P2.7_-_Radioactivity_answers 730KB Jun 06 2014 10:44:25 AM
advertisement

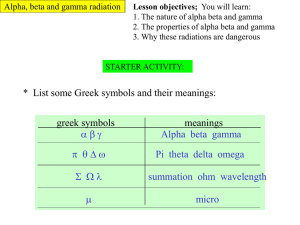
Radioactivity Nucleus Electrons Particle Relative mass Relative charge Proton 1 +1 Neutron 1 0 Electron almost zero -1 1) a) Fill in the labels on the atom. (1 mark) b) Fill in the table with the correct values. (3 marks) Isotopes 2 3 1 1 c) Fill in the blanks for the Hydrogen isotopes. (2 marks) Decay 2) What three types of radioactive decay are there? …Alpha Beta and Gamma (accept symbols)… (1 mark) 3) Describe each type of decay. 1…Alpha – Helium Nucleus 2 protons and 2 neutrons 2…Beta – 1 electron (released when a neutron turns into a proton and gives out an electron) 3…Gamma – Electromagnetic ray (releases when an atomic particle moves down an energy level and gives off energy) (3 marks) 4) Uranium-230 nuclei emit alpha radiation and become nuclei of thorium (Th). a) Complete the equation. (2 marks) U __Th __ He 230 92 __ 226 4__ 90 2 5) Potassium-40 decays, via Beta emission, to Calcium 40. Write a balanced equation for this decay. (use the periodic table on the next page to help.) 40 19 K Ca 40 20 0 1 Detecting radiation The following readings were taken using an unknown source of radiation. Counts in 300 seconds Readings No source present Average 102 94 110 102 No lead present 3466 3420 3410 3432 Thick lead plate present 105 109 89 101 Aluminium sheet in place of thick lead sheet 1834 1787 1818 1813 Source present at fixed distance from tube 6) a) Complete the table by calculating the average readings. b) What equipment would you use to count the emitted radiation? ………… geiger muller (GM) tube………(1 mark) c) Why are the readings on each line not the same? …………Radiation is a random process therefore in a given time there will almost never be the same count……..(2 marks) 7) What can you say, from the table, about the effect on the radiation of: a) The lead plate? …The lead stops all the radiation from the source and the only radiation that is left is the background radiation. …..(2 marks) b) The aluminium plate? ………The aluminium plate stops most but not all of the radiation. It stops less than the lead plate.(2 marks) 8) Why is it possible to say from the readings that: a) Gamma radiation is emitted by the source? ……Not all the radiation from the source is stopped by the aluminium plate. Both alpha and beta will be stopped by the aluminium plate do the only radiation left from the source will be gamma...(2 marks) b) Alpha and beta radiation might be emitted by the source? …most of the radiation from the source is stopped by the aluminium which could be both alpha and beta...(2 marks) 9) What further tests could you make to find out whether or not the source emits alpha radiation? …Try using thinner aluminium or paper or just increase the distance of the GM tube from the source. If the count drops then alpha could be present ………..(2 marks) 10) (a) Uranium-234 (234U) is a radioactive element. The graph shows the number of protons and neutrons in the nuclei of the elements formed when uranium-234 decays. (i) How does the graph show that uranium-234 (234U) and thorium-230 (230Th) emit alpha particles? ........ both lose 2 protons and (2) neutrons................ (1 mark) (ii) What makes uranium and thorium different elements? ............ different number of protons (in the nucleus)(1 mark) (iii) Radioactive decay may also produce gamma radiation. Why does the emission of gamma radiation not cause a new element to be formed? ..... gamma involves no change in the number of protons (in the nucleus) or gamma is a wave (not a particle). (1 mark) (b) The graph shows how the thickness of different materials needed to absorb 90% of the gamma radiation emitted by a source depends on the energy of the radiation. The energy of the gamma radiation is given in units called electron-volts. (i) Which of the materials shown is least effective at absorbing gamma radiation? Use the information in the graph to give a reason for your answer. . water because for all energy values the thickness of water needed to absorb (90% of) the radiation is more than the other materials.. (1 mark) (ii) For gamma radiation of energy 1.5 million electron-volts, how many times more effective is steel than water at absorbing the radiation? Show clearly how you obtain your answer. .......water thickness = 72cm steel thickness = 12cm Answer = 6 times (2 marks) (c) Scientists in the early twentieth century thought that atoms were made up of electrons scattered inside a ball of positive charge. This was called the ‘plum-pudding’ model of the atom. Rutherford and Marsden did an experiment, in which a beam of alpha particles was aimed at a thin sheet of gold. Explain how the results of this experiment led to a new model of the atom. You may include one or more diagrams in your answer. any three from: • most (alpha) particles passed undeflected / straight through the gold • suggesting most of the atom is empty (space) • a few (alpha) particles scattered / deflected through (very) large angles • suggesting a concentrated / small nucleus • nucleus is positive because it repels the positive (alpha) particles may be scored on annotated diagram provided not negated elsewhere accept repelled do not accept reflected / rebound / bounce back no reference to experiment, maximum 1 mark ....................................................................... (3 marks) 11) (a) When an unstable barium nucleus changes into a lanthanum nucleus, a beta particle is emitted. (i) What is a beta particle? (high energy) electron (1 mark) (ii) How is the nucleus of a lanthanum atom different from the nucleus of a barium atom? ..... one less neutron one more proton (both required for mark)....... (1 mark) (iii) Describe how a neutral atom may be changed by a collision with a beta particle. ................... becomes charged / ionised......(1 mark) (b) The diagram shows how radiation can be used to kill the cells of a brain tumour. Why is a beta emitting radioactive source unsuitable for this purpose? ...... will not pass through the skull / bone......................(1 mark)