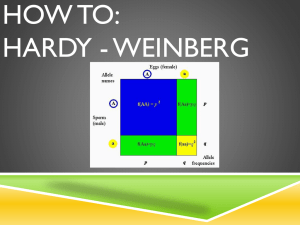
Hot Seat - Inheritance Patterns
Inheritance Patterns
Hot Seat
The phenotype of a guinea pig’s hair color can best be determined by a. Test cross b. Looking at the guinea pig c. Pedigree chart d. Knowing the genotype of the mother pig
If a trait that is visible in the parent organisms is not seen in the offspring but then returns in the F2 generation, the most probable cause is that this trait in question is a. Recessive b. Dominant c. Codominant d. Mutated
Which of the following genotypes below shows a pure dominant genotype?
a. Aa b. aa c. AA d. AB
Genes that are located at the same position on homologous chromosomes are called
• Recessive
• Dominant
• Alleles
• Homozygotes
In garden pea plants, the offspring formed from a cross between two heterozygous tall parents would most likely be
• 25% tall
• 50% tall
• 75% tall
• 100% tall
A pink flower is produced by crossing a plant that has white flowers with a plant that has red flowers. This example most likely shows what condition in genetics?
• Incomplete dominance
• Codominance
• Dominance
• Recessive trait
Who was Gregor Mendel?
• Gregor Mendel was a monk who grew pea plants to study genetics
What is the difference between a dominant allele and a recessive allele?
• Dominant allele – capital letter
• Recessive allele – lowercase letter
The parents of three girls are expecting another child, what are the chances the child will be a boy?
• 25%
• 50%
• 75%
• 100%
If an colorblind man and a woman who is a carrier for colorblindness have a child, what
• percentage of their female children will be colorblind?
0%
• 25%
• 50%
• 100%
Which of the following would represent the sex chromosomes of a normal female?
• XX
• XY
• YY
• XXY
Match the genetic cross of the parents on the left with the genotypes on the right of the offspring most likely to be produced from that cross. You may use an answer choice more than once or not at all.
Genetic Cross Predicted Offspring
1. BB x bb
2. Bb x Bb
3. BB x BB
4. bb x bb
5. Bb x bb a. 25% BB 50% Bb 25% bb b. 100% bb c. 100% Bb d. 50% Bb 50% bb e. 100% BB f. 75% Bb 25% bb
Match the genetic cross of the parents on the left with the phenotypes on the right of the offspring most likely to be produced from that cross. You may use an answer choice more than once or not at all.
Genetic Cross Predicted Offspring
1. TT x tt
2. tt x Tt
3. Tt x Tt
4. TT x TT
5. tt x tt a. 100% short b. 75% tall 25% short c. 100% tall d. 25% tall 75% short e. 50% tall 50% short
What organisms did Mendel use in his famous genetic experiments?
• Mice
• Pea plants
• Rose plants
• Horses
What would be the expected phenotypes of the offspring from the following cross?
(TT x Tt) a. 50% tall, 50% short b. 100% tall c. 100% short d. 75% tall, 25% short
What is the name given to a particular cross used to determine the unknown genotype of an organism?
a. Test cross b. Homologous cross c. Heterozygous cross d. Target cross
In humans, skin color is controlled by at least four genes, this is an example of a. Sex-linked trait b. Recessive trait c. Polygenic trait d. Codminant trait
A female that has an allele for color blindness but not the phenotype for color blindness would be considered a. Color-blind b. A carrier for color blindness c. Homozygous dominant for color blindness d. Homozygous recessive for color blindness
If a human male that is heterozygous for blood type B has a child with a woman who is heterozygous for blood type A, what percent of their children can be expected to have blood type B?
a. 25% b. 50% c. 75% d. 100%
In Mendel’s first experiment, true-breeding plants with contrasting forms for one trait were crossed. Only one form appeared in the hybrid F 1 offspring. What did this show?
• [A] one inheritable unit (element) came from each parent
• [B] one form was dominant over the other
• [C] the parents were not true breeding
• [D] the traits separate during gamete formation
After the first experiment described above, Mendel then self-pollinated the F 1 generation and obtained an
F 2 generation with both parental forms in the ratio of
3 to 1. What additional information did this show?
• [A] the traits separate during gamete formation
• [B] one inherited unit came from each parent
• [C] the parents were not true breeding
• [D] one form was dominant over the other
How would you describe the P and F 1 plants in Mendel’s first experiment in modern terms? The P plants were
• [A] heterozygous as were the F 1 plants
• [B] homozygous as were the F 1 plants
• [C] heterozygous and the F 1 plants were homozygous
• [D] homozygous and the F 1 plants were heterozygous
Today geneticists refer to Mendel’s true-breeding parent pea plants as
• [A] codominant for the traits
• [B] dominant for the traits
• [C] homozygous for the traits
• [D] heterozygous for the traits
An individual’s genotype for an inherited trait is the
• [A] set of alleles carried for the trait
• [B] family pedigree for the trait
• [C] sex of the individual in relation to the trait
• [D] physical appearance caused by the trait
Hybrid means the same as
• [A] homozygous
• [B] dominant
• [C] mutant
• [D] heterozygous
A gene whose effect remains hidden when it is paired with a different gene is called
• [A] mutant
• [B] recessive
• [C] codominant
• [D] dominant
Different genes that affect the same single trait are called
• [A] alleles
• [B] genes
• [C] chromosomes
• [D] hybrids
An individual in which the two alleles of a pair that affect a particular trait are identical is said to be
• [A] heterozygous
• [B] hybrid
• [C] homozygous
• [D] dihybrid
The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait being studied is called that
• [A] phenotype individual’s
• [B] pedigree
• [C] genotype
• [D] variability
Let’s say that “A” represents the gene for a dominant characteristic and “a” its recessive allele. If an Aa individual mates with an aa individual
• [A] all offspring will show recessive trait
• [B] half the offspring will show the dominant trait and half will show the recessive trait
• [C] three quarters of the offspring will show the dominant trait and one quarter will show the recessive trait
• [D] all offspring will show the dominant trait
How many heterozygous offspring would you expect if two parents who were heterozygous for a trait produced an F 1 generation of 40 individuals?
• [A]5
• [B] 10
• [C] 15
• [D] 20
Human blood type is determined by
• [A] polygenic inheritance
• [B] a single gene
• [C] linked gene pairs
• [D] multiple alleles
What is the relationship between two unlike alleles of a pair if they both express their effects on an individual’s phenotype?
• [A] codominance
• [B] linkage
• [C] X-linkage
• [D] dominance
The relationship between the I B allele for Type B blood and the i allele for
Type O blood is
• [A] codominance
• [B] different loci
• [C] dominant/recessive
• [D] unknown
In the AB blood type, the relationship between the I A allele and the I B allele is
• [A] X-linked
• [B] dominant/recessive
• [C] codominance
• [D] unknown
Mr. Sandival has Type B blood. Mrs. Sandival has Type
O blood. They have three children of their own and one adopted child. Owen has Type AB blood, Mary Type O,
Susie Type B, and Carl Type B. Which child is adopted?
• [A] Susie
• [B] Owen
• [C] Mary
• [D] Carl
A homozygous clover with a “v-shaped” leaf pattern is crossed with a homozygous clover that has a large pale center to its leaves. The leaves of every plant in the F1 generation show a vshaped pattern on a large pale center (expressing characteristics of both parents). This is an example of
• [A] segregation
• [B] breeding
• [C] mutation
• [D] codominance
Identification bracelets were accidentally removed from three newborn babies. Blood samples were taken to help the identification procedures. The blood types for the babies and their parents were
• Baby I—Type A Baby II—Type O Baby III—Type AB
• Mr. Black—Type A Mr. Brown—Type AB Mr. White—Type O
• Mrs. Black—Type B Mrs. Brown—Type O Mrs. White—Type O
• Which baby could belong to Mr. and Mrs. Black?
– [A] Baby I
– [B] Baby II
– [C] Baby III
– [D] any of the three
• Which baby could belong to Mr. and Mrs. Brown?
– [A] Baby I
– [B] Baby II
– [C] Baby III
– [D] any of the three
• Which baby could belong to Mr. and Mrs. White?
– [A] Baby I
– [B] Baby II
– [C] Baby III
– [D] any of the three
Use the following information to answer the questions.
• In peas, yellow seed (Y) is dominant to green seed (y), and round seed (R) is dominant to wrinkled (r).
• How many types of gametes could be produced by a YYRr plant?
– [A]1
– [B]2
– [C]3
– [D]4
• How many types of gametes could be produced by a YyRr plant?
– [A]1
– [B]2
– [C]3
– [D]4
• How many types of gametes could be produced by a yyRR plant, the most common garden variety of pea?
– [A]1
– [B]2
– [C]3
– [D]4
If AaBb is crossed with aabb, what proportion of the offspring would be expected to be aabb?
a. 9/16 b. 1/8 c. 1/4 d. 1/16
If the offspring of a cross show a 9/16 to
3/16 to 3/16 to 1/16 ratio (9:3:3:1), the parents of the cross have the genotypes
a. AaBb x AaBb b. AaBb x aaBB c. aaBb x aabb d. aaBb x Aabb
If W = purple flower and w = white, and D = tall plants and d = short plants, a wwDd plant would be
a. purple and tall b. purple and short c. white and tall d. white and short
If aaBb is crossed with AAbb, what proportion of the offspring will be
Aabb?
a. 1/2 b. 3/16 c. 9/16 d. 1/4
In Summer Squash, the allele for white fruit (W) is dominant over that for yellow fruit (w). Similarly, the allele for disk-shaped fruit (D) is dominant over that for sphere-shaped fruit (d). The Punnett square below shows a cross between two squash plant with genotype ‘WwDd’. How many offspring will have yellow disk-shaped fruits?
a. 9 b. 3 c. 2 d. 1
In guinea pigs, the allele for black fur (B) is dominant over that for brown fur
(b). Similarly, the allele for short fur (S) is dominant over that for long fur (s).
The Punnett square below shows a cross between two guinea pigs with the genotype ‘BbSs’. What is the phenotypic outcome of the offspring produced by this cross?
a.
13 Black short fur, 1 Black long fur, 1 Brown short fur, 1 Brown long fur b.
12 Black short fur, 1 Black long fur, 1 Brown short fur, 2 Brown long fur c.
4 Black short fur, 4 Black long fur,
4 Brown short fur, 4 Brown long fur d.
9 Black short fur, 3 Black long fur,
3 Brown short fur, 1 Brown long fur
What phenotypes and phenotypic ratios would you expect in a test cross of a pink flowered and a red flowered snapdragon?
a. 1 white: 2 pink: 1 red b. 3 red: 1 pink c. 1 red : 1 pink d. 2 pink: 1 red e. 3 pink: 1 red
If a pedigree shows that a human trait seems to skip generations the trait is probably
__________.
a. Sex linked b. Polygenic c. Dominant d. Recessive
In this pedigree, the shaded individuals are homozygous recessive. What is the genotype of individual B?
a. heterozygous b. homozygous recessive c. homozygous dominant d. none of the above e. can not tell from the diagram
What type of inheritance mechanism —dominant, recessive, or sex-lined recessive —is shown in the pedigree? Support your answer with evidence.
• Recessive because it skips a generation and is present in both males and females
What type of inheritance mechanism —dominant, recessive, or sex-lined recessive —is shown in the pedigree? Support your answer with evidence.
• Recessive because it skips a generation and is present in both males and females
What type of inheritance mechanism —dominant, recessive, or sex-lined recessive —is shown in the pedigree? Support your answer with evidence.
• Sex linked recessive because only males are affected.
Mothers of affected males are most likely carriers.
What type of inheritance mechanism —dominant, recessive, or sex-lined recessive —is shown in the pedigree? Support your answer with evidence.
• Dominant because the trait is present in each generation.
A female whose father was red-green colorblind marries and normal male whose father was also redgreen colorblind. What is the probability that their son will be colorblind?
a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75%
*Remember red-green colorblindness is a sexlinked recessive trait.
A female whose father was colorblind marries and normal male whose father was also colorblind. What is the probability that their daughter will be colorblind?
a. 0% b. 25% c. 50% d. 75%
*Remember red-green colorblindness is a sexlinked recessive trait.
A woman whose brother has hemophilia is concerned about passing this trait to her offspring. What is the risk that she will have a son with hemophilia?
a. 1/8 b. ¼ c. ½ d. 100%
*Remember hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive trait.
Can a male be a carrier for a sex-linked disease?
a. yes, if the trait is recessive b. yes, if the male's father and mother were carriers c. no, males have only a single copy of sexlinked genes d. no way to predict
Achondroplasia is a dominant inherited disorder that causes a form of dwarfism. The homozygous dominant condition for this allele is lethal. If one parent is an achondroplasic dwarf, and the other parent is of normal height, then what proportion of their a. All children will be expected to be of normal height?
b. ½ c. ¼ d. None e. 3/4
If a woman who is red-green color blind marries a man with normal vision, what phenotypes would you expect their children to have?
a. All their daughters will be carriers and all their sons will be color-blind.
b. All their daughters will be color-blind, but all their sons will have normal vision.
c. All their daughters will have normal vision and will not be carriers, but all their sons will be color-blind.
d. Half of their daughters will be carriers and the other half will be fully normal, half of their sons will be color-blind and the other half will have normal vision.
e. All their children will be color-blind
In 1944 Charlie Chaplin was involved in a legal battle over the paternity of a child born to Joan Berry, a young starlet. The baby was blood type B, the mother A, and
Chaplin O. From what you know about inheritance of blood types, could Chaplin have been the father of the child? (At the time of the trial, blood group evidence was not admissible in California courts. Charlie Chaplin was declared responsible for the child's support).
a. If Chaplin's blood was B, then he must be the father.
b. No, he could not possibly have fathered the child.
c. Yes he could of fathered the child.
d. Perhaps, these results are inconclusive.