Macros
advertisement

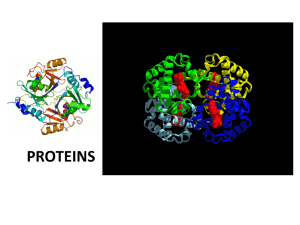
WOW Macromolecules Polymers. • What do all macromolecules have in common? 1. They all contain Carbon 1. Has 4 valence electrons What do all macromolecules have in common? What is a polymer? How are polymers assembled? 2. They are all polymers – A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks called monomers 3. They are all assembled by a Dehydration reaction (Condensation). Dehydration (Condensation) Reaction HO 1 3 2 H Unlinked monomer Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond HO Figure5.2A 1 2 H HO 3 H2O 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer • Polymers are disassembled by – Hydrolysis HO 1 2 3 4 Hydrolysis adds a water molecule, breaking a bond HO Figure 5.2B 1 2 3 (b) Hydrolysis of a polymer H H2O H HO H 1. Carbohydrates- polysaccharide Examples in the cell Starch- plants storage sugar Cellulose plant cell wall Chitinexoskeleton of insects Glycogen- how the body stores sugar Carbohydrates • Monomer = Monosaccharide (simple sugar) • Type of bond = glycosidic linkage • Function: – Storage and structural support 2. Lipids Examples in the cell Fats- lipids in animals Oils – Lipids in plants Phospholipids -make up cell membrane Steroids –Hormones in the cell. Lipids • Monomer = Fatty acid tail Ester linkage • Type of bond = ester linkage • Function: – Energy storage – Protection 3. Proteins • Proteins - more than 50% of dry mass of cells • Functions include: – – – – – Enzymes Structural Storage Transport Hormonal (cellular communication) – Receptor – Contractile (movement) – Defensive Proteins in mouse cells Animation: Protein Functions Proteins Examples in the cell Enzymes- speed up chemical reactions Proteins • Monomer = Amino Acid • Type of bond = Peptide Bond • Function: – Diverse and many LE 5-20a Proteins level of structure 1. Primary Amino end Amino acid subunits Carboxyl end LE 5-20b Proteins level of structure 2. Secondary b pleated sheet Amino acid subunits helix LE 5-20d Proteins level of structure 3. Tertiary Hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals interactions Polypeptide backbone Hydrogen bond Disulfide bridge Ionic bond LE 5-20e Proteins level of structure 4. Quaternary Polypeptide chain b Chains Iron Heme Polypeptide chain Collagen Chains Hemoglobin 4. Nucleic Acids Examples in the cell DNA stores genetic information RNA – Carries genetic code to cell. Nucleic Acids • Monomer = Nucleotide • Type of bond = Covalent and Hydrogen bond between bases • Function: – Store genetic information