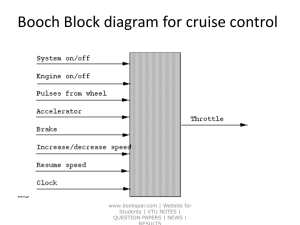
turbines ppt
advertisement

www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 1 ‘Turbo Machine’ is defined as a device that extracts energy from a continuously flowing fluid by the dynamic action of one or more rotating elements . The prefix ‘turbo’ is a Latin word meaning ‘spin’ or ‘whirl’ implying that turbo machines rotate in some way. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 2 Types of Turbines 1. 2. 3. Steam Turbines Gas Turbines (Combustion Turbines) Water (Hydraulic) Turbines www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 3 Steam Turbines A steam turbine is mainly used as an ideal prime mover in which heat energy is transformed into mechanical energy in the form of rotary motion. A steam turbine is used in 1. 2. 3. Electric power generation in thermal power plants. Steam power plants. To propel the ships, submarines. In steam turbines, the heat energy of the steam is first converted into kinetic (velocity) energy which in turn is transformed into mechanical energy of rotation and then drives the generator for the power generation. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 4 Based on action of steam or type of expansion: 1. 2. 3. Impulse or velocity or De Laval turbine Reaction or pressure or Parson’s turbine Combination turbine Based on number of stages: 1. Single stage turbine 2. Multi-stage turbine Based on type of steam flow: 1. Axial flow turbine 2. Radial flow turbine www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 5 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 6 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 7 . The steam is made to fall in its pressure by expanding in a nozzle. Due to this fall in pressure, a certain amount of heat energy is converted into kinetic energy, which sets the steam to flow with a greater velocity. The rapidly moving particles of the steam enter the rotating part of the turbine, where it undergoes a change in the direction of motion, which gives rise to a change of momentum and therefore a force. This constitutes the driving force of the turbine. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 8 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 9 Impulse Turbine) Turbines (De Laval In this type of turbine, steam is initially expanded in a nozzle from high pressure to low pressure. High velocity jet of steam coming out of the nozzle is made to glide over a curved vane, called ‘Blade’. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 10 The jet of steam gliding over the blade gets deflected very closely to surface. This causes the particles of steam to suffer a change in the direction of motion, which gives rise to a change of momentum and therefore a force, which will be centrifugal in nature. Resultant of all these centrifugal forces acting on the entire curved surface of the blade causes it to move. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 11 Q VH NOZZLE PH HIGH PRESSURE STEAM A EXHAUST STEAM R VL P PL C Velocity Variation Pressure Variation B TURBINE SHAFT MOVING BLADES Schematic of Impulse Turbine Nozzle Rotor Blades Pressure-Velocity diagram in Impulse Turbine www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 12 Principle of working In this type of turbine, the high pressure steam does not initially expand in the nozzle as in the case of impulse turbine, but instead directly passes onto the moving blades. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 13 Blade shapes of reaction turbines are designed in such a way that the steam flowing between the blades will be subjected to the nozzle effect. Hence, the pressure of the steam drops continuously as it flows over the blades causing, simultaneous increase in the velocity of the steam. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 14 Reaction force: is due to the change in momentum relative velocity of the steam while passing over the blade passage. Centrifugal force: is the force acting on the blade due to change in radius of steam entering and leaving the turbine. Resultant force: is the resultant of Reaction force and Centrifugal force. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 15 Fixed Blade Moving Blade www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 16 Difference between Impulse & Reaction Turbines Impulse Turbine Reaction Turbine The steam expands (pressure drops) completely in nozzles or in the fixed blades The blades have symmetrical profile of uniform section The steam pressure while passing over the blades remains constant Because of large initial pressure drop, the steam and turbine speeds are very The steam expands both in the fixed and moving blades continuously as it flows over them The blades have converging (aerofoil) profile The steam pressure while passing over the blades gradually drops Because of gradual pressure drop, the steam and turbine 17 speeds are low www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS Impulse Turbine Reaction Turbine Power is obtained only due to the impulsive force of the incoming steam Power is obtained due to impulsive force of incoming steam as well as reaction of exit steam Suitable for small capacity Suitable for medium & of power generation & high capacity power occupies less space per generation and occupies unit power more space per unit power Efficiency is lesser Efficiency is higher Compounding is Compounding is not necessary to reduce necessary speed www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 18 Compounding of Impulse Turbines As the complete expansion of steam takes in one stage (i.e., the entire pressure drop from high pressure to low pressure takes place in only one set of nozzles), the turbine rotor rotates at very high speed of about 30,000 rpm (K.E. is fully absorbed). High speed poses number of technical difficulties like destruction of machine by the large centrifugal forces developed, increase in vibrations, quick overheating of blades, impossibility of direct coupling to other machines, etc. To overcome the above difficulties, the expansion of steam is performed in several stages. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 19 Utilization of the high pressure energy of the steam by expanding it in successive stages is called Compounding. Methods of Compounding: Velocity compounding (Curtis Impulse Turbine) Pressure compounding Pressure-velocity compounding www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 20 Velocity compounding Comprise of nozzles and two or more rows of moving blades arranged in series. In between two rows of moving blades, one set of guide (fixed) blades are suitably arranged. Guide (fixed) blades are fixed to casing stationary. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS and are 21 N – Nozzle M – Moving Blade F – Fixed Blade Velocity Compounding (Curtis Impulse Turbine) www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 22 • Consists of two stage of nozzles followed by two rows of moving blades. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 23 Pressure Compounding www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 24 Pressure-Velocity Compounding (Combined Impulse Turbine) A – Axial clearance, N – Nozzle, M – Moving Blade, F – Fixed Blade Pi and Pe – Pressure at inlet & exit, Vi and Ve - Velocity at inlet & exit Total pressure drop is divided into two stages & the total velocity obtained in each stage is also compounded www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 25 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 26 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 27 A Gas turbine uses the hot gases of combustion directly to produce the mechanical power. Fuels used - Kerosene, coal, coal gas, bunker oil, gasoline, producer gas, etc., Classification: 1. 2. Open cycle gas turbine Closed cycle gas turbine www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 28 Applications Gas turbines are used in: Electric power generation plants Steel, oil and chemical industries Aircrafts, Ship propulsion Turbo jet and turbo-propeller engines like rockets, missiles, space ships etc., www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 29 Open cycle gas turbine: The entire flow of the working substance comes from atmosphere and is returned to the atmosphere back in each cycle. Closed cycle gas turbine: The flow of the working substance of specified mass is confined within the cyclic path. ( Air or Helium is the working substance) www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 30 • COMPRESSOR: draws in air and compress it before it is fed into combustion chamber • COMBUSTOR: fuel is added to the compressed air and burnt to produce high velocity exhaust gas • TURBINE: extracts energy from exhaust gas www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 31 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 32 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 33 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 34 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 35 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 36 Difference between open & closed cycle turbine Open cycle Lesser thermal efficiency Loss of working fluid Bigger in size Big compressor is needed Possibility of corrosion of blades and rotor Economical Exhaust gases from turbine exit to atmosphere Closed cycle Higher No loss of working fluid Smaller Smaller one is sufficient Free from corrosion Not economical Fed back into the cycle www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 37 Pharmaceutical Pharmaceutical www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 38 Hospitals Hospitals www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 39 Pulp Pulp and and Paper Paper www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 40 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 41 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 42 It is a prime mover, which converts hydro power (energy of water) into mechanical energy and further into hydroelectric power. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 43 Classification of Water Turbines Based on action of water: 1. 2. Impulse turbine – pelton wheel. Reaction turbine – francis and kaplan. Based on name of originator: 1. 2. 3. Pelton turbine or Pelton wheel Francis turbine Kaplan turbine Based on head of water: 1. 2. 3. Low head turbine Medium head turbine High head turbine www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 44 Pelton Turbine (Pelton Wheel or Free Jet Turbine) High head, tangential flow, horizontal shaft, impulse turbine www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 45 PELTON TURBINE www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 46 Pelton Turbine Runner www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 47 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 48 Only a part of the pressure energy of the water is converted into K.E. and the rest remains as pressure head. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 49 First, the water passes to the guide vanes which guide or deflect the water to enter the blades, called moving blades, mounted on the turbine wheel, without shock. The water from the guide blades are deflected on to the moving blades, where its part of the pressure energy is converted into K.E., which will be absorbed by the turbine wheel. The water leaving the moving blades will be at a low pressure. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 50 The difference in pressure between the entrance and the exit of the moving blades is called Reaction pressure, which acts on moving blades of the turbine wheel and sets up the turbine wheel into rotation in the opposite direction. Examples: Francis turbine, Kaplan turbine, Propeller turbine, Thompson turbine, Bulb turbine. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 51 Francis Turbine Mixed flow, medium head reaction turbine. Consists of a spiral casing enclosing a number of stationary guide blades fixed all round the circumference of an inner ring of moving blades (vanes) forming the runner, which is keyed to the turbine shaft. Radial entry of water along the periphery of the runner and discharge at the center of the runner at low pressure through the diverging conical tube called draft tube. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 52 FRANCIS TURBINE www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 53 Francis Inlet Scroll, Grand Coulee Dam www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 54 Francis Runner, Grand Coulee Dam www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 55 www.bookspar.com | Website for FRANCIS TURBINE & GENERATOR Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 56 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 57 Kaplan Turbine Axial flow, low head. Similar to Francis turbine except the runner and draft tube. The runner (Boss or Hub) resembles with the propeller of the ship, hence some times it is called as Propeller turbine. Water flows parallel to the axis of the shaft. www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 58 (GUIDE VANE) (RUNNER VANE) (SCROLL CASING) KAPLAN TURBINE www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 59 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 60 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 61 Vertical Kaplan Turbine www.bookspar.com | Website for (Courtesy: VERBUND-Austrian Hydro Power) Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 62 Propeller Turbine Runner www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 63 www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS 64