DRB1 – Heterozygotes: 9% risk of pancreatitis – Homozygotes: 17% risk of pancreatitis