Sexual
Asexual
Vocabulary
Reproduction Reproduction
Meiosis
Mitosis
10 pt
10 pt
10 pt
10 pt
10 pt
20 pt
20 pt
20 pt
20 pt
20 pt
30 pt
30 pt
30 pt
30 pt
30 pt
40 pt
40 pt
40 pt
40 pt
40 pt
50 pt
50 pt
50 pt
50 pt
50 pt
Meiosis
___________ are
formed by the
process known
as meiosis?
Gametes
Meiosis
How do the daughter
cells that result from
meiosis compare to
each other?
They are
genetically
different.
Meiosis
What happens to the
chromosome
number as a result
of meiosis?
It is reduced
by half. (50%)
Most animals reproduce
sexually. The egg
and sperm cells
involved in sexual
reproduction are
formed by what
process?
Meiosis
Meiosis
Why is meiosis
important?
The process
produces cells
with half the
normal number
of chromosomes
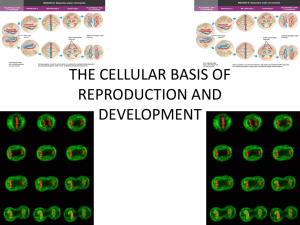
Mitosis
What are the 4
phases of
mitosis in
order?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Mitosis
What is the role of the
spindle in mitosis and
what would happen if the
spindle fibers in the cell
were damaged?
Spindle Fibers help
separate the chromosomes,
and damaging the spindle
fibers in the cell would
prevent the chromosomes
from moving away from the
equator during metaphase
of mitosis.
Mitosis
If organism A has 92
chromosomes in its
body cells, how many
chromosomes will
each daughter cell
have after mitosis?
92
Mitosis
Using the diagram, label the
phases of mitosis.
A. Prophase
B. Telophase
C. Metaphase
E. Anaphase
Mitosis
What structure found
in animal cells but
not plant cells aids
in the process of
mitosis?
Centrioles
Sexual Reproduction
Describe the number of
parents involved for sexual
reproduction and how the
offspring compare to each
other and their parents.
Sexual = 2 parents
Sexual =
different offspring
Sexual Reproduction
What are the
advantages and
disadvantages of sexual
reproduction?
Major Advantage:
Genetic Variation
Disadvantages:
Requires much time
and energy, Have to
find a mate, Have to
create sex cells.
Sexual Reproduction
What is the offspring
referred to when two
different species mate
to produce a unique
offspring?
Hybrid
(Usually these
offspring are
sterile. Ex. A
Mule)
Sexual Reproduction
Explain the difference
between a haploid cell and
a diploid cell.
Haploid: A cell with half
the number of
chromosomes as a diploid
cell. (n)
Diploid: Having two
copies of each
chromosome. (2n)
Sexual Reproduction
How many cell divisions
are present in Meiosis,
and how many
daughtercells does this
process result in?
2: Meiosis I and II
The end result is 4
daughter cells
Asexual Reproduction
Describe the number of
parents involved for
asexual reproduction and
how the offspring compare
to each other and their
parent(s).
Asexual= 1 parent
Asexual =
identical offspring
Asexual Reproduction
What are the
advantages and
disadvantages of
asexual reproduction?
Advantages: Fast, no
mate required, not much
energy involved
Major Disadvantage:
Being identical, especially
if parent cannot adapt or
if parent has genetic
disorder.
Asexual Reproduction
What is fission and
what is an example of
an organism that
reproduces in this
manner?
Fission is when the
parent cell simply
divides into two equal
parts. An example is
bacteria.
Asexual Reproduction
What is fragmentation
and what is an example
of an organism that uses
this process for
reproduction?
When the parent
breaks into different
fragments, which
eventually form new
individuals. An
example is a worm.
Asexual Reproduction
Name the six methods
of asexual
reproduction.
Budding
Fission
Fragmentation
Regeneration
Spores
Vegetative Propagation
Vocabulary
What are Gametes
and how are they
formed?
Gametes: Sex cells
that are formed by
meiosis; both
sperm and eggs
Vocabulary
Define the Cell
Cycle and list
the three stages
involved.
Cell Cycle: A series of
events that cells go
through as they grow
and divide.
3 Stages: Interphase,
Mitosis, and Cytokinesis
Vocabulary
Define Binary Fission
Binary Fission: A form
of asexual reproduction
that prokaryotes use in
which a cell divides into
two cells with identical
genetic information.
What is fertilization
and what type of
reproduction involves
this process?
Fertilization:
The process in
which a sperm and
egg join together to
form a zygote.
Sexual Reproduction
Vocabulary
What is the
definition of Crossing
Over?
The process that can cause
genetic variation in which
homologous chromosomes
exchange DNA.